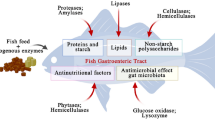
Abstract
Macroalgae with high nutritional value are a potential ingredient for aquafeed. However, the presence of anti-nutritional factors such as non-starch polysaccharides (NSPs) in macroalgae prevents their application. The present study was conducted to investigate whether the supplementation of exogenous NSP-degrading enzymes in macroalgae-containing diets can avoid the above disadvantage in the rabbitfish Siganus canaliculatus. Seven isoproteic (32%) and isolipidic (8%) diets (D1–D7) were prepared for the culture of rabbitfish juveniles lasting 10 weeks. D1 without macroalgae and NSP-degrading enzymes were used as control diet, D2–D4 contained 12% dry powder of macroalgae Ulva prolifera, Gracilaria lemaneiformis, or Ulva pertusa, respectively, while D5–D7 were supplemented with 0.05% NSP-degrading enzymes on the base of D2–D4. The results showed that the growth performance of fish-fed D5–D7 displayed as good as those fed D1 and was significantly higher than those fed D2–D4 (P < 0.05). The activities of serum lysozyme, superoxide dismutase, and acid phosphatase were significantly elevated in fish-fed diets with addition of macroalgae (D2–D7) compared with fish-fed D1 (P < 0.05). The amino acid and fatty acid composition of fillet showed no difference among different dietary groups (P > 0.05). By the end of the growth trial, 60 fish from each dietary group were subjected with Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge by intra-peritoneally injection at 105 cfu mL−1 and 0.01 mL g−1 body mass. The survival at day 15 post-challenge in fish-fed D4–D7 was significantly higher than those fed D1. The results demonstrated that macroalgae can be used as a dietary ingredient for S. canaliculatus at 12% when supplemented with 0.05% NSP-degrading enzymes. Moreover, the addition of macroalgae in diet can improve the innate immune capability of S. canaliculatus and enhance the disease resistance against V. parahaemolyticus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbary P, Aminikhoei Z (2018) Effect of water-soluble polysaccharide extract from the green alga Ulva rigida on growth performance, antioxidant enzyme activity, and immune stimulation of grey mullet Mugil cephalus. J Appl Phycol 30:1345–1353
Ai QH, Mai KS, Zhang WB, Xu W, Tan BP, Zhang CX, Li HT (2007) Effects of exogenous enzymes (phytase, non-starch polysaccharide enzyme) in diets on growth, feed utilization, nitrogen and phosphorus excretion of Japanese seabass, Lateolabrax japonicas. Comp Biochem Physiol A 147:502–508
Arockiaraj J, Palanisamy R, Bhatt P, Kumaresan V, Gnanam AJ, Pasupuleti M, Kasi M (2014) A novel murrel Channa striatus mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase: gene silencing, SOD activity, superoxide anion production and expression. Fish Physiol Biochem 40:1937e1955
Araújo M, Rema P, Sousa-Pinto I, Cunha LM, Peixoto MJ, Pires MA, Seixas F, Brotas V, Beltrán C, Valente LM (2016) Dietary inclusion of IMTA-cultivated Gracilaria vermiculophylla in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) diets: effects on growth, intestinal morphology, tissue pigmentation, and immunological response. J Appl Phycol 28:679–689
Bansemer MS, Qin JG, Harris JO, Howarth GS, Stone DA (2016) Nutritional requirements and use of macroalgae as ingredients in abalone feed. Rev Aquacult 8:121–135
Castillo S, Gatlin DM (2015) Dietary supplementation of exogenous carbohydrase enzymes in fish nutrition: a review. Aquaculture 45:286–292
Castro LSEW, Pinheiro TS, Castro AJ, Dore CM, da Silva NB, Alves MGDCF, Santos MSN, Leite EL (2014) Fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown macroalgae Lobophora variegata with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumoral effects. J Appl Phycol 26:1783–1790
Chi C, Giri SS, Jun JW, Kim HJ, Kim SW, Yun S, Park SC (2017) Effects of algal toxin okadaic acid on the non-specific immune and antioxidant response of bay scallop (Argopecten irradians). Fish Shellfish Immunol 65:111–117
Chiu ST, Tsai RT, Hsu JP, Liu CH, Cheng W (2008) Dietary sodium alginate administration to enhance the non-specific immune responses, and disease resistance of the juvenile grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus. Aquaculture 277:66–72
Dantagnan P, Hernández A, Borquez A, Mansilla A (2009) Inclusion of macroalgae meal (Macrocystis pyrifera) as feed ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): effect on flesh fatty acid composition. Aquac Res 41(1):87–94
Choi YH, Lee BJ, Nam TJ (2015) Effect of dietary inclusion of Pyropia yezoensis extract on biochemical and immune responses of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 435:347e353
Cian RE, Drago SR, de Medina FS, Martínez-Augustin O (2015) Proteins and carbohydrates from red seaweeds: evidence for beneficial effects on gut function and microbiota. Mar Drugs 13:5358–5383
Christaki E, Florou-Paneri P, Bonos E (2011) Microalgae: a novel ingredient in nutrition. Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:794–799
Cohen SA, Meys M, Tarvin T, (1989) The pico-tag method: a manual of advanced techniques for amino acid analysis. Waters Chromatography Division. Milford, MA, p124
Diler I, Tekinay AA, Gliroy D, Gliroy BK, Soyutllrk M (2007) Effects of Ulva rigida on the growth, feed intake and body composition of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J Biol Sci 7:305–308
Ehrig K, Alban S (2015) Sulfated galactofucan from the brown alga Saccharina latissimi: variability of yield, structural composition and bioactivity. Mar Drugs 13:76–101
FAO (2014) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2014. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome (223 pp.)
Felix N, Brindo RA (2014) Evaluation of raw and fermented seaweed, Ulva lactuca as feed ingredient in giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Int J Fish Aquat Stud 1:199–204
Güroy B, Ergün S, Merrifield DL, Güroy D (2013) Effect of autoclaved Ulva meal on growth performance, nutrient utilization and fatty acid profile of rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquacult Int 21:605–615
Hernández AJ, Romero A, Gonzalez-Stegmaier R, Dantagnan P (2016) The effects of supplemented diets with a phytopharmaceutical preparation from herbal and macroalgal origin on disease resistance in rainbow trout against Piscirickettsia salmonis. Aquaculture 454:109–117
Holdt SL, Kraan S (2011) Bioactive compounds in seaweed: functional food applications and legislation. J Appl Phycol 23:543–597
Hu C, Li D, Chen C, Ge J, Muller-Karger FE, Liu J, Yu F, He MX (2010) On the recurrent Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. J Geophys Res 115:C5
Huttenhuis HBT, Taverne-Thiele AJ, Grou CPO, Bergsma J, Saeij JPJ, Nakayasu C, Rombout JHWM (2006) Ontogeny of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) innate immune system. Dev Compar Immunol 30:557–574
Kalla A, Yoshimatsu T, Araki T, Zhang DM, Yamamoto T, Sakamoto S (2008) Use of Porphyra spheroplasts as feed additive for red sea bream. Fish Sci 74:104–108
Kamalam BS, Medale F, Panserat S (2017) Utilisation of dietary carbohydrates in farmed fishes: new insights on influencing factors, biological limitations and future strategies. Aquaculture 467:3–27
Kazir M, Abuhassira Y, Robin A, Nahor O, Luo J, Israel A, Golberg A, Livney YD (2019) Extraction of proteins from two marine macroalgae, Ulva sp. and Gracilaria sp., for food application, and evaluating digestibility, amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of the protein concentrates. Food Hydrocoll 87:194–203
Kumar V, Saurabh S, Sahu NP, Pal AK (2005) Glucan, a feed additive to manage aquatic animal health. Aqua Feeds: Formulation & Beyond 2:9–11
Li JS, Li JL, Wu TT (2009) Effects of non-starch polysaccharides enzyme, phytase and citric acid on activities of endogenous digestive enzymes of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus). Aquac Nutr 15:415–420
Lozano I, Wacyk JM, Carrasco J, Cortez-San Martín MA (2016) Red macroalgae Pyropia columbina and Gracilaria chilensis: sustainable feed additive in the Salmo salar diet and the evaluation of potential antiviral activity against infectious salmon anemia virus. J Appl Phycol 28:1343–1351
Maisashvili A, Bryant H, Richardson J, Anderson D, Wickersham T, Drewery M (2015) The values of whole algae and lipid extracted algae meal for aquaculture. Algal Res 9:133–142
Macartain P, Gill CIR, Brooks M, Campbell R, Rowland IR (2007) Nutritional value of edible seaweeds. Nutr Rev 65:535–543
Magalhães R, Lopes T, Martins N, Díaz-Rosales P, Couto A, Pousão-Ferreira P, Oliva-Teles A, Peres H (2016) Carbohydrases supplementation increased nutrient utilization in white seabream (Diplodus sargus) juveniles fed high soybean meal diets. Aquaculture 463:43–50
Magnoni LJ, Martos-Sitcha JA, Queiroz A, Calduch-Giner JA, Gonçalves JFM, Rocha CM, Abreu HT, Schrama JW, Ozorio ROA, Pérez-Sánchez J (2017) Dietary supplementation of heat-treated Gracilaria and Ulva seaweeds enhanced acute hypoxia tolerance in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Biol Open 6:897–908
Mohamed S, Hashim SN, Rahman HA (2012) Seaweeds: a sustainable functional food for complementary and alternative therapy. Trends Food Sci Technol 23:83–96
Moutinho S, Linares F, Rodríguez JL, Sousa V, Valente LMP (2018) Inclusion of 10% seaweed meal in diets for juvenile and on-growing life stages of Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis). J Appl Phycol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1482-6
Norambuena F, Hermon K, Skrzypczyk V, Emery JA, Sharon Y, Beard A, Turchini GM (2015) Algae in fish feed: performances and fatty acid metabolism in juvenile Atlantic salmon. PLoS One 10:e0124042
Øverland M, Mydland LT, Skrede A (2018) Marine macroalgae as a source of protein and bioactive compounds in feed for monogastric animals. J Sci Food Agr doi. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9143
Pereira H, Barreira L, Figueiredo F, Custódio L, Vizetto-Duarte C, Polo C, Rešek E, Engelen A, Varela J (2012) Polyunsaturated fatty acids of marine macroalgae: potential for nutritional and pharmaceutical applications. Mar Drugs 10:1920–1935
Pinteus S, Lemos MF, Silva J, Alves C, Neugebauer A, Freitas R, Duarte A, Pedrosa R (2017) An insight into Sargassum muticum cytoprotective mechanisms against oxidative stress on a human cell in vitro model. Mar Drugs 15:353
Ragaza JA, Koshio S, Mamauag RE, Ishikawa M, Yokoyama S, Villamor SS (2015) Dietary supplemental effects of red seaweed Eucheuma denticulatum on growth performance, carcass composition and blood chemistry of juvenile Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquac Res 46:647–657
Ramos LR, Pedrosa VF, Mori A, Andade CFD, Romano LA, Abreu PC, Tesser MB (2017) Exogenous enzyme complex prevents intestinal soybean meal-induced enteritis in Mugil liza (Valenciennes, 1836) juvenile. Ann Acad Bras Ciênc 89:341–353
Rajendran P, Subramani PA, Michael D (2016) Polysaccharides from marine macroalga, Padina gymnospora improve the nonspecific and specific immune responses of Cyprinus carpio and protect it from different pathogens. Fish Shellfish Immun 58:220–228
Sáez MI, Barros AM, Martinez TF, Rico RM, Tapia ST, Mancera JM, Alarcon FJ, (2012) Effect of dietary inclusion of seaweeds on intestinal proteolytic activity of juvenile seabream, Sparus aurata. 15th Int. Symp of Nutrition and Feeding of Fish
Saurabh S, Sahoo PK (2008) Lysozyme: an important defense molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac Res 39:223–239
Shannon E, Abu-Ghannam N (2016) Antibacterial derivatives of marine algae: an overview of pharmacological mechanisms and applications. Mar Drugs 14(4):81
Shpigel M, Guttman L, Shauli L, Odintsov V, Ben-Ezra D, Harpaz S (2017) Ulva lactuca from an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) biofilter system as a protein supplement in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) diet. Aquaculture 481:112–118
Sotoudeh E, Jafari M (2017) Effects of dietary supplementation with red seaweed, Gracilaria pygmaea, on growth, carcass composition and hematology of juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquacult Int 25:1857–1867
Sinha AK, Kumar V, Makkar HP, De Boeck G, Becker K (2011) Non-starch polysaccharides and their role in fish nutrition–a review. Food Chem 127:1409–1426
Trivedi N, Reddy CRK, Radulovich R, Jha B (2015) Solid state fermentation (SSF)-derived cellulase for saccharification of the green seaweed Ulva for bioethanol production. Algal Res 9:48–54
Walker AB, Fournier HR, Neefus CD, Nardi GC, Berlinsky DL (2009) Partial replacement of fish meal with laver Porphyra spp. in diets for Atlantic cod. N Am J Aquacult 71:39–45
Wan AH, Soler-Vila A, O’Keeffe D, Casburn P, Fitzgerald R, Johnson MP (2016) The inclusion of Palmaria palmata macroalgae in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) diets: effects on growth, haematology, immunity and liver function. J Appl Phycol 28:3091–3100
Wang CY, Shan SS, Xu SA (2012) Preliminary study on enzymolysis of non-starch polysaccharide in feed seaweed powder using pre-digestion method. Feed Ind 33:44–48 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Xie D, Xu S, Wu Q, Chen F, Wang S, You C, Li Y (2018a) Changes of visceral properties and digestive enzymes in the herbivorous marine teleost Siganus canaliculatus fed on different diets. Acta Oceanol Sinica 37:85–93
Xie D, Liu X, Wang S, You C, Li Y (2018b) Effects of dietary LNA/LA ratios on growth performance, fatty acid composition and expression levels of elovl5, Δ4 fad and Δ6/Δ5 fad in the marine teleost Siganus canaliculatus. Aquaculture 484:309–316
Xie D, Yang L, Yu R, Chen F, Lu R, Qin C, Nie G (2017) Effects of dietary carbohydrate and lipid levels on growth and hepatic lipid deposition of juvenile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 479:696–703
Xie D, Xu S, Wang S, You C, Li Y (2016) Cloning, tissue expression, and nutritional regulation of the α-amylase gene in the herbivorous marine teleost Siganus canaliculatus. Aquaculture 454:229–236
Xu S, Zhang L, Wu S, Liu X, Wang S, You C, Li Y (2011) Evaluation of dried seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis as an ingredient in diets for teleost fish Siganus canaliculatus. Aquacult Int 19:1007–1018
Xuan X, Wen X, Li S, Zhu D, Li Y (2013) Potential use of macro-algae Gracilaria lemaneiformis in diets for the black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii, juvenile. Aquaculture 412-413:167–172
Yang H, Li ZB, Chen Q, Li WJ, Sun YZ, Lu J (2016) Effect of fermented Enteromopha prolifera on the growth performance, digestive enzyme activities and serum non-specific immunity of red tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus× Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac Res 47:4024–4031
Yangthong M, Hutadilok-Towatana N, Thawonsuwan J, Phromkunthong W (2016) An aqueous extract from Sargassum sp. enhances the immune response and resistance against Streptococcus iniae in the Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer Bloch). J Appl Phycol 28:3587–3598
You C, Li X, Wang S, Li Y (2014) Effects of non -starch polysaccharide enzymes in diets with seaweed Ulva pertusa on growth, dietary apparent digestibility and flesh nutrition composition of Siganus canaliculatus. Prog Fish Sci 35:46–53 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Yu YY, Chen WD, Liu YJ, Niu J, Chen M, Tian LX (2016) Effect of different dietary levels of Gracilaria lemaneiformis dry power on growth performance, hematological parameters and intestinal structure of juvenile Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 450:356–362
Zhang X, Wu H, Li Z, Li Y, Wang S, Zhu D, Wen X, Li S (2018) Effects of dietary supplementation of Ulva pertusa and non-starch polysaccharide enzymes on gut microbiota of Siganus canaliculatus. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 36:438–449
Zhou S, You C, Wang S, Li Y (2013) Effects of dietary seaweed Enteromorpha prolifera on growth performance, physiological and biochemical characteristics of rabbitfish Siganus canaliculatus. J Fish Sci China 20:1257–1265 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Zhu D, Wen X, Xuan X, Li S, Li Y (2016) The green alga Ulva lactuca as a potential ingredient in diets for juvenile white spotted snapper Lutjanus stellatus Akazaki. J Appl Phycol 28:703–711
Funding
This work was financially supported by China Agriculture Research System (CARS-47) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31873040 and 31602176).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental figure1
(DOCX 83 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, D., Li, X., You, C. et al. Supplementation of macroalgae together with non-starch polysaccharide-degrading enzymes in diets enhanced growth performance, innate immune indexes, and disease resistance against Vibrio parahaemolyticus in rabbitfish Siganus canaliculatus. J Appl Phycol 31, 2073–2083 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1662-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-018-1662-4