Abstract
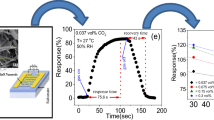
ZnO nanorods were prepared via a hydrothermal reaction in a solution containing Zn(NO3)2⋅6H2O, NaOH, cyclohexylamine, ethanol and water, and their NO2 and CO sensing behaviors were investigated. The morphology and agglomeration of ZnO nanorods could be manipulated by controlling the amount of water in the solution, which was explained by the variation in the [OH−] due to an interaction between the water and cyclohexylamine. Sea-urchin-like and well-dispersed ZnO nanorods were prepared at low and high water content, respectively. Well-dispersed ZnO nanorods showed 1.8 fold change in resistance at 1 ppm NO2 while there was no significant change in resistance at 50 ppm CO. The present ZnO nanorods can be used in automated car ventilation systems to detect NO2 in the presence of CO.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Nakagawa, S. Okazaki, S. Asakusa, K. Fukuda, H. Akimoto, S. Takahashi, and S. Shigemori, Sensors and Actuators B., 65, 133 (2000).
K. Oto, A. Shinobe, M. Manabe, H. Kakuuchi, Y. Yoshida, and T. Nakahara, Sensors and Actuators B., 77, 525 (2001).
C. Pijolat, C. Pupier, M. Sauvan, G. Tournier, and R. Lalauze, Sensors and Actuators B., 59, 195 (1999).
N. Yamazoe and N. Miura, Chemical Sensor Technology, Vol. 4, edited by S. Yamauchi (Kodansha and Elsevier, Tokyo, 1992), p. 19.
C.O. Park and S.A. Akbar, J. Mater. Sci., 38, 4611 (2003).
C.C. Wang, S.A. Akbar, and M.J. Madou, J. Electroceramics, 2(4), 273 (1998).
Y. Shimizu, T. Takeo, and M. Egashira, J. Euro. Ceram. Soc., 24, 1389 (2004).
A. Kolmakov, Y. Zhang, G. Cheng, and M. Moskovits, Adv. Mater., 15, 997 (2003).
C. Li, D.D. Zhang, X. Liu, S. Han, T. Tang, and J. Han, Appl. Phys. Lett., 82, 1613 (2003).
O.K. Oomman, K. Varghese, D. Gong, M. Paulose, K.G. Ong, E.C. Dickey, and C.A. Grimmes, Adv. Mater., 15, 624 (2003).
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd ed. (Addison-Wesley, 1978), p. 102.
H. Zhang, D. Yang, Y. Ji, X. Ma, and D. Que, J. Phys. Chem. B., 108, 3955 (2004).
H. Wei, Y. Wu, N. Lun, and C. Hu, Mater. Sci. and Eng. A, 393, 80 (2005).
Y. Min, H.L. Tuller, S. Palzer, J. Wöllenstein, and H. Bottner, Sensors and Actuators B, 93, 435 (2003).
N. Koshizaki and T. Oyama, Sensors and Actuators B, 66, 119 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presenting author in conference: PYEONG-SEOK CHO
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, PS., Kim, KW. & Lee, JH. NO2 sensing characteristics of ZnO nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method. J Electroceram 17, 975–978 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-006-8146-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10832-006-8146-7