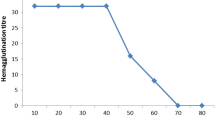
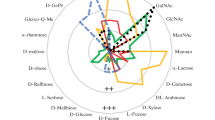
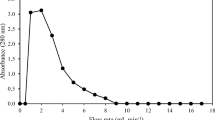
Abstract
Extracts from 44 species of Vietnamese marine algae, including 15 Chlorophyta, 18 Rhodophyta and 11 Phaeophyta species, were examined for hemagglutination activity with a variety of different animal and human erythrocytes that were untreated or treated with enzymes. Almost all extracts showed activity toward at least one type of erythrocytes, although those from three Chlorophyta and two Rhodophyta species showed no hemagglutination with any type of erythrocytes examined. Strong activity was detected in extracts from two Chlorophyta (Anadyomene plicata and Avrainvillea erecta) and four Rhodophyta species (Gracilaria eucheumatoides, Gracilaria salicornia, Kappaphycus alvarezii, and Kappaphycus striatum) with enzyme-treated rabbit and sheep erythrocytes. The hemagglutinins of seven Chlorophyta and eight Rhodophyta species were examined for sugar-binding specificity, pH- and temperature-stability, and divalent cation-independency of hemagglutination using ammonium sulfate-precipitates prepared from their extracts. In a hemagglutination-inhibition test with various monosaccharides and glycoproteins, none of the hemagglutinins had affinity for monosaccharides, except the Codium arabicum and Gracilaria euchematoides hemagglutinins, whose activities were inhibited by both N-acetyl-d-galactosamine and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine. On the other hand, all of the hemagglutinins activities were inhibited by some glycoproteins. The inhibition profiles with glycoproteins were different depending on hemagglutinin species, and suggest the presence of lectins specific for high mannose N-glycans, complex N-glycans, or O-glycans. The activities of these algal hemagglutinins were stable over a wide range of pH and temperature, and independent of the presence of divalent cations. These results indicate that Vietnamese marine algae are a good source of novel and useful lectins.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainouz IL, Sampaio AH (1991) Screening of Brazilian marine algae for hemagglutinins. Bot Mar 34:211–214
Ainouz IL, Sampaio AH, Benevides NMB, Freitas ALP, Costa FHF, Carvalho MC, Pinheiro-Joventino F (1992) Agglutination of enzyme treated erythrocytes by Brazilian marine algae. Bot Mar 35:475–479
Bewley CA, Cai M, Ray S, Ghirlando R, Yamaguchi M, Muramoto K (2004) New carbohydrate specificity and HIV-1 fusion blocking activity of the cyanobacterial protein MVL: NMR, ITC and sedimentation equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol 339:901–914
Bird KT, Chiles TC, Longley RE, Kendrick AF, Kinkema MD (1993) Agglutinins from marine macroalgae of the Southeastern United States. J Appl Phycol 5:212–213
Botos I, O’Keefe BR, Shenoy SR, Cartner LK, Ratner DM, Seeberger PH, Boyd MR, Wlodawer A (2002) Structures of the complexes of a potent anti-HIV protein cyanovirin-N and high mannose oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem 277:34336–34342
Boyd MR, Gustafson KR, Mcmahon JB, Shoemaker RH, O’Keefe BR, Mori T, Gulakowski RJ, Wu L, Rivera MI, Laurencot CM, Currens MJ, Cardellina JH II, Buckheit RW Jr, Nara PL, Pannell LK, Sowder RC II, Henderson LE (1997) Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: potential aplications to microbicide development. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:1521–1530
Boyd WC, Almodovar LR, Boyd LG (1966) Agglutinins in marine algae for human erythrocytes. Transfusion (Philadelphia) 6:82–83
Blunden G, Rogers DJ, Farnham WF (1975) Survey of British seaweeds for hemagglutinins. Lloydia 38:162–168
Blunden G, Rogers DJ, Farnham WF (1978) Hemagglutinins in British marine algae and their possible taxonomic value. In: Irvine DEG, Price JH (eds) Modern approaches to the taxonomy of red and brown algae. Academic, London, pp 21–45
Chiles TC, Bird KT (1989) A comparative study of the animal erythrocyte agglutinins from marine algae. Comp Biochem Physiol 94B:107–111
Fábregas J, Llovo J, Muñoz A (1985) Hemagglutinins in red seaweeds. Bot Mar 28:517–520
Fabregas J, Muñoz A, Llovo J, Carracedo A (1988) Purification and partial characterization of tomentine. An N-acetylglucosamine-specific lectin from the green alga Codium tomentosum (Huds.) Stackh. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 124:21–30
Fábregas J, López A, Llovo J, Muñoz A (1992) A comparative study of seafish erythrocytes and agglutinins from seaweeds. Comp Biochem Physiol 103A:307–313
Freitas ALP, Teixeira DIA, Costa FHF, Farias WRL, Lobato ASC, Sampaio AH, Benevides NMB (1997) A new survey of Brazilian marine algae for agglutinins. J Appl Phycol 9:495–501
Goldstein IJ, Poretz RD (1986) Isolation, physicochemical characterization, and carbohydrate-binding specificity of lectins. In: Liener IE, Sharon N, Goldstein IJ (eds) The lectins—properties, functions, and applications in biology and medicine. Academic, New York, pp 33–124
Griffin RL, Rogers DJ, Spencer-Phillips PT, Swain L (1995) Lectin from Codium fragile ssp. tomentosoides conjugated to colloidal gold: a new histochemical reagent. Br J Biomed Sci 52:225–227
Hori K, Miyazawa K, Ito K (1981) Hemagglutinins in marine algae. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 47:793–798
Hori K, Miyazawa K, Ito K (1986a) Preliminary characterization of agglutinins from seven marine algal species. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 52(2):323–331
Hori K, Miyazawa K, Fusetani N, Hashimoto K, Ito K (1986b) Hypnins, low-molecular weight peptidic agglutinins isolated from a marine red alga Hypnea japonica. Biochim Biophys Acta 873:228–236
Hori K, Oiwa C, Miyazawa K, Ito K (1988) Evidence for wide distribution of agglutinins in marine algae. Bot Mar 31:133–138
Hori K, Miyazawa K, Ito K (1990) Some common properties of lectins from marine algae. Hydrobiologia 204/205:561–566
Hori K, Matsubara K, Miyazawa K (2000) Primary structures of two hemagglutinins from the marine red alga, Hypnea japonica. Biochim Biophys Acta 1474:226–236
Hori K, Sato Y, Ito K, Fujiwara Y, Iwamoto Y, Makino H, Kawakubo A (2007) Strict specificity for high mannose-type N-glycans and primary structure of a red alga Eucheuma serra lectin. Glycobiology 17:479–491
Kim GH, Klochkova T, Yoon K-S, Song Y-S, Lee PK (2006) Purification and characterization of a lectin, bryohealin, involved in the protoplast formation of a marine green alga Bryopsis plumosa (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 42:86–95
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mori T, O’Keefe BR, Sowder RC II, Bringans S, Gardella RS, Berg S, Cochran P, Turpin JA, Buckheit RW Jr, McMahon JB, Boyd MR (2005) Isolation and characterization of griffithsin, a novel HIV-inactivating protein, from the red alga Griffithsia sp. J Biol Chem 280:9345–9353
Nagano CS, Moreno FBMB, Bloch C Jr, Prates MV, Calvete JJ, Saker- Sampaio S, Farias WRL, Tavares TD, Nascimento KS, Grangeiro TB, Cavada BS, Sampaio AH (2002) Purification and characterization of a new lectin from the red marine alga Hypnea musciformis. Prot Peptide Lett 9:159–165
Nang HQ, Dinh NH (1998) The seaweed resources of Vietnam. In: Critchley AT, Ohno M (eds) Seaweed resources of the World. JICA, Japan, pp 62–69
Rogers DJ, Blunden G, Topliss JA, Guiry MD (1980) A survey of some marine organisms for haemagglutinins. Bot Mar 23:569–577
Rogers DJ, Fish BC (1991) Marine algal lectins. In: Kilpatrick DC, Van Driessche E, Bøg-Hansen TC (eds) Lectin reviews. Sigma, St. Louis, 1:129–142
Rogers DJ, Hori K (1993) Marine algal lectins: new developments. Hydrobiologia 260/261:589–593
Rogers DJ, Loveless RW, Balding P (1986) Isolation and characterization of the lectins from sub-species of Codium fragile. In: Bøg-Hansen TC, Van Driessche E (eds) Lectins, vol V. Gruyter, Berlin, pp 154–160.
Sato Y, Okuyama S, Hori K (2007) Primary structure and carbohydrate-binding specificity of a potent anti-HIV lectin isolated from the filamentous cyanobacterium, Oscillatoria agardhii. J Biol Chem 282:11021–11029
Sharon N, Lis H (2003) Lectins, 2nd edn. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Wu AM, Song SC, Chang SC, Wu JH, Chang KS, Kabat EA (1997) Further characterization of the binding properties of a GalNAc specific lectin from Codium fragile subspecies tomentosoides. Glycobiology 7:1061–1066
Wu AM, Song SC, Hwang PY, Wu JH, Chang KS (1995) Binding studies on the combining site of a GalNAc alpha 1-->-specific lectin with Thomsen-Friedenreich activity prepared from green marine algae Codium fragile subspecies tomentosoides. Eur J Biochem 233:145–151
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the staff of the Institute of Materials Science NhaTrang Branch, Vietnam for collection and identification of algal samples, and to the staff of the Laboratory of Marine Bioresource Chemistry, Hiroshima University for providing expert technical assistance. This work was supported by the JSPS- RONPAKU Program, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinh, H.L., Hori, K. & Quang, N.H. Screening and preliminary characterization of hemagglutinins in Vietnamese marine algae. J Appl Phycol 21, 89–97 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-008-9330-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-008-9330-8