Abstract
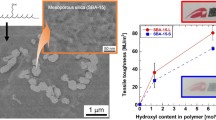
This paper reports on the morphologies of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA)/mesoporous silica (MCM-41) composites prepared by melt compounding with various MCM-41 contents in the range of 0.1–5 wt%, the interactions between the polymer and filler in these composites, and their thermomechanical, mechanical and thermal degradation properties. The composites formed transparent films at low filler loadings (<0.5 wt%) because of well-dispersed, unagglomerated particles. The presence of polymer did not alter the pore dimensions in the MCM-41 structure and it maintained its hexagonal structure, even though the polymer chains partially penetrated the pores during composite preparation. The PMMA interacted with the MCM-41 through hydrogen bonding. The glass transition temperature, as well as storage and loss modulus of PMMA increased with addition of, and increase in the amount of, MCM-41 due to the interaction of the polymer chains with the porous filler which restricted the mobility of the polymer chains and increased the stiffness of the composites. The thermal stability of PMMA apparently increased in the presence of MCM-41, although this observation probably was the result of delayed mass loss because of the trapping of volatile degradation products in the pores of MCM-41. The presence of MCM-41, up to 1.0 wt%, increased the impact strength of PMMA.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wei L, Hu N, Zhang Y (2010) Synthesis of polymer-mesoporous silica nanocomposites. Materials 3:4066–4079. doi:10.3390/ma3074066
Wacharawichanant S, Thongyai S, Phutthaphan A, Eiamsam-ang C (2008) Effect of particle sizes of zinc oxide on mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of polyoxymethylene/zinc oxide nanocomposites. Polym Test 27:971–976. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2008.08.012
Ramanathan T, Stankovich S, Dikin DA, Liu H, Shen H, Nguyen ST, Brinson LC (2007) Graphitic nanofillers in PMMA nanocomposites—an investigation of particle size and dispersion and their influence on nanocomposites properties. J Polym Sci Part B 45:2097–2112. doi:10.1002/polb.21187
Zhang FA, Song C, Yu CL (2011) Effects of preparation methods on the property of PMMA/SBA-15 mesoporous silica composites. J Polym Res 18:1757–1764. doi:10.1007/s10965-011-9582-x
Caponetti E, Minoja A, Saladino ML, Spinella A (2008) Characterization of Nd-MCM-41 obtained by impregnation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 113:490–498. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.12.007
Zhang FA, Luo M, Chen ZJ, Wei ZB, Pinnavaia TJ (2014) Effects of mesoporous silica particles on the emulsion polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Polym Eng Sci 54:2746–2752. doi:10.1002/pen.23830
Zhang FA, Lee DK, Pinnavaia TJ (2009) PMMA-mesocellular foam silica nanocomposites prepared through batch emulsion and compression molding. Polymer 50:4768–4774. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2009.08.007
Etienne S, Becker C, Ruch D, Grignard B, Cartigny G, Detrembleur C, Calberg C, Jerome R (2007) Effects of incorporation of modified silica nanoparticles on the mechanical and thermal properties of PMMA. J Therm Anal Calorim 87:101–104. doi:10.1007/s10973-006-7827-4
Zheng S, Li J, Guo Q, Mi Y (1997) In situ polymerization preparation of blends of poly (methyl methacrylate) and poly (styrene-co-acrylonitrile). J Mater Sci 32:3463–3468. doi:10.1023/A:1018633003127
Zhang FA, Lee DK, Pinnavaia TJ (2010) PMMA/mesoporous nanocomposites: effect of framework structure and pore size on thermomechanical properties. Polym Chem 1:107–113. doi:10.1039/b9py00232d
Perez LD, Giraldo LF, Brostow W, Lopez BL (2007) Poly(methyl acrylate) plus mesoporous silica nanohybrids: mechanical and thermophysical properties. e-Polymers 7:324–334. doi:10.1515/epoly.2007.7.1.324
Run MT, Wu SZ, Zhang DY, Wu G (2007) A polymer/mesoporous molecular sieve composite: preparation structure and properties. Mater Chem Phys 105:341–347. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.04.070
Dinari M, Mallakpour S, Mohammadnezhad G (2015) Organo-modification of mesoporous SBA-15 with chiral diacid and its utilization for the preparation of l-phenylalanine-based poly(amide-imide) nanocomposites. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 54:549–555. doi:10.1080/03602559.2014.961085
Dinari M, Mohammadnezhad G, Nabiyan A (2015) Organo-modified mesoporous carbon FDU-15 as new nanofiller for the preparation of nanocomposite materials based on nylon-6. Colloid Polym Sci 293:1569–1575. doi:10.1007/s00396-015-3556-1
Mallakpour S, Dinari M, Mohammadnezhad G (2015) Ultrasonic assisted organo-modification of mesoporous SBA-15 with N-trimellitylimido-l-methionine and preparation of the poly(amide-imide)/SBA nanocomposites. Prog Org Coat 78:300–306. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2014.08.005
Mohammadnezhad G, Dinari M, Soltani R, Bozorgmehr Z (2015) Thermal and mechanical properties of novel nanocomposites from modified ordered mesoporous carbon FDU-15 and poly(methyl methacrylate). Appl Surf Sci 346:182–188. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.04.005
Jiao J, Wang L, Wu G, Lv P, Cui Y (2015) Effects of framework structure and coupling modification on the properties of mesoporous silica/poly(methyl methacrylate) composites. J Reinf Plast Compos 34:222–231. doi:10.1177/0731684414567014
Garcia N, Corrales T, Guzman J, Tiemblo P (2007) Understanding the role of nanosilica particle surfaces in the thermal degradation of nanosilica-poly(methyl methacrylate) solution-blended nanocomposites: from low to high silica concentration. Polym Degrad Stab 92:635–643. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.01.006
Katsikis N, Zahradnik F, Helmschrott A, Munstedt H, Vital A (2007) Thermal stability of poly(methyl methacrylate)/silica nano- and microcomposites as investigated by dynamic-mechanical experiments. Polym Degrad Stab 92:1966–1976. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.08.009
Kashiwagi T, Morgan AB, Antonucci JM, Vanlandingham MR, Harris RH Jr, Awad WH, Shields JR (2003) Thermal and flammability properties of a silica-poly(methylmethacrylate) nanocomposite. J Appl Polym Sci 89:2072–2078. doi:10.1002/app.12307
Hu YH, Chen CY, Wang CC (2004) Viscoelastic properties and thermal degradation kinetics of silica/PMMA nanocomposites. Polym Degrad Stab 84:545–553. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2004.02.001
Fu HP, Hong RY, Zhang YJ, Li HZ, Xu B, Zheng Y, Wei DG (2009) Preparation and properties investigation of PMMA/silica composites derived from silicic acid. Polym Adv Technol 20:84–91. doi:10.1002/pat.1226
Saladino ML, Motaung TE, Luyt AS, Spinella A, Nasillo G, Caponetti E (2012) The effect of silica nanoparticles on the morphology, mechanical properties and thermal degradation kinetics of PMMA. Polym Degrad Stab 97:452–459. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.11.006
Wang L, Han X, Li J, Zheng D (2012) Preparation of modified mesoporous MCM-41 silica spheres and its application in pervaporation. Powder Technol 231:63–69. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2012.07.044
Araujo JA, Cruz FT, Cruz IH, Cardoso D (2013) Encapsulation of polymers in CTA-MCM-41 via microemulsion. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 180:14–21. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.05.010
Young RJ, Lovell PA (2011) Introduction to polymers, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton. ISBN 978-0-8493-3929-5
Mendonza AM, Warzywoda J, Sacco A Jr (2006) Investigation of structural order and morphology of MCM-41 mesoporous silica using an experimental design methodology. J Porous Mater 13:37–47. doi:10.1007/s10934-006-5488-0
Horcajada P, Ramila A, Perez-Pariente J, Vallet-Regi M (2004) Influence of pore size of MCM-41 matrices on drug delivery rate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 68:105–109. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2003.12.012
Hui KS, Chao CYH (2006) Synthesis of MCM-41 from coal fly ash by a green approach: influence of synthesis pH. J Hazard Mater B137:1135–1148. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.03.050
Gnanou Y, Fontanille M (2008) Organic and physical chemistry of polymers. Wiley, New Jersey
Li X, McKenna GB, Miquelard-Garnier G, Guinault A, Sollogoub C, Regnier G, Rozanski A (2013) Forced assembly by multilayer coextrusion to create oriented graphene reinforced polymer nanocomposites. Polymer 55:248–257. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2013.11.025
Ibbett RN (1993) NMR spectroscopy of polymers. Blackie Academic & Professional, London. ISBN 0-7514-0005-X
Hatada K, Kitayama T (2004) NMR spectroscopy of polymers. Springer, New York. ISBN 3-540-40220-9
Avolio R, Gentile G, Avella M, Capitani D, Errico ME (2010) Synthesis and characterization of poly(methylmethacrylate)/silica nanocomposites: study of the interphase by solid-state NMR and structure/properties relationships. J Polym Sci Part A 48:5618–5629. doi:10.1002/pola.24377
Zanotto A, Spinella A, Nasillo G, Caponetti E, Luyt AS (2012) Macro-micro relationship in nanostructured functional composites. Express Polym Lett 6:410–416. doi:10.3144/expresspolymlett.2012.43
Zhang B, Blum FD (2003) Thermogravimetric study of ultrathin PMMA films on silica: effect of tacticity. Thermochim Acta 396:211–217. doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00515-X
Rittigstein P, Torkelson JM (2006) Polymer-nanoparticles interfacial interactions in polymer nanocomposites: confinement effects on glass transition temperature and suppression of physical aging. J Polym Sci Part B 44:2935–2943. doi:10.1002/polb.20925
Wang N, Gao N, Jiang S, Fang Q, Chen E (2011) Effect of different structure MCM-41 fillers with PP-g-MA on mechanical and crystallization performances of polypropylene. Compos B 42:1571–1577. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.04.012
Menczel JD, Prime RB (2009) Thermal analysis of polymers: fundamentals and applications. Wiley, New Jersey. ISBN 978-0-471-76917-0
Pothan LA, Oommen Z, Thomas S (2003) Dynamic mechanical analysis of banana fiber reinforced polyester composites. Compos Sci Technol 63:283–293. doi:10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00254-3
Romanzini D, Lavoratti A, Ornaghi HL Jr, Amico SC, Zattera AJ (2013) Influence of fiber content on the mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of glass/ramie polymer composites. Mater Des 47:9–15. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2012.12.029
Nielsen LE, Landel RF (1994) Mechanical properties of polymers and composites. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York. ISBN 0-8247-8964-4
Wang N, Mi L, Wu Y, Wang X, Fang Q (2013) Enhanced flame retardancy of natural rubber composite with addition of microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate and MCM-41 fillers. Fire Saf J 62:281–288. doi:10.1016/j.firesaf.2013.09.008
Huang HX, Zhang JJ (2009) Effects of filler–filler and polymer–filler interactions on rheological and mechanical properties of HDPE-wood composites. J Appl Polym Sci 111:2806–2812. doi:10.1002/app.29336
Majoni S, Su S, Hossenlopp J (2010) The effect of boron-containing layered hydroxyl salt (LHS) on the thermal stability and degradation kinetics of poly(methy methacrylate). Polym Degrad Stab 95:1593–1604. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.05.033
Cao C, Tan Z, Sun S, Liu Z, Zhang H (2011) Enhancing the thermal stability of poly(methyl methacrylate) by removing the chains with weak links in a continuous polymerization. Polym Degrad Stab 96:2209–2214. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.09.005
Luyt AS (2015) Using thermogravimetric analysis to determine polymer thermal stability: relevance of changes in onset temperature of mass loss. Express Polym Lett 9:756. doi:10.3144/expresspolymlett.2015.70
Holland BJ, Hay JN (2002) The value and limitations of non-isothermal kinetics in the study of polymer degradation. Thermochim Acta 388:253–273. doi:10.1016/S0040-6031(02)00034-5
Gao Z, Kaneko T, Hou D, Nakada M (2004) Kinetics of thermal degradation of poly(methyl methacrylate) studied with the assistance of the fractional conversion at the maximum reaction rate. Polym Degrad Stab 84:399–403. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2003.11.015
Acknowledgements
The National Research Foundation of South Africa is acknowledged for providing the bursary funding which enabled the student to do the research presented in this paper. The University of Palermo supported this research through the CORI2013 (Bando per la concessione di contribute per l’avvio e lo sviluppo di collaborazioni dell’Ateneo 2013-Azione D—prot 32827 del 2/5/2013). NMR and TEM experimental data were provided by Centro Grandi Apparecchiature-UniNetLab-Universita` di Palermo funded by P.O.R. Sicilia 2000–2006, Misura 3.15 Azione C Quota Regionale.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sibeko, M.A., Saladino, M.L., Luyt, A.S. et al. Morphology and properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) filled with mesoporous silica (MCM-41) prepared by melt compounding. J Mater Sci 51, 3957–3970 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9714-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9714-5