Abstract
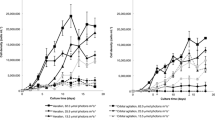
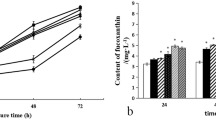
In this study, the correlation between the specific growth rate of Phaeodactylum tricornutum and fucoxanthin (fucoxanthin) biosynthesis was investigated both in batch and in semi-continuous cultures. Fucoxanthin content from P. tricornutum biomass showed a positive correlation with specific growth rate during the normal culture period. The maximum yield of fucoxanthin (2.42 mg g−1 dry biomass) was observed at day 5, and the highest specific growth rate (1.91) was observed at day 4, both of which were during the exponential phase. Upon treatment with growth inhibitors (AZD-8055 or norflurazon) during the exponential phase, fucoxanthin content decreased with growth rate in a concentration-dependent manner. In a semi-continuous culture of P. tricornutum with dilution rates from 0.1 to 0.5 day−1, we found a positive correlation between specific growth rate and fucoxanthin biosynthesis in a steady-state condition. Based on the transcriptome analysis results, different metabolic and key regulatory genes were active at different growth phases. Particularly, during the exponential growth phase, various genes related to regulatory mechanisms, such as cell growth and replication, were expressed, whereas in the stationary phase, their expression was reduced. In the fucoxanthin biosynthesis pathway, 1-deoxy-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate synthase (ISPD) and violaxanthin deepoxidase (VDE) genes showed higher expression levels in the exponential phase, thus indicating that they are critical genes for the regulation of fucoxanthin biosynthesis in P. tricornutum. Our results are valuable to our understanding of the basic mechanism of fucoxanthin biosynthesis, thus providing theoretical guidance for the commercial production of fucoxanthin derived from P. tricornutum.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer C, Schmitz C, Corrêa R, Herrera C, Ramlov F, Oliveira E, Pizzato A, Varela L, Cabral D, Yunes R (2019) In vitro fucoxanthin production by the Phaeodactylum tricornutum diatom. Stud Nat Prod Chem 63:211–242
Branco-Vieira M, San Martin S, Agurto C, Santos MA d, Freitas MA, Mata TM, Martins AA, Caetano NS (2018) Potential of Phaeodactylum tricornutum for biodiesel production under natural conditions in Chile. Energies 11:54
Butler T, Kapoore RV, Vaidyanathan S (2020) Phaeodactylum tricornutum: a diatom cell factory. Trends Biotechnol 38:606–622
Cerón-García M, Fernández-Sevilla J, Sánchez-Mirón A, García-Camacho F, Contreras-Gómez A, Molina-Grima E (2013) Mixotrophic growth of Phaeodactylum tricornutum on fructose and glycerol in fed-batch and semi-continuous modes. Bioresour Technol 147:569–576
Conceição D, Lopes R, Derner R, Cella H, Carmo A, D’Oca M, Petersen R, Passos M, Vargas J, Galli-Terasawa L, Kava V (2020) The effect of light intensity on the production and accumulation of pigments and fatty acids in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Appl Phycol 32:1017–1025
Cui Y, Thomas-Hall SR, Schenk PM (2019) Phaeodactylum tricornutum microalgae as a rich source of omega-3 oil: progress in lipid induction techniques towards industry adoption. Food Chem 297:124937–124946
Dai J, Kim JC (2016) In vivo anti-obesity efficacy of fucoxanthin-loaded emulsions stabilized with phospholipid. J Pharm Investig 46:669–675
Desbois AP, Lebl T, Yan L, Smith VJ (2008) Isolation and structural characterization of two antibacterial free fatty acids from the marine diatom, Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:755–764
Eilers U, Bikoulis A, Breitenbach J, Büchel C, Sandmann G (2016) Limitations in the biosynthesis of fucoxanthin as targets for genetic engineering in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Appl Phycol 28:123–129
Fabregas J, Patino M, Morales ED, Cordero B, Otero A (1996) Optimal renewal rate and nutrient concentration for the production of the marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum in semicontinuous cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:266–268
Gómez-Loredo A, Benavides J, Rito-Palomares M (2016) Growth kinetics and fucoxanthin production of Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Isochrysis galbana cultures at different light and agitation conditions. J Appl Phycol 28:849–860
Guillard RR (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Springer, Boston, pp 29–60
Guler B, Deniz I, Demirel Z, Oncel S, Imamoglu E (2019) Transition from start-up to scale-up for fucoxanthin production in flat plate photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 31:1525–1533
Hempel F, Lau J, Klingl A, Maier UG (2011) Algae as protein factories: expression of a human antibody and the respective antigen in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. PloS One 6:e28424. doi:
Imamura S, Kawase Y, Kobayashi I, Shimojima M, Ohta H, Tanaka K (2016) TOR (target of rapamycin) is a key regulator of triacylglycerol accumulation in microalgae. Plant Signal Behav 11:e1149285
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kim SM, Jung YJ, Kwon ON, Cha KH, Um BH, Chung D, Pan CH (2012) A potential commercial source of fucoxanthin extracted from the microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Appl Environ Microbiol 166:1843–1855
Koo SY, Hwang JH, Yang SH, Um JI, Hong KW, Kang K, Pan CH, Hwang KT, Kim SM (2019) Anti-obesity effect of standardized extract of microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum containing fucoxanthin. Mar Drugs 17:311–326
Li Y, Xu J, Gao K (2014) Light-modulated responses of growth and photosynthetic performance to ocean acidification in the model diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. PloS One 9:e96173
Li F, Beardall J, Collins S, Gao K (2017) Decreased photosynthesis and growth with reduced respiration in the model diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum grown under elevated CO2 over 1800 generations. Glob Chang Biol 23:127–137
Liu J, Zhong Y, Sun Z, Huang J, Sandmann G, Chen F (2010) One amino acid substitution in phytoene desaturase makes Chlorella zofingiensis resistant to norflurazon and enhances the biosynthesis of astaxanthin. Planta 232:61–67
Madhuri S, Bártulos CR, Serif M, Lepetit B, Kroth PG (2019) A strategy to complement PtAUREO1a in TALEN knockout strains of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Algal Res 39:101469–101478
Niu YF, Yang ZK, Zhang MH, Zhu CC, Yang WD, Liu JS, Li HY (2012) Transformation of diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum by electroporation and establishment of inducible selection marker. Biotechniques 52:1–3
Peng J, Yuan JP, Wu CF, Wang JH (2011) Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and diatoms: metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health. Mar Drugs 9:1806–1828
Pérez EB, Pina IC, Rodríguez LP (2008) Kinetic model for growth of Phaeodactylum tricornutum in intensive culture photobioreactor. Biochem Eng J 40:520–525
Petrushkina M, Gusev E, Sorokin B, Zotko N, Mamaeva A, Filimonova A, Kulikovskiy M, Maltsev Y, Yampolsky I, Guglya E (2017) Fucoxanthin production by heterokont microalgae. Algal Res 24:387–393
Prioretti L, Avilan L, Carrière F, Montane MH, Field B, Grégori G, Menand B, Gontero B (2017) The inhibition of TOR in the model diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum promotes a get-fat growth regime. Algal Res 26:265–274
Rodríguez-León JA, de Carvalho JC, Pandey A, Soccol CR, Rodríguez-Fernández DE (2018) Kinetics of the solid-state fermentation process. In: Pandey A, Larroche C, Soccol C (eds) Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering: current advances in solid-state fermentation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 57–82
Saoudi-Helis L, Dubacq JP, Marty Y, Samain JF, Gudin C (1994) Influence of growth rate on pigment and lipid composition of the microalga Isochrysis aff. galbana clone T. iso. J Appl Phycol 6:315–322
Serif M, Dubois G, Finoux AL, Teste MA, Jallet D, Daboussi F (2018) One-step generation of multiple gene knock-outs in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum by DNA-free genome editing. Nat Commun 9:1–10
Sørensen M, Berge GM, Reitan KI, Ruyter B (2016) Microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum in feed for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)—effect on nutrient digestibility, growth and utilization of feed. Aquaculture 460:116–123
Steinbrenner J, Sandmann G (2006) Transformation of the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis with a phytoene desaturase for accelerated astaxanthin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7477–7484
Taparia Y, Zarka A, Leu S, Zarivach R, Boussiba S, Khozin-Goldgerg I (2019) A novel endogenous selection marker for the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum based on a unique mutation in phytoene desaturase 1. Sci Rep 9:8217–8229
Thiriet-Rupert S, Carrier G, Chénais B, Trottier C, Bougaran G, Cadoret JP, Schoefs B, Saint-Jean B (2016) Transcription factors in microalgae: genome-wide prediction and comparative analysis. BMC Genom 17:282–298
Undabeytia T, Nir S, Tel-Or E, Rubin B (2000) Photostabilization of the herbicide norflurazon by using organoclays. J Agric Food Chem 48:4774–4779
Vuppaladadiyam AK, Prinsen P, Raheem P, Lique R, Zhao M (2018) Microalgae cultivation and metabolites production: a comprehensive review. Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 12:304–324
Wang S, Verma SK, Said IH, Thomsen L, Ullrich MS, Kuhnert N (2018) Changes in the fucoxanthin production and protein profiles in Cylindrotheca closterium in response to blue light-emitting diode light. Microb Cell Factories 17:1–13
Xin L, Hong-Ying H, Yu-Ping Z (2011) Growth and lipid accumulation properties of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. under different cultivation temperature. Bioresour Technol 102:3098–3102
Xu J, Fan X, Li X, Fiu G, Zhang Z, Zhu Y, Fu Z, Qian H (2017) Effect of salicylic acid on fatty acid accumulation in Phaeodactylum tricornutum during stationary growth phase. J Appl Phycol 29:2801–2810
Yang R, Wei D (2020) Improving fucoxanthin production in mixotrophic culture of marine diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum by LED light shift and nitrogen supplementation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:820–834
Yi Z, Su Y, Cherek P, Nelson D, Lin J, Folfsson O, Wu H, Ashtiani K, Brynjolfsson S, Fu W (2019) Combined artificial high-silicate medium and LED illumination promote carotenoid accumulation in the marine diatome Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Microb Cell Fact 18:209–220
Zarekarizi A, Hoffmann L, Burritt D (2019) Approaches for the sustainable production of fucoxanthin, a xanthophyll with potential health benefits. J Appl Phycol 31:281–299
Zhu L (2015) Microalgal culture strategies for biofuel production: a review. Biofuel Bioprod Biorefin 9:801–814
Funding
This work was supported by the intramural grant (2Z06110) from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 215 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, D.Y., Vuong, T.T., Choi, J. et al. Fucoxanthin biosynthesis has a positive correlation with the specific growth rate in the culture of microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum. J Appl Phycol 33, 1473–1485 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02376-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-021-02376-5