Abstract
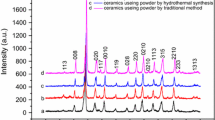
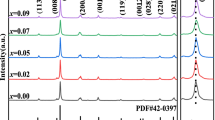
Calcium bismuth niobate CaBi2Nb2O9 (CBN) ceramic is a promising candidate for high-temperature piezoelectric applications due to its high Curie temperature. However, the extremely low piezoelectric properties hinder its application. A combination method with element doping and texturing was used to improve the electric properties of CBN ceramic. First of all, the Mn element was chosen to be doped to improve the piezoelectric and resistance properties of CBN ceramic. Then, an optimal composition was subsequently textured by templated grain growth (TGG) method to further improve the piezoelectric properties. The piezoelectric properties, Curie temperature (Tc), and resistivity of textured Ca0.95Mn0.05Bi2Nb2O9 ceramics (d 33 = 21, k p = 10.9 %, Tc = 942 °C, ρ = 2.1 × 105Ω·cm at 600 °C) were improved obviously compared to pure random CBN ceramics (d 33 = 6, k p = 4.6 %, Tc = 930 °C, ρ = 0.6 × 105Ω · cm at 600 °C). Furthermore, it has excellent resistance to thermal depoling and keep about 5.7 % kp until the temperature up to 600 °C. This combination method makes the textured Ca0.95Mn0.05Bi2Nb2O9 ceramics to be a promising candidate for high-temperature piezoelectric applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.B. Chen, F. Fu, J.W. Zhai, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 50, 050207 (2011)
X.D. Zhang, H.X. Yan, M.J. Reece, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 2928 (2008)
H.X. Yan, H.T. Zhang, R. Ubic, M.J. Reece, J. Liu, Z.J. Shen, Z. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 17, 1261 (2005)
C.M. Wang, S.J. Zhang, J.F. Wang, M.L. Zhao, C.L. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 118, 21 (2009)
Z.G. Gai, Y.Y. Feng, J.F. Wang, M.L. Zhao, L.M. Zheng, C.M. Wang, S.J. Zhang, T.R. Shrout, Phys. Status Solidi a-Appl. Mater. Sci. 207, 1792 (2010)
H.T. Zhang, H.X. Yan, M.J. Reece, J. Appl. Phys. 106, 044106 (2009)
W. Wang, D. Shan, J.B. Sun, X.Y. Mao, X.B. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 044102 (2008)
H.X. Yan, H.T. Zhang, Z. Zhang, R. Ubic, M.J. Reece, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2785 (2006)
C.M. Wang, J.F. Wang, S.J. Zhang, T.R. Shrout, Phys. Status Solidi-R. 3, 49 (2009)
H. T. Zhang, H. X. Yan, M. J. Reece, J. Appl. Phys. 108 (2010).
K. Shoji, M. Aikawa, Y. Uehara, K. Sakata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1 37, 5273 (1998)
A. Moure, L. Pardo, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 084103 (2005)
H. Zhang, H. Yan, X. Zhang, M.J. Reece, J. Liu, Z. Shen, Y. Kan, P. Wang, Mat. Sci. Eng. a-Struct. 475, 92 (2008)
J. Liu, Z.J. Shen, M. Nygren, Y.M. Kan, P.L. Wang, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 3233 (2006)
Z.Y. Zhou, X.L. Dong, H.X. Yan, Scr. Mater. 55, 791 (2006)
X.L. Dong, Z.Y. Zhou, H.X. Yan, H. Chen, C.L. Mao, J. Appl. Phys. 100, 044112 (2006)
S.J. Zhang, F.P. Yu, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3153 (2011)
G.R. Li, L.Y. Zheng, Q.R. Yin, B. Jiang, W.W. Cao, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 064108 (2005)
Y.Y. Wu, X.H. Wang, C.F. Zhong, L.T. Li, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3877 (2011)
L.N. Zhang, G.R. Li, S.C. Zhao, A.L. Ding, Q.R. Yin, Integr. Ferroelectr. 79, 253 (2006)
L.N. Zhang, S.C. Zhao, H.F. Yu, L.Y. Zheng, G.R. Li, Q.R. Yin, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1 43, 7613 (2004)
I. Pribosic, D. Makovec, M. Drofenik, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 1327 (2001)
F. Gao, R.Z. Hong, J.J. Liu, Y.H. Yao, C.S. Tian, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 2063 (2008)
S.K. Rout, A. Hussain, E. Sinha, C.W. Ahn, I.W. Kim, Solid State Sci. 11, 1144 (2009)
Y. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama, K. Takatori, T. Homma, T. Nagaya, M. Nakamura, Nature 432, 84 (2004)
F. Fu, B. Shen, J.W. Zhai, Z.K. Xu, X. Yao, Ceram. Int. 38, S287 (2012)
Y. Chen, X.L. Dong, R.H. Liang, J.T. Li, Y.L. Wang, J. Appl. Phys. 98, 064107 (2005)
Y. Wu, M.J. Forbess, S. Seraji, S.J. Limmer, T.P. Chou, C. Nguyen, G.Z. Cao, J. Appl. Phys. 90, 5296 (2001)
H.X. Yan, H.T. Zhang, M.J. Reece, X.L. Dong, Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 082911 (2005)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under grant No. 50932007, the “hundred Talent Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Western Light Foundation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Shen, B., Xu, J. et al. A combination method for improving electrical property of Calcium bismuth niobate ceramics. J Electroceram 30, 133–138 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-012-9774-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-012-9774-8