Abstract
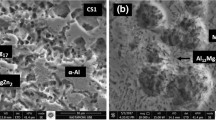
In this paper, rapid solidified Mg95Zn4.3Y0.7 (at.%) alloy powders produced by an inert gas atomizer were consolidated using a severe plastic deformation technique of high pressure torsion (HPT) at room temperature and 373 K. The behavior of powder consolidation, matrix microstructural evolution, and mechanical properties of the powders and compacts were investigated using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, microhardness, and tensile testing. As the HPT processing temperature increases, the powders are more plastically deformed due to decreased deformation resistance, grain boundaries are more in equilibrium, powder bonding is enhanced due to increased interparticle diffusion, hence, tensile ductility and strength increases. On the other hand, hardness decreases with the increased processing temperature, due to less dislocation density.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnesium. Accessed 17 March 2012
Estrin Y, Yi SB, Brokmeier HG, Zuberova Z, Yoon SC, Kim HS, Hellmig RJ (2008) Int J Mater Res 99:50
Kim WJ, Hong SI, Lee KH (2010) Metal Mater Inter 16:171
Kim DH, Lim HK, Kim YK, Kyeong JS, Kim WT, Kim DH (2011) Metal Mater Inter 17:383
Suzuki M, Kimura T, Koike J, Maruyama K (2003) Scripta Mater 48:997
Kim SH, Kim DH, Kim NJ (1997) Mater Sci Eng A 226–228:1030
Shin B, Kim Y, Bae D (2008) J Korean Inst Met Mater 46:1
Shin B, Yoon S, Ha C, Yun S, Bae D (2010) Korean J Met Mater 48:116
Kang MG, So TI, Jung HC, Shin KS (2011) Korean J Met Mater 49:686
Lee BD, Baek UH, Jang KS, Han JW, Son HT (2011) Korean J Met Mater 49:440
Bae DH, Kim SH, Kim DH, Kim WT (2002) Acta Mater 50:2343
Kim DH, Kim YK, Kim WT, Kim DH (2011) Korean J Met Mater 49:145
Cai J, Ma GC, Liu Z, Zhang HF, Hu ZQ (2006) J Alloy Compd 422:92
Nishida M, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto T (2004) Mater Sci Eng A 375–377:1217
Crivello J-C, Nobuki T, Kuji T (2007) Intermetallics 15:1432
Kawamura Y, Hayashi K, Inoue A, Masumoto T (2001) Mater Trans 42:1172
Inoue A, Kawamura Y, Matsushita M, Hayashi K, Koike J (2001) J Mater Res 16:1894
Yoon SC, Bok CH, Seo MH, Hong SJ, Kim HS (2008) J Korean Powder Metal Inst 15:31
Kim HS (2002) Mater Sci Eng A 328:317
Kim TS, Chae HJ, Lee JK, Jung HG, Bae JC (2007) Mater Sci Forum 534:793
Kim HS, Estrin Y, Bush MB (2000) Acta Mater 48:493
Valiev RZ, Islamgaliev RK, Alexandrov IV (2000) Prog Mater Sci 45:103
Valiev RZ, Estrin Y, Horita Z, Langdon TG, Zehetbauer MJ, Zhu YT (2006) JOM 58:33
Kim HS, Seo MH, Hong SI (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 291:86
Zhilyaev AP, Langdon TG (2008) Prog Mater Sci 53:893
Song YP, Yoon EY, Lee DJ, Lee JW, Kim HS (2011) Mater Sci Eng A 528:4840
Stolyarov VV, Zhu YT, Lowe TC, Islamgaliev RK, Valiev RZ (2000) Mater Sci Eng A 282:78
Alexandrov IV, Zhang K, Kilmametov AR, Lu K, Valiev RZ (1997) Mater Sci Eng A 234–236:331
Hong SJ, Kim T-S, Kim HS, Kim WT, Chun BS (1999) Mater Sci Eng A 271:469
Kim T-S, Chae HJ (2008) Rev Adv Mater Sci 18:769
Kim T-S (2010) J Alloys Compd 504S:S496
Amaral LF, Oliveira IR, Salomao R, Frollini E, Pandolfelli VC (2010) Ceram Int 36:1047
Chae HJ, Kim YD, Kim T-S (2011) J Alloys Compd 509S:S250
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (No. 2010-0026981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, E.Y., Lee, D.J., Kim, TS. et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloy consolidated from gas-atomized powders using high-pressure torsion. J Mater Sci 47, 7117–7123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6408-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6408-0