Abstract
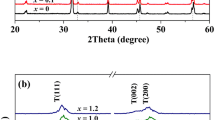
Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 + xmol% MnO2 lead-free ceramics have been prepared by a conventional sintering method and the effects of MnO2 and sintering temperature on microstructure, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 lead-free ceramics have been studied. The addition of 0.25 mol% MnO2 promotes grain growth, improves the ferroelectricity of the ceramics and strengthens ferroelectric tetragonal–ferroelectric orthorhombic phase transition near 40 °C. Because of the coexistence of tetragonal and orthorhombic phases and the combinatory effects of soft and hard doping of Mn ions, the ceramic with x = 0.25 exhibits the optimum piezoelectric properties (d 33 = 306 pC/N and k p = 42.2 %, respectively). Excess MnO2 inhibits the grain growth and degrades the ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of the ceramics. Sintering temperature has an important influence on the microstructure, tetragonal–orthorhombic phase transition near 40 °C, ferroelectric and piezoelectric properties of the ceramics. The increase in sintering temperature leads to large grains and more noticeable tetragonal–orthorhombic phase transition near 40 °C, enhances ferroelectricity and thus improves effectively the piezoelectricity of the ceramics. The Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 ceramic sintered at 1350 °C possesses the optimum piezoelectric constant d 33 value of 373 pC/N.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kuang SJ, Tang XG, Li LY, Jiang YP, Liu QX (2009) Scr Mater 61:68
Wei X, Wan X, Xi Y (2008) J Electroceram 21:226
Haertiling GH (1999) J Am Ceram Soc 82:797
Bechmann R (1956) J Acoust Soc Am 28:347
Liu W, Ren X (2009) Phys Rev Lett 103:257602
Li W, Xu Z, Chu R, Fu P, Zang G (2010) Mater Lett 64:2325
Zhang SW, Zhang HL, Zhang BP, Yang S (2010) J. Alloys Compd 506:131
Wu J, Xiao D, Wu W, Chen Q, Zhu J, Yang Z, Wang J (2011) Scr Mater 65:771
Li W, Xu Z, Chu R, Fu P, Zang G (2011) Mater Sci Eng, B 176:65
Wang P, Li Y, Lu Y (2011) J Eur Ceram Soc 31:2005
Wu J, Xiao D, Wu W, Zhu J, Wang J (2011) J Alloys Compd 509:L359
Su S, R. Zuo Z, Lu SB, Xu ZK, Wang XH, Li LT (2011) Curr Appl Phys 11:120–121
Li G, Zheng L, Yin Q (2005) J Appl Phys 98:064108
Hou Y, Zhu M, Gao F, Wang H, Wang B, Yan H, Tian C (2004) J Am Ceram Soc 87:847
Yu CS, Hsieh HL (2005) J Eur Ceram Soc 25:2425
Li SM, Lee SH, Yoon CB, Kim HE, Lee KW (2007) J Electroceram 18:311
Yan Y, Cho KH, Priya S (2011) J Am Ceram Soc 94:3953
Mgbemere HE, Herber RP, Schneider GA (2009) J Eur Ceram Soc 29:1729
Nagata H, Takenaka T (2001) J Eur Ceram Soc 21:1299
Fan X, Wang Y, Jiang Y (2011) J Alloys Compd 509:6652
Qiao L, Bi X (2009) J Eur Ceram Soc 29:1995
Buixaderas E, Bovtun V, Kempa M, Savinov M, Nuzhnyy D, Kadlec F, Vaněk P, Petzelt J, Eriksson M, Shen Z (2010) J Appl Phys 107:014111
Park Y, Lee WJ, Kim HG (1997) J Phys: Condens Matter 9:9445
Chattopadhyay S, Ayyub P, Palkar VR, Multani M (1995) Phys Rev B 52:13177
Damjanovic D, Demartin M (1997) J Phys: Condens Matter 9:4943
Zhang L, Zhong WL, Wang CL, Zhang PL, Wang YG (1998) Phys Stat Sol (a) 168:543
Martirenat HT, Burfoot JC (1974) J Phys C: Solid State Phys 7:1974
Cao W, Randall CA (1996) J Phys Chem Solids 57:1505
Randall CA, Kim N, Kucera JP, Cao W, Shrout TR (1998) J Am Ceram Soc 81:677
Demartin M, Damjanovic D (1996) Appl Phys Lett 68:3046
Damjanovic D (1998) Rep Prog Phys 61:1267
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the projects of Education Department of Sichuan Province (11ZA104), Science and Technology Bureau of Sichuan Province (2010JQ0046) and the Open Projects of State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for Nonmetal Composites and Functional Materials of Southwest University of Science and Technology (10zxfk27) and State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (KFJJ201108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Lin, Q., Lin, D. et al. Effects of MnO2 and sintering temperature on microstructure, ferroelectric, and piezoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Ti0.90Zr0.10O3 lead-free ceramics. J Mater Sci 48, 1035–1041 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6835-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6835-y