Abstract
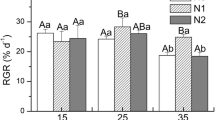
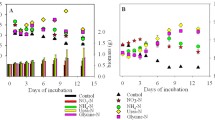
The green-tide macroalga, Ulva prolifera, was tested in the laboratory to determine its nutrient uptake and photosynthesis under different conditions. In the nutrient concentration experiments U. prolifera showed a saturated uptake for nitrate but an escalating uptake in the tested range for phosphorus. Both N/P and NO3 −/NH4 + ratios influenced nutrient uptake significantly (p < 0.05) while the PSII quantum yield [Y(II)] (p > 0.05) remained unaffected. The maximum N uptake rate (33.9 ± 0.8 μmol g−1 DW h−1) and P uptake rate (11.1 ± 4.7) was detected at N/P ratios of 7.5 and 2.2, respectively. U. prolifera preferred NH4 +-N to NO3 −-N when the NO3 −-N/NH4 +-N ratio was less than 2.2 (p < 0.05). But between ratios of 2.2 and 12.9, the uptake of NO3 −-N surpassed that of NH4 +-N. In the temperature experiments, the highest N uptake rate and [Y(II)] were observed at 20 °C, while the lowest rates were detected at 5 °C. P uptake rates were correlated with increasing temperature.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu MH, Pereira R, Buschmann AH, Sousa-Pinto I, Yarish C (2011) Nitrogen uptake responses of Gracilaria vermiculophylla (Ohmi) Papenfuss under combined and single addition of nitrate and ammonium. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 407:190–199
Ale MT, Mikkelsen JD, Meyer AS (2011) Differential growth response of Ulva lactuca to ammonium and nitrate assimilation. J Appl Phycol 23:345–351
Aslan S, Kapdan IK (2006) Batch kinetics of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from synthetic wastewater by algae. Ecol Eng 28:64–70
Bricker SB, Longstaff B, Dennison W, Jones A, Boicourt K, Wicks C, Woerner J (2008) Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries: a decade of change. Harmful Algae 8:21–32
Carpenter SR (2008) Phosphorus control is critical to mitigating eutrophication. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:11039–11040
Chan F, Barth JS, Lubchenco J, Kirincich A, Weeks H, Peterson WT, Menge BA (2008) Emergence of anoxia in the California current large marine ecosystem. Science 319:920
Copertino MS, Tormena T, Seeliger U (2009) Biofiltering efficiency, uptake and assimilation rates of Ulva clathrata (Roth) J. Agardh (Clorophyceae) cultivated in shrimp aquaculture waste water. J Appl Phycol 21:31–45
Henley WJ, Ramus J (1989) Optimization of pigment content and the limits of photoacclimation for Ulva rotundata (Chlorophyta). Mar Biol 103:267–274
Henley WJ, Levavasseur G, Franklin LA, Osmond CB, Ramus J (1991) Photoacclimation and photoinhibition in Ulva rotundata as influenced by nitrogen availability. Planta 184:235–243
Howarth R, Chan F, Conley DJ, Garnier J, Doney SC, Marino R, Billen G (2011) Coupled biogeochemical cycles: eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Front Ecol Environ 9:18–26
Kim JH, Kang EJ, Park MG, Lee BG, Kim KY (2011) Effects of temperature and irradiance on photosynthesis and growth of a green-tide-forming species (Ulva linza) in the Yellow Sea. J Appl Phycol 23:421–432
Kraufvelin P, Lindholm A, Pedersen MF, Kirkerud LA, Bonsdorff E (2010) Biomass diversity and production of rocky shore macroalgae at two nutrient enrichment and wave action levels. Mar Biol 157:29–47
Lapointe BE, Barile PJ, Littler MM, Littler DS, Bedford BJ, Gasque C (2005) Macroalgal blooms on Southeast Florida coral reefs. I. Nutrient stoichiometry of the invasive green alga Codium isthmocladum in the wider Caribbean indicates nutrient enrichment. Harmful Algae 4:1092–1105
Leliaert F, Zhang X, Ye N, Malta EJ, Engelen AE, Mineur F, Verbruggen H, De Clerck O (2009) Identity of the Qingdao algal bloom. Phycol Res 57:147–151
Li X, Hu HY, Gan K, Sun YX (2010) Effects of different nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on the growth, nutrient uptake, and lipid accumulation of a freshwater microalga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour Technol 101:5494–5500
Liu DY, Keesing JK, Xing QG, Shi P (2009) World’s largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar Pollut Bull 58:888–895
Liu F, Pang SJ, Chopin T, Xu N, Shan TF, Gao SQ, Sun S (2010) The dominant Ulva strain of the 2008 green algal bloom in the Yellow Sea was not detected in the coastal waters of Qingdao in the following winter. J Appl Phycol 22:531–540
Luo M, Liu F, Xu Z (2012) Growth and nutrient uptake capacity of two co-occurring species, Ulva prolifera and Ulva linza. Aquat Bot 100:18–24
Merceron M, Antoine V, Auby I, Morand P (2007) In situ growth potential of the subtidal part of green tide forming Ulva spp. stocks. Sci Total Environ 284:293–305
Mou SL, Zhang XW, Ye NH, Dong MT, Liang CW, Liang Q, Miao JL, Xu D, Zheng Z (2012) Cloning and expression analysis of two different LhcSR genes involved in stress adaptation in an Antarctic microalga, Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L. Extremophiles 16:193–203
Naldi M, Wheeler PA (2002) 15N measurements of ammonium and nitrate uptake by Ulva fenestrata (Chlorophyta) and Gracilaria pacifica (Rhodophyta): comparison of net nutrient disappearance, release of ammonium and nitrate, and 15N accumulation in algal tissue. J Phycol 38:135–144
Nelson TA, Haberlin K, Nelson AV, Ribarich H, Hotchkiss R, Van Alstyne KL, Buckingham L, Simunds DJ, Fredrickson K (2008) Ecological and physiological controls of species composition in green macroalgal blooms. Ecology 89:1287–1298
North RL, Guildford SJ, Smith REH, Havens SM, Twiss MR (2007) Evidence for phosphorus, nitrogen, and iron colimitation of phytoplankton communities in Lake Erie. Limnol Oceanogr 52:315–328
Pedersen MF, Borum J (1996) Nutrient control of algal growth in estuarine waters: nutrient limitation and the importance of nitrogen requirements and nitrogen storage among phytoplankton and species of macroalgae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 142:261–272
Pedersen MF, Borum J, Fotel FL (2010) Phosphorus dynamics and limitation of fast- and slow-growing temperate seaweeds in Oslofjord, Norway. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 399:103–115
Qiao F, Dai D, Simpson J, Svendsen H (2009) Banded structure of drifting macroalgae. Mar Pollut Bull 58:1785–1792
Reith JH, Huijgen W, van Hal Lenstra J (2009) Seaweed potential in the Netherlands. Macroalgae—Bioenergy Research Forum. Plymouth, UK
Taylor R, Fletcher RL, Raven JA (2001) Preliminary studies on the growth of selected ‘green tide’ algae in laboratory culture: effects of irradiance, temperature, salinity and nutrients on growth rate. Bot Mar 44:327–336
Tyrrell T (1999) The relative influences of nitrogen and phosphorus on oceanic primary production. Nature 400:525–531
Van Mooy BAS, Fredricks HF, Pedler BE, Dyhrman ST, Karl DM, Koblížek M, Lomas MW, Mincer TJ, Moore LR, Moutin T, Rappé MS, Webb EA (2009) Phytoplankton in the ocean use non-phosphorus lipids in response to phosphorus scarcity. Nature 458:69–72
Vitousek PM, Howarth RW (1991) Nitrogen limitation on the land and in the sea: how can it occur? Biogeochemistry 13:87–115
Vonk JA, Middelburg JJ, Stapel J, Bouma TJ (2008) Dissolved organic nitrogen uptake by seagrasses. Limnol Oceanogr 53:542–548
Wang YT, Xu D, Fan X, Zhang XW, Ye NH, Wang WQ, Mao YZ, Mou SL, Cao SN (2013) Variation of photosynthetic performance, nutrient uptake, and elemental composition of different generations and different thallus parts of Saccharina japonica. J Appl Phycol 25:631–637
Xu D, Gao Z, Zhang X, Qi Z, Meng C, Zhuang Z, Ye N (2011) Evaluation of the potential role of the macroalga Laminaria japonica for alleviating coastal eutrophication. Bioresour Technol 102:9912–9918
Ye NH, Zhang XW, Mao YZ, Liang CW, Xu D, Zou J, Zhuang ZM, Wang QY (2011) ‘Green tides’ are overwhelming the coastline of our blue planet: taking the world’s largest example. Ecol Res 29:541–546
Zhang X, Wang H, Mao Y, Liang C, Zhuang Z, Wang Q, Ye N (2010) Somatic cells serve as a potential propagule bank of Enteromorpha prolifera forming a green tide in the Yellow Sea, China. J Appl Phycol 22:173–180
Zhang XW, Xu D, Mao YZ, Li YX, Xue SY, Zou J, Lian W, Liang CW, Zhuang ZM, Wang QY, Ye NH (2011) Vegetative fragments of Ulva prolifera in settlement confirmed as an important seed source for succession of a large-scale green tide bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 56:233–242
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Shandong Science and Technology plan project (2011GHY11528), the Specialized Fund for the Basic Research Operating expenses Program (20603022012004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41176153), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (2009ZRA02075), Qingdao Municipal Science and Technology plan project (11-3-1-5-hy), National Marine Public Welfare Research Project (200805069).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiao Fan and Dong Xu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1655 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, X., Xu, D., Wang, Y. et al. The effect of nutrient concentrations, nutrient ratios and temperature on photosynthesis and nutrient uptake by Ulva prolifera: implications for the explosion in green tides. J Appl Phycol 26, 537–544 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0054-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-0054-z