Abstract
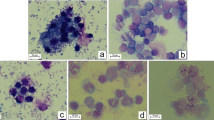
A sulfated polysaccharide purified from a brown alga Ecklonia cava, having high anticoagulant activity was investigated for its antiproliferative effect on murine colon carcinoma (CT-26), human leukemic monocyte lymphoma (U-937), human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60), and mouse melanoma (B-16) cell lines. The sulfated polysaccharide isolated and purified from an enzymatic extract of E. cava had a good selective tumor cell growth inhibition effect; its effect on HL-60 and U-937 was especially promising. The IC50 value for the sulfated polysaccharide from E. cava (ECSP) on U-937 was 43.9 μg mL−1. The presence of the sample in the cell culture media stimulated the induction of apoptosis, revealed by nuclear staining with Hoechst 33342. The apoptosis induction was confirmed by the cell cycle analysis, while pronounced sub-G1 phase arrests of 9.5% and 13.8% were also clearly observed when the cells were treated at 15 and 30 μg mL−1 of ECSP in the U-937 cell line, respectively. After a 24-h incubation period, ECSP dose-dependently enhanced the DNA fragmentation on the U-937 cell line as observed in the agarose gel electrophoresis assay. To rule out the action mechanism of ECSP for its anticancer activity, some western blot analyses were conducted with several antibodies (caspase-7, caspase-8, Bax, Bcl-xL, and PARP) and ECSP had a clear effect on the caspase -7 and 8 which cleave protein substrates, including PARP, an inducer of apoptosis responsible for DNA cleavage. Moreover, ECSP controlled the cellular transmembrane molecules like Bax and Bcl-xL. Taken together, the above results demonstrate that the apoptosis for antiproliferative effect of ECSP was clearly induced on U-937 cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn GN, Kim KN, Cha SH, Song CB, Lee J, Heo MS et al (2007) Antioxidant activities of phlorotannins purified from Ecklonia cava on free radical scavenging using ESR and H2O2-mediated DNA damage. Eur Food Res Technol 226:71–79 doi:10.1007/s00217-006-0510-y
Asia Y, Miyakawa Y, Nakazatao T, Shibata H, Saito K, Ikeda Y et al (2005) Fucoidan induces apoptosis of human HS-Sultan cells accompanied by activation of caspase-3 and down-regulation of ERK pathways. Am J Hematol 78:7–14 doi:10.1002/ajh.20182
Athukorala Y, Jung WK, Vasanthan T, Jeon YJ (2006) An anticoagulative polysaccharide from an enzymatic hydrolysate of Ecklonia cava. Carbohydr Polym 66:84–191 doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.03.002
Cavas L, Baskin Y, Yurdakoc K, Olgum N (2006) Antiproliferative and newly attributed apoptotic activities from an invasive marine alga: Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 339:111–119 doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2006.07.019
Gschwind M, Huber G (1995) Apoptotic cell death induced by β-amyloid 1–42 peptide is cell type dependent. J Neurochem 65:292–300
Jung WK, Athukorala Y, Lee YJ, Cha SH, Lee CH, Vasanthan T et al (2007) Sulfated polysaccharide purified from Ecklonia cava accelerates antithrombin III-mediated plasma proteinase inhibition. J Appl Phycol 19:425–430 doi:10.1007/s10811-006-9149-0
Kim KN, Lee KW, Song CB, Jeon YJ (2006a) Cytotoxic activities of green and brown seaweeds collected from Jeju Island against four tumor cell lines. J Food Sci Nutr 11:17–24
Kim KN, Lee KW, Song CB, Ahn CB, Jeon YJ (2006b) Cytotoxic activities of red algae collected from Jeju Island against four tumor cell lines. J Food Sci Nutr 11:177–183
Kuda T, Taniguchi E, Nishizawa M, Araki Y (2002) Fate of water-soluble polysaccharides in dried Chorda filum, a brown alga during water washing. J Food Compost Anal 15:3–9 doi:10.1006/jfca.2001.1037
Lizard G, Fournel S, Genestier L, Dhedin N, Chaput C, Flacher M et al (1995) Kinetics of plasma membrane and mitochondrial alterations in the cells undergoing apoptosis. Cytometry 21:275–283 doi:10.1002/cyto.990210308
Mans DRA, Rocha AB, Schwavtsann G (2000) Anti-cancer drug discovery and development in Brazil: targeted plant collection as a rational strategy to acquire candidate anti-cancer compounds. Oncology 5:185–198
Matsubara K (2004) Recent advances in marine algal anticoagulants. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents 2:13–19 doi:10.2174/1568016043477314
Matsuda M, Yamori T, Naitoh M, Okutani K (2003) Structural revision of sulfated polysaccharide B-1 isolated from a marine Pseudomonas species and Its cytotoxic activity against human cancer cell lines. Mar Biotechnol 5:13–19 doi:10.1007/s10126-002-0046-5
Mossman T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63 doi:10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC, Grignani F, Riccardi C (1991) A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods 139:271–279 doi:10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-O
Park HY, Lim CW, Kim YK, Yoon HD, Lee KJ (2006) Immunostimulating and anticancer activities of hot water extract from Capsosiphon fulvescens. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 49:343–348
Teruya T, Konishi T, Uechi S, Tamaki H, Tako M (2007) Anti-proliferative activity of oversulfated fucoidan from commercially cultured Cladosiphon okamuranus TOKIDA in U-937 cells. Int J Biol Macromol 41:221–226. doi:10.1016/j.ibiomac.2007.02.010
Wang XW, Zhan Q, Coursen JD, Khan MA, Kontny HU, Yu L et al (1999) GADD45 induction of a G2/M cell cycle checkpoint. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3706–3711 doi:10.1073/pnas.96.7.3706
Yamamoto I, Takahashi M, Suzuki T, Seino H, Mori H (1984) Antitumor effect of seaweeds. IV. Enhancement of antitumor activity by sulfation of a crude fucoidan fraction from Sargassum kjellmanianum. Jap J Exp Med 54:143−151
Ye J, Li Y, Teruya K, Katakura Y, Ichikawa A, Eto H et al (2005) Enzyme-digested fucoidan extracts derived from seaweed Mozuku of Cladosiphon novae-caledoniae Kylin inhibit invasion and angiogenesis of tumor cells. Cytotechnology 47:117–126 doi:10.1007/s10616-005-3761-8
Zhang CX, Huang KX (2005) Apoptosis induction on HL-60 cells of a novel polysaccharide from the mucus of the loach, Misgurnus anguillicaudatus. J Ethnopharmacol 99:385–390 doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.02.033
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by a grant (M2007-03) from Marine Bioprocess Research Center of the Marine Bio 21 Center funded by the Ministry of Maritime Affairs & Fisheries, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Athukorala, Y., Ahn, G.N., Jee, YH. et al. Antiproliferative activity of sulfated polysaccharide isolated from an enzymatic digest of Ecklonia cava on the U-937 cell line. J Appl Phycol 21, 307–314 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-008-9368-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-008-9368-7