Abstract
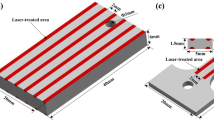
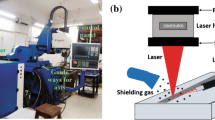
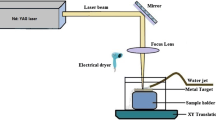
Laser surface melting was used to treat electro-metallurgic WC/steel composites. The microstructure and properties of the melted zone were investigated. It was found that a homogenous and fine microstructure was formed in the melted zone. A significant phase precipitated was the herringbone eutectic carbide of Fe3W3C. The volume fraction of the eutectics was related to the thermal absorption increasing with the decrease of scanning rate. Preheating was beneficial to form the orientation dendrite structure and to increase the volume fraction of the eutectics. The laser melted surface possessed better microhardness and wear resistance compared to the substrate. The volume fraction of the eutectics played an important role on the wear resistance which increased with the increase of the volume fraction of the eutectics. The wear resistance was mainly depended on the content of the primary WC, as increased with the increase of the content of WC. The improvement of interface bonding, fine eutectic precipitation and structure refinement etc. were regarded as the micro-mechanism of enhancing the surface properties.











Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Hashim J, Looney L, Hashmi MSJ (1999) J Mater Process Technol 92–93:1
Kambakas K, Tsakiropoulos P (2005) Mater Sci Eng A 413–414:538
Zhao M, Liu A, Guo M et al (2006) Surface Coating Technol 201:1655
Zhang G-S, Xing J-D, Gao Y-M (2006) Wear 260:728
Panchal PM, Vela T, Robisch T (1990) Fabrication of particulate reinforced metal composites. ASM International, Metals Park, OH, pp 245–260
You XQ, Song XF, Ren H (2005) Trans Nonferrous Metal Soc China 15(6):1333
Kwok CT, Leong KI, Cheng FT et al (2003) Mat Sci Eng A 357:94
Colac R, Vilar R (2004) Mat Sci Eng A 385:123
Pirso J, Letunovitš S, Viljus M (2004) Wear 257:259
Archard JF (1953) J Appl Phys 24:981
Allmen MV (1987) Laser-beam interactions with materiais: physical principles and applications. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany
Kac S, Kusinski J (2004) Surface Coating Technol 180:612
Shen ZH, Zhang SY, Lu J et al (2001) Optic Laser Technol 33:533
Choi J, Choudhuri SK, Mazumder J (2000) J Mat Sci 35:3213
Yang Y, Zhu Y, Liu Z et al (2000) Mat Sci Eng 291:171
Ocelı´k V, Matthews D, De Hosson JThM (2005) Surface Coating Technol 197:304
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the supports of the laboratory center of institute of material science and engineering at Hefei University of Technology. This research was sponsored by the natural science research foundation of department of education of An Hui province in china under Grant NO 2006KG083A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, X., Zhang, C., Liu, N. et al. Laser surface melting of electro-metallurgic WC/steel composites. J Mater Sci 43, 2929–2934 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1798-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1798-0