Abstract
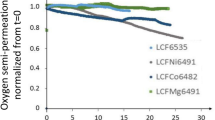
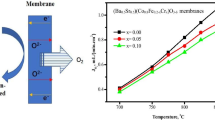
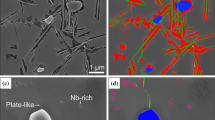
Bao.8La0.2Co0.88−x Fe x Nb0.12O3−δ membranes (BLCFN) with different Fe-doping were successfully prepared by solid-state reaction method. The microstructure, oxygen permeability, thermal analysis, and oxygen permeation stability using CO2 as sweep gas were systematically investigated. After being calcined under pure CO2, BLCFN membranes remain their major perovskite phase but diffraction peaks of BaCO3, CoO appeared on the membranes which Fe content is less than 0.2. Apparent activation energy of oxygen permeation are around 60–70 kJ/mol for all membranes. With the increase of Fe-doping content, the flux through BLCFN membranes decreases but the degradation of oxygen flux becomes less pronounced when CO2 is used as sweep gas at 850 °C. Enhanced CO2 resistance of the perovskite would be resulted from an increasing average binding energy due to the Fe-doping. For the membrane where the Fe-doped content equals to 0.2, the oxygen permeation flux is 0.96 mL cm−2 min−1 at 900 °C with He sweeping. When using pure CO2 as sweep gas, the oxygen permeation flux decreases slightly in the first 50 h and then reaches a steady state of ~0.31 mL cm−2 min−1 for more than 60 h in a prolonged continuous oxygen operation. The observations indicated that a stable oxygen permeation could be realized by suitable elemental doping in a single perovskite membrane.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stadler H, Beggel F, Habermehl M, Persigehl B, Kneer R, Modigell M, Jeschke P (2011) Oxyfuel coal combustion by efficient integration of oxygen transport membranes. Int J Greenh Gas Control 5:7–15
Carbo MC, Jansen D, Hendriks C, de Visser E, Jan Ruijg G, Davison J (2009) Opportunities for CO2 capture through oxygen conducting membranes at medium-scale oxyfuel coal boilers. Energy Procedia 1:487–494
Sunarso J, Baumann S, Serra JM, Meulenberg WA, Liu S, Lin YS, Diniz da Costa JC (2008) Mixed ionic–electronic conducting (MIEC) ceramic-based membranes for oxygen separation. J Membr Sci 320:13–41
Zhang K, Sunarso J, Shao ZP, Zhou W, Sun CH, Wang SB, Liu SM (2011) Research progress and materials selection guidelines on mixed conducting perovskite-type ceramic membranes for oxygen production. RSC Adv 1:1661–1676
Arnold M, Wang HH, Feldhoff A (2007) Influence of CO2 on the oxygen permeation performance and the microstructure of perovskite-type (Ba0.5Sr0.5)(Co0.8Fe0.2)O3−δ membranes. J Membr Sci 293:44–52
Yi JX, Schroeder M, Weirich T, Mayer J (2010) Behavior of Ba(Co, Fe, Nb)O3−δ perovskite in CO2-containing atmospheres: degradation mechanism and materials design. Chem Mater 22:6246–6253
Chen W, Chen CS, Winnubst L (2011) Ta-doped SrCo0.8Fe0.2O3−δ membranes: phase stability and oxygen permeation in CO2 atmosphere. Solid State Ion 196:30–33
Zeng Q, Zu YB, Fan CG, Chen CS (2009) CO2-tolerant oxygen separation membranes targeting CO2 capture application. J Membr Sci 335:140–144
Yi J, Brendt J, Schroeder M, Martin M (2012) Oxygen permeation and oxidation states of transition metals in (Fe, Nb)-doped BaCoO3−δ perovskites. J Membr Sci 387–388:17–23
Yi JX, Schroeder M, Martin M (2013) CO2-tolerant and cobalt-free SrFe0.8Nb0.2O3-delta perovskite membrane for oxygen separation. Chem Mater 25:815–817
Klande T, Ravkina O, Feldhoff A (2013) Effect of A-site lanthanum doping on the CO2 tolerance of SrCo0.8Fe0.2O3−δ oxygen-transporting membranes. J Membr Sci 437:122–130
Zhang X, Wu C, Zhou J, Yang G, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Ding W (2015) Oxygen permeation property and structural stability of La-doped BaCo0.88Nb0.12O3−δ membranes in CO2 atmosphere. Chem J Chin Univ 36:1246–1253
Wu C, Gai Y, Zhou J, Tang X, Zhang Y, Ding W, Sun C (2015) Structural stability and oxygen permeability of BaCo1−xNbxO3−δ ceramic membranes for air separation. J Alloys Compd 638:38–43
Geng Z, Ding WZ, Wang HH, Wu CZ, Shen PJ, Meng XY, Gai YQ, Ji FT (2012) Influence of barium dissolution on microstructure and oxygen permeation performance of Ba1.0Co0.7Fe0.2Nb0.1O3−δ membrane in aqueous medium. J Membr Sci 403:140–145
Wu CZ, Wang H, Zhang XX, Zhang YW, Ding WZ, Sun CH (2014) Microstructure evolution and oxidation states of Co in perovskite-type oxide Ba1.0Co0.7Fe0.2Nb0.1O3−δ annealed in CO2 atmosphere. J Energy Chem 23:575–581
Tan XY, Liu N, Meng B, Sunarso J, Zhang K, Liu SM (2012) Oxygen permeation behavior of La0.6Sr0.4Co0.8Fe0.2O3 hollow fibre membranes with highly concentrated CO2 exposure. J Membr Sci 389:216–222
Yang Q, Lin YS, Bulow M (2006) High temperature sorption separation of air for producing oxygen-enriched CO2 stream. AIChE J 52:574–581
Czuprat O, Arnold M, Schirrmeister S, Schiestel T, Caro J (2010) Influence of CO2 on the oxygen permeation performance of perovskite-type BaCoxFeyZrzO3−δ hollow fiber membranes. J Membr Sci 364:132–137
Tong JH, Yang WS, Zhu BC, Cai R (2002) Investigation of ideal zirconium-doped perovskite-type ceramic membrane materials for oxygen separation. J Membr Sci 203:175–189
Sammells AF, Cook RL, White JH, Osborne JJ, MacDuff RC (1992) Rational selection of advanced solid electrolytes for intermediate temperature fuel cells. Solid State Ion 52:111–123
Luo HX, Jiang HQ, Klande T, Liang FY, Cao ZW, Wang HH, Caro J (2012) Rapid glycine-nitrate combustion synthesis of the CO2-stable dual phase membrane 40Mn1.5Co1.5O4−δ -60Ce0.9Pr0.1O2−δ for CO2 capture via an oxy-fuel process. J Membr Sci 423:450–458
Zheng Q, Xue J, Liao Q, Wei YY, Li Z, Wang HH (2013) CO2-tolerant alkaline-earth metal-free single phase membrane for oxygen separation. Chem Eng Sci 101:240–247
Luo HX, Klande T, Cao ZW, Liang FY, Wang HH, Caro J (2014) A CO2-stable reduction-tolerant Nd-containing dual phase membrane for oxyfuel CO2 capture. J Mater Chem A 2:7780–7787
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51274139 and 51174133), Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (11ZR1412900), the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (13YZ019) and Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (20123108120020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Zhang, X., Luo, W. et al. Iron-doping effects on the CO2 tolerance of a perovskite oxygen permeable membrane. J Mater Sci 51, 3971–3978 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9715-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9715-4