Abstract
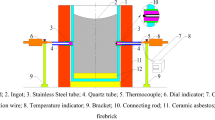
Contraction and distortion of a casting during cooling within a mould can force their respective surfaces together, with the associated increased interfacial pressure resulting in increased interfacial heat transfer. This problem has been examined for the case of gravity and low pressure die casting of an Al alloy, where an insulating coating is applied to the die cavity to assist filling of the mould. The degree of interfacial pressure was estimated to be, for a typical small die casting, at most about 21 MPa. Repeated applications of a compressive load showed that a freshly applied die coating became thinner and smoother, until a stable situation was reached after about ten applications. The interfacial heat transfer coefficient was estimated to be increased by about 20%, with an increase in the applied pressure by a factor of two, from 7 MPa to 14 MPa, and increased by about 40%, with an increase in the applied pressure by a factor of three, from 7 MPa to 21 MPa. The heat transfer mechanisms between the casting and the die surfaces were evaluated to produce a simple model of interfacial heat transfer which included conduction through the points of actual contact, in parallel with conduction through the interfacial gas between the points of actual contact, both mechanisms being in series with the heat transfer by conduction through the die coating. Evaluation of the model produced agreement with experimentally determined values of the interfacial heat transfer coefficient to within about 15%.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hattel J (ed) (2005) Fundamentals of numerical modelling of casting processes. Polyteknisk Forlag, Kgs. Lyngby
Ho K, Pehlke RD (1985) Met Trans B 16B:359
Narayan Prabhu K, Griffiths WD (2002) Mat Sci Technol 18:804
Sahin HM, Kocatepe K, Kayikci R, Akar N (2006) Energy Convers Manag 47:19
O’Mahoney D, Browne DJ (2000) Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 22:111
Ferreira IL, Spinelli JE, Nestler B, Garcia A (2008) Mat Chem Phys 111:444
Cheung N, Ferreira IL, Pariona MM, Quaresma JMV, Garcia A (2009) Mat Design 30:3592
Ferreira IL, Spinelli JE, Pires JC, Garcia A (2005) Mat Sci Eng A 408:317
Arunkumar S, Sreenivas Rao KV, Prasanna Kumar TS (2008) Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:2676
Nayak RK, Sundarraj S (2009) Int J Cast Met Res 22:294
Campbell J (1991) Castings. Butterworth-Heinemann, London
Cheung N, Santos NS, Quaresma JMV, Dulikravich GS, Gracia A (2009) Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:451
Spinelli JE, Ferreira IL, Garcia A (2006) Struct Multidisc Optim 31:241
Mirbagheri SMH, Shrinparvar M, Chirazi A (2007) Mat Design 28:2106
Mirbagheri SMH (2007) Commun Numer Methods Eng 23:295
Meneghini A, Sangiorgi Cellini G, Tomesani L (2007) Int J Cast Met Res 20:159
Aweda JO, Adeyemi MB (2009) J Mat Proc Technol 209:1477
Chattopadhyay H (2007) J Mat Proc Technol 186:174
Guo Z-P, Xiong S-M, Cho S-H, Choi J-K (2008) J Mater Sci Technol 24:131
Guo Z-P, Xiong S-M, Liu BC, Li M, Allison J (2008) Met Mat Trans A 39A:2896
Guo Z-P, Xiong S-M, Liu BC, Li M, Allison J (2009) Int J Cast Met Res 327-330
Guo Z-P, Xiong S-M, Liu BC, Li M, Allison J (2008) Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:6032
Dour G, Dargusch M, Davidson C, Nef A (2005) J Mat Proc Technol 169:223
Hamasaiid A, Dour G, Dargusch MS, Loulou T, Davidson C, Savage G (2008) Met Mat Trans A 39A:853
Dargusch MS, Hamasaiid A, Dour G, Loulou T, Davidson CJ, StJohn DH (2007) Adv Eng Mat 9:995
Sun RC (1970) AFS Cast Metals Res J 6:105
Kumar TSP, Prabhu KN (1991) Met Mat Trans B 22B:717
Trovant M, Argyropoulis S (2000) Met Mat Trans B 31B:75
Griffiths WD (2000) Met Mat Trans B 31B:285
Griffiths WD (2000) Mat Sci Technol 16:255
Hallam CP, Griffiths WD (2004) Met Mat Trans B 35B:721
Isaac J, Reddy GP, Sharma GK (1985) Br Foundryman 78:465
Chiesa F (1990) AFS Trans 98:193
Lee Z-H, Kim T-G, Choi Y-S (1998) Met Mat Trans B 29B:1051
Hamasaiid A, Dargusch MS, Davidson CJ, Tovar S, Loulou T, Rezai-Aria F, Dour G (2007) Met Mat Trans A 38A:1303
Martorano MA, Capocchi JDT (2000) Int J Heat Mass Transf 43:2541
www.magmasoft.com (2009)
Griffiths WD (1999) Met Mat Trans B 30B:473
Kawai K (2004) PhD thesis, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of Mr. Adrian Caden and Dr. Jean-Christophe Gebelin of the School of Metallurgy and Materials Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom, B15 2TT. The authors would also like to gratefully acknowledge the funding of a PhD studentship which enabled this work to be carried out by Foseco (FS) Ltd., Tamworth, Staffs., United Kingdom, B78 3XQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffiths, W.D., Kawai, K. The effect of increased pressure on interfacial heat transfer in the aluminium gravity die casting process. J Mater Sci 45, 2330–2339 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4198-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4198-9