Abstract
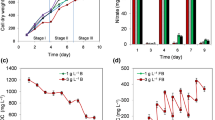
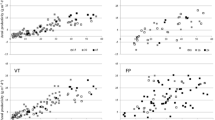
The biomass productivity of Scenedesmus obliquus was investigated outdoors during all seasons in solar tracked flat panel photobioreactors (PBR) to evaluate key parameters for process optimization. CO2 was supplied by flue gas from an attached combined block heat and power plant. Waste heat from the power plant was used to heat the culture during winter. The parameters pH, CO2, and inorganic salt concentrations were automatically adjusted to nonlimiting levels. The optimum biomass concentration increased directly with the photosynthetic active radiation (PAR) from 3 to 5 g dry weight (DW) L−1 for a low PAR of 10 mol photons m−2 day−1 and high PAR of 40–60 mol photons m−2 day−1, respectively. The annual average biomass yield (photosynthetic efficiency) was 0.4 ± 0.5 g DW mol−1 photons. However, biomass yields of 1.5 g DW mol−1 photons close to the theoretical maximum were obtained at low PAR. The productivity (including the night biomass losses) ranged during all seasons from −5 up to 30 g DW m−2 day−1 with a mean productivity of 9 ± 7 g DW m−2 day−1. Low night temperatures of the culture medium and elevated day temperatures to the species-specific optimum increased the productivity. Thus, continuous regulation of the biomass concentration and the culture temperature with regard to the fluctuating weather conditions is essential for process optimization of outdoor microalgal production systems in temperate climates.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan L, Owende P (2010) Biofuels from microalgae—a review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products. Ren Sust Energy Rev 14:557–577
Carvalho A, Silva S, Baptista J, Malcata F (2011) Light requirements in microalgal photobioreactors: an overview of biophotonic aspects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1275
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Collet P, Hélias A, Lardon L, Ras M, Goy R-A, Steyer J-P (2011) Life-cycle assessment of microalgae culture coupled to biogas production. Bioresour Technol 102:207–214
Cornet J-F (2010) Calculation of optimal design and ideal productivities of volumetrically lightened photobioreactors using the constructal approach. Chem Eng Sci 65:985
Cornet J-F, Dussap C-G (2009) A simple and reliable formula for assessment of maximum volumetric productivities in photobioreactors. Biotechnol Prog 25:424–435
Csőgör Z, Herrenbauer M, Schmidt K, Posten C (2001) Light distribution in a novel photobioreactor—modelling for optimization. J Appl Phycol 13:325–333
Cuaresma Franco M, Buffing M, Janssen M, Vílchez Lobato C, Wijffels R (2012) Performance of Chlorella sorokiniana under simulated extreme winter conditions. J Appl Phycol 24:693
Cuaresma M, Janssen M, Vílchez C, Wijffels RH (2009) Productivity of Chlorella sorokiniana in a short light-path (SLP) panel photobioreactor under high irradiance. Biotechnol Bioeng 104:352–359
Doucha J, Straka F, Lívanský K (2005) Utilization of flue gas for cultivation of microalgae (Chlorella sp.) in an outdoor open thin-layer photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 17:403–412
Eberhard S, Finazzi G, Wollman FA (2008) The dynamics of photosynthesis. Annu Rev Genet 42:463–515
Grobbelaar J (2007) Photosynthetic characteristics of Spirulina platensis grown in commercial-scale open outdoor raceway ponds: what do the organisms tell us? J Appl Phycol 19:591–598
Grobbelaar J (2009) Factors governing algal growth in photobioreactors: the “open” versus “closed” debate. J Appl Phycol 21:489–492
Grobbelaar JU, Soeder CJ (1985) Respiration losses in planktonic green algae cultivated in raceway ponds. J Plankton Res 7:497–506
Grobbelaar JU, Soeder CJ, Stengel E (1990) Modeling algal productivity in large outdoor cultures and waste treatment systems. Biomass 21:297–314
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) Past: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9pp
Hartig P, Grobbelaar JU, Soeder CJ, Groeneweg J (1988) On the mass culture of microalgae: areal density as an important factor for achieving maximal productivity. Biomass 15:211–221
Hindersin S, Leupold M, Kerner M, Hanelt D (2013) Irradiance optimization of outdoor microalgal cultures using solar tracked photobioreactors. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 36:345–355
Ho SH, Lu WB, Chang JS (2012) Photobioreactor strategies for improving the CO2 fixation efficiency of indigenous Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N: statistical optimization of CO2 feeding, illumination, and operation mode. Bioresour Technol 105:106–113
Hu Q, Hu ZY, Cohen Z, Richmond A (1997) Enhancement of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) production by manipulating algal density of outdoor cultures of Monodus subterraneus (Eustigmatophyta) and Spirulina platensis (Cyanobacteria). Eur J Phycol 32:81–86
Jackson DA (1993) Stopping rules in principal components analysis: a comparison of heuristical and statistical approaches. Ecology 74:2204–2214
Janssen M, Tramper J, Mur LR, Wijffels RH (2003) Enclosed outdoor photobioreactors: light regime, photosynthetic efficiency, scale-up, and future prospects. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:193–210
Jimenez C, Cosso BR, Niell FX (2003) Relationship between physicochemical variables and productivity in open ponds for the production of Spirulina: a predictive model of algal yield. Aquaculture 221:331–345
Kliphuis AM, de Winter L, Vejrazka C, Martens DE, Janssen M, Wijffels RH (2010) Photosynthetic efficiency of Chlorella sorokiniana in a turbulently mixed short light-path photobioreactor. Biotechnol Prog 26:687–696
Li X, Hu HY, Gan K, Yang J (2010) Growth and nutrient removal properties of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp LX1 under different kinds of nitrogen sources. Ecol Eng 36:379–381
Ma X, Chen KW, Lee YK (1997) Growth of Chlorella outdoors in a changing light environment. J Appl Phycol 9:425–430
Maeda K, Owada M, Kimura N, Omata K, Karube I (1995) CO2 fixation from the flue gas on coal-fired thermal power plant by microalgae. Energy Convers Manag 36:717–720
Melis A (2009) Solar energy conversion efficiencies in photosynthesis: minimizing the chlorophyll antennae to maximize efficiency. Plant Sci 177:272–280
Moheimani NR, Borowitzka MA (2007) Limits to productivity of the alga Pleurochrysis carterae (Haptophyta) grown in outdoor raceway ponds. Biotechnol Bioeng 96:27–36
Negoro M, Shioji N, Ikuta Y, Makita T, Uchiumi M (1992) Growth characteristics of microalgae in high-concentration CO2 gas, effects of culture medium trace components, and impurities thereon. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 34–35:681–692
Negoro M, Shioji N, Miyamoto K, Micira Y (1991) Growth of microalgae in high CO2 gas and effects of SOx and NOx. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 28–29:877–886
Petkov G, Ivanova A, Iliev I, Vaseva I (2012) A critical look at the microalgae biodiesel. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 114:103–111
Pruvost J, Cornet JF, Goetz V, Legrand J (2012) Theoretical investigation of biomass productivities achievable in solar rectangular photobioreactors for the cyanobacterium Arthrospira platensis. Biotechnol Prog 28:699–714
Quinn GP, Keough MJ (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sukenik A, Shelef G (1984) Algal autoflocculation—verification and proposed mechanism. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:142–147
Uduman N, Qi Y, Danquah MK, Forde GM, Hoadley A (2010) Dewatering of microalgal cultures: a major bottleneck to algae-based fuels. J Renew Sustain Energy 2. doi:10.1063/1.3294480
Vandamme D, Foubert I, Meesschaert B, Muylaert K (2010) Flocculation of microalgae using cationic starch. J Appl Phycol 22:525–530
Vandamme D, Pontes SCV, Goiris K, Foubert I, Pinoy LJJ, Muylaert K (2011) Evaluation of electro-coagulation–flocculation for harvesting marine and freshwater microalgae. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:2320–2329
Weyer K, Bush D, Darzins A, Willson B (2010) Theoretical maximum algal oil production. Bioenergy Res 3:204–213
Wiley PE, Brenneman KJ, Jacobson AE (2009) Improved algal harvesting using suspended air flotation. Water Environ Res 81:702–708
Williams PJB, Laurens LML (2010) Microalgae as biodiesel & biomass feedstocks: review & analysis of the biochemistry, energetics & economics. Energy Environ Sci 3:554–590
Acknowledgments
Special thanks are dedicated to Jens Oldeland from the Institute of Biodiversity, Evolution and Ecology of Plants, University of Hamburg, for the helpful hints on the principal component analysis. Many thanks to Dirk Warnecke for comments about the manuscript. The study was funded by the Federal Ministry of Economy and Technology and the city of Hamburg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hindersin, S., Leupold, M., Kerner, M. et al. Key parameters for outdoor biomass production of Scenedesmus obliquus in solar tracked photobioreactors. J Appl Phycol 26, 2315–2325 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0261-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-014-0261-2