Abstract
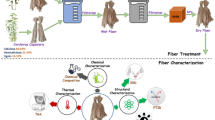
Jute fibres, an environmentally and ecologically friendly product, were chemically modified by treatment with 1.26 M (5 wt%) solution of NaOH solution at room temperature for 2, 4 and 8 h. The above samples were characterized by small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) technique and XRD for macromolecular and microstructural parameters of fibres before and after alkali treatment where as FT-IR and SEM was used for fine structural details and morphological studies of the fibres. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and instron 1185 analyzed thermal and mechanical behaviour of the fibres. Comparison and analysis of results confirmed some changes in the macromolecular structure and microstructure of the fibres after chemical treatment due to swelling of macromolecules and removal of some non-crystalline constituents of the fibres. The findings conclude that change in crystallinity developed after alkali treatment resulting improvement in mechanical strength of the fibres. However, the removal of structural constituents after alkali treatment leads the thermal decomposition temperature of the cellulose went down to 360.62 °C after 8 h alkali treatment from 365.26 °C for raw jute fibre.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khan F, Ahmed SR (1996) Polym Degrad Stabil 52:335
Bledzki AK, Reihmane S, Gassan J (1996) J Appl Polym Sci 59:1329
Gassan J, Bledzki AK (1999) J Appl Polym Sci 71(4):623
Sarkar PB (1935) Indian J Chem Soc 12:23
Samal RK, Mohanty M, Panda BB (1995) J Polym Mater 12:235
Prasad SV, Pavithran C, Rohatgi PK (1983) J Mater Sci 18:1443
Rout J, Mishra M, Nayak SK, Tripathy SS, Mohanty AK (1999) Polymer 99:489
Barton HM (1950) Phys Rev 79:211
Vineyard GH (1948) Phys Rev 74:1076
Kratky O, Laggner P (1987) Encycl Phys Sci Technol 14:693
Ratho T, Patel A (1995) J Poly Sci Poly Chem Ed 13(10):2345
Mark H (1932) Physik and chemic der zellulose. Springer, Berlin, p 139
Ratho T, Patel A (1981) J Phys D Appl Phys 14:2169; Hendricks SB (1930) Z Kristallogr 74:534–545 & the reference therein
Porod G (1951) Kolloid Z 124:83. doi:10.1007/BF01512792
Porod G (1952) Kolloid Z 125:51. doi:10.1007/BF01519615
Vonk CG (1973) J Appl Cryst 6:81
Roy AK, Bag SC, Sardar D, Sen SK (1991) J Appl Polym Sci 43:2187
Roy SC (1960) Text Res J 30:451
Porod G (1953) Kolloid Z Z Polym 133:16. doi:10.1007/BF01513900
Ratho T, Sahu NC (1970) Kolloid ZZ Polym 236:43
Sarkar PB, Mazumdar AK, Pal KB (1948) J Tex Inst T44:39
Misra T, Patra KC, Patel T (1984) Colloid Polym Sci 262:611
Mering J, Tchoubar D (1968) J Appl Cryst 1:153
Gerber T, Walter G, Krenold R (1982) J Appl Cryst 15:143
Kortleve G, Vonk CG (1968) Kolloid Z Z Polym 225:124
Mittelbach P, Porod G (1965) Kolloid Z Z Polym 202:40. doi:10.1007/BF01497184
Ruland W (1971) J Appl Cryst 4:70
Young RJ, Bowden PB, Ritchie JM, Rider JG (1973) J Mater Sci 8:23
Cullity BD (1978) Elements of X-ray diffraction. Addision wisely Publishing Company Inc, London, p 286
Segal L, Creely J, Martin, Conrad CM (1959) Tex Res J 29:786
Ray D, Sarkar BK, Rana AK, Bose NR (2001) Comp Part A 32:119
Gassan J, Bledzki AK (1999) Comp Sci Tech 59:1303
Khan MA, Hassan MM, Drzal LT (2005) Comp Part A 36:71
Tshboi M (1957) J Polym Sci 25:159
Liang CY, Bassett KH, Mc Ginnes EA, Marchessault RH (1960) Tappi 43:1917
Sarkar PB, Mazumdar AK (1955) Text Res J 12:1016
Vonk CG (1975) J Appl Cryst 8:340
Prasad N, Patnaik J, Bohidar N, Mishra T (1998) J Appl Poly Sci 67:1735
Mohlethaler K (1949) Biochem Biophys Acta 3:15
Misra T, Bisoyi DK, Patel T, Patra KC, Patel A (1988) Poly J 20:739
Khan MN (1995) Small angle x-ray scattering study of sisal fibre using correlation functions, PhD thesis, Sambalpur University, Orissa, India
Topping J (1972) Error of observation and their treatment, 4th edn. Chapman and Hall, Science paper back
Aziz SH, Ansell MP (2004) Comp Sci Tech 64:1219
Paunikallio T, Suvanto M, Pakkanen TT (2004) J Appl Poly Sci 91:2676
Ray D, Sarkar BK, Basak RK, Rana AK (2002) J App Poly Sci 85:2594
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge Prof J. Belare, IIT, Bombay, India, for providing the SAXS facility. Prof. N.V. Bhat, Emeritus Professor of Physics, Bombay Textile Research Association, is acknowledged for usefull discussion and suggestion on SAXS data analysis. Prof. T.N. Tiwari, retired Professor of Physics, NIT, Rourkela, is acknowledged for thorough reading of the paper and valuable suggestion. Prof. S. Saha, NIRJAFT, Kolkata, is also acknowledged for help during the mechanical properties analysis and result interpretation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, E., Rout, S.K. Influence of fibre-surface treatment on structural, thermal and mechanical properties of jute. J Mater Sci 43, 2590–2601 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2478-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-2478-4