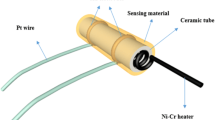
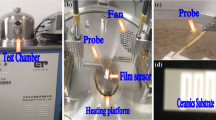
Abstract
ZnO spheres composed of porous flakes were prepared by template-free, economical hydrothermal method combined with heat treatment. The high-density pores with the size in tens of nanometers were found distributed through each piece of the flake. The sensor based on porous ZnO spheres showed improved ethanol response compared to that based on commercial ZnO powders. ZnO spheres sensor showed obvious response to 2 ppm ethanol at the operation temperature of 280 °C, with the corresponding response value of 2.8 and the response and recovery times of 10 and 15 s, respectively. The response of the sensor increased linearly with the concentration of ethanol in the range of 2–500 ppm. The good sensing performance of the ZnO sphere sensor to ethanol gas indicated that the ZnO sphere could be a promising candidate as the building block for highly sensitive and reliable gas sensor.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J, Guo Z, Meng F, Luo T, Li M, Liu J (2009) Nanotechnology 20:125501
Stewart ME, Anderton CR, Thompson LB, Maria J, Gray SK, Rogers JA, Nuzzo RG (2008) Chem Rev 108:494
Venkatesan BM, Dorvel B, Yemenicioglu S, Watkins N, Petrov I, Bashir R (2009) Adv Mater 21:2771
Ahn MW, Park KS, Heo JH, Park JG, Kim DW, Choi KJ, Lee JH, Hong SH (2008) Appl Phys Lett 93:263103
Kauffman DR, Star A (2008) Angew Chem Int Ed 47:6550
Lee JH (2009) Sens Actuators, B 140:319
Seiyama T, Kato A, Fulishi K, Nagatani M (1962) Anal Chem 34:1502
Deng L, Ding X, Zeng D, Zhang S, Xie C (2012) IEEE Sens J 12:2209
Xu J, Chen Y, Li Y, Shen J (2005) J Mater Sci 40:2919
He L, Jia Y, Meng F, Li M, Liu J (2009) J Mater Sci 44:4326
Vanheusden K, Warren WL, Seager CH, Tallant DR, Voigt JA, Gnade BE (1996) J Appl Phys 79:7983
Korsunska NO, Borkocska LV, Bulakh BM, Khomenkova LY, Kushnirenko VI, Markevich IV (2003) J Lumin 102–103:733
Janotti A, Van de Walle CG (2005) Appl Phys Lett 87:122102
Hyodo T, Sasahara K, Shimizu Y, Egashira M (2005) Sens Actuators, B 106:580
Zhang J, Wang S, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhu B, Xia H, Guo X, Zhang S, Huang W, Wu S (2009) Sens Actuators, B 135:610
Hosono E, Fujihara S, Honma I, Zhou H (2005) Adv Mater 17:2091
Bie LJ, Yan XN, Yin J, Duan YQ, Yuan ZH (2007) Sens Actuators, B 126:604
Barsan N, Weimar U (2001) J Electroceram 7:143
Hongsith N, Viriyaworasakul C, Mangkorntong P, Mangkorntong N, Choopun S (2008) Ceram Int 34:823
Chen J, Li J, Li JH, Xiao GQ, Yang XF (2011) J Alloys Compd 509:740
Chen YJ, Zhu CL, Xiao G (2008) Sens Actuators, B 129:639
Xue X, Chen Z, Xing L, Ma C, Chen Y, Wang T (2010) J Phys Chem C 114:18607
Wan Q, Li QH, Chen YJ, Wang TH, He XL, Li JP, Li CL (2004) Appl Phys Lett 84:3654
Veldsink JW, Van Damme RMJ, Versteeg GF, Van Swaaij WPM (1995) Chem Eng J Biochem Eng J 57:115
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50602040, 11104253 and 10574112), and the Science and Technology Project on Key Problems of Henan Province (Grant No. 082101510007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Tian, Y., Wang, X. et al. Ethanol sensing properties of porous ZnO spheres via hydrothermal route. J Mater Sci 48, 3232–3238 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-7103-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-7103-x