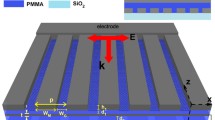
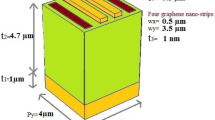
Plasmonic effects can be used in high sensitivity sensors, which have attracted widespread attention. However, most of the previously reported refractive index sensors can no longer be adjusted once fabricated, and their figure of merit (FOM) is undesirable. Concerning this, we propose a refractive index sensor consisting of a graphene waveguide and a graphene elliptical cavity working in the mid-infrared range. Its performance can be adjusted in real time by applying a bias voltage to the graphene patterns. The sensitivity of the proposed sensor can reach 2850 nm/refractive index unit and FOM up to 633, respectively. Owing to its excellent sensing properties of high sensitivity and high FOM, the proposed sensor can be applied in gas sensing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. H. L. Koppens, D. E. Chang, and G. D. A. F. Javier, Nano Lett., 11, No. 8, Article ID 3370 (2011).
A. S. Rodin, Z. Fei, A. S. Mcleod, et al., Physics (2016).
L. Ju, B. Geng, J. Horng, et al., Nature Nanotech., 6, No. 10, 630 (2011).
D. B. Farmer, D. Rodrigo, T. Low, et al., Nano Lett., 15, No. 4, 2582–2587 (2015).
P. Li, T. Wang, H. Böckmann, et al., Nano Lett., 14, No. 8, Article ID 4400 (2014).
B. Vasić, G. Isić, and R. Gajić, J. Appl. Phys., 113, No. 1, Article ID 21556 (2013).
Y. Li, H. Yan, D. B. Farmer, et al., Nano Lett., 14, No. 3, 1573 (2014).
W. Wei, J. Nong, Y. Zhu, et al., Opt. Commun. (2016).
J. N. Anker, W. P. Hall, O. Lyandres, et al., Nanosci. Technol.: A Collection Rev. from Nature J., 308–319 (2010).
L. A. Falkovsky, Phys. Usp., 51, No. 9, 887–897 (2008).
S. A. Maier, Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications, Springer Science & Business Media (2007).
V. G. Kravets, R. Jalil, Y. J. Kim, et al., Sci. Reports, 4, 5517 (2014).
O. Salihoglu, S. Balci, and C. Kocabas, Appl. Phys. Lett., 100, No. 21, Article ID 213110 (2012).
P. R. Griffiths and J. A. D. Haseth, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry, 2nd Ed., Proteomics (2007).
D. Rodrigo, O. Limaj, D. Janner, et al., Mid-Infrared Plasmonic Biosensing with Graphene. Science, 349(6244), 165–168 (2015).
J. Homola, S. S. Yee, and G. Gauglitz, Sens. Actuators B Chem., 54, Nos. 1–2, 3–15 (1999).
S. Law, V. Podolskiy, and D. Wasserman, Nanophotonics, 2, No. 2, 103–130 (2013).
J. M. Bingham, J. N. Anker, L. E. Kreno, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 132, No. 49, 17358–17359 (2010).
M. W. Sigrist, R. Bartlome, D. Marinov, et al., Appl. Phys. B, 90, No. 2, 289–300 (2008).
X. Yan, T. Wang, X. Han, et al., Plasmonics, 1–7 (2016).
T. Wenger, G. Viola, J. Kinaret, et al., Materials, 4, No. 2 (2017).
R. E. Peale, J. W. Cleary, W. R. Buchwald, et al., Proc. SPIE, The Int. Soc. Opt. Eng., 767306(95), 730–734 (2010).
B. Wang and G. P. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett., 87, No. 1, Article ID 013107(1–3) (2005).
L. A. Falkovsky, J. Exp. Theor. Phys., 106, No. 3, 575–580 (2008).
B. Ruan, Q. You, J. Zhu, et al., IEEE Sensors J., 18, 7436–7441 (2018).
D. Wu, J. Tian, L. Li, et al., Opt. Commun., 412, 41–48 (2018).
G. W. Hanson, J. Appl. Phys., 103, No. 6, Article ID 064302 (2008).
A. Moreau, C. Ciracì, et al., Nature, 492(7427), 86–89 (2012).
B. Zhu, G. Ren, S. Zheng, et al., Opt. Express, 21, No. 14, 17089–17096 (2013).
X . Wang, T. He, M. A. Mohammad, et al., Nat. Commun., 6, Article ID 7767 (2015).
D. Yadav, S. B. Tombet, T. Watanabe, et al., Materials, 3, No. 4, Article ID 045009 (2016).
X. Binggang, T. Shengjun, A. Fyffe, and Z. Shi, Opt. Express, 28, 4048–4057 (2020).
Y. Zhang and M. Cui, J. Electron. Mater., 48, No. 2, 1005–1010 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 89, No. 5, pp. 719–725, September–October, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Li, X., Lin, H. et al. Tunable Refractive Index Sensor Made Using Graphene with a High Figure of Merit. J Appl Spectrosc 89, 923–929 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01449-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01449-8