Abstract
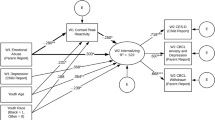
Exposure to stress is associated with a wide range of internalizing and externalizing problems in adolescents, including aggressive behavior. Extant research examining mechanisms underlying the associations between stress and youth aggression has consistently identified social information processing pathways that are disrupted by exposure to violence and increase risk of aggressive behavior. In the current study, we use longitudinal data to examine emotion dysregulation as a potential mechanism linking a broader range of stressful experiences to aggressive behavior in a diverse sample of early adolescents (N = 1065). Specifically, we examined the longitudinal associations of peer victimization and stressful life events with emotion dysregulation and aggressive behavior. Structural equation modeling was used to create latent constructs of emotion dysregulation and aggression. Both stressful life events and peer victimization predicted subsequent increases in emotion dysregulation over a 4-month period. These increases in emotion dysregulation, in turn, were associated with increases in aggression over the subsequent 3 months. Longitudinal mediation models showed that emotion dysregulation mediated the relationship of both peer victimization (z = 2.35, p = 0.019) and stressful life events (z = 2.32, p = 0.020) with aggressive behavior. Increasing the use of adaptive emotion regulation strategies is an important target for interventions aimed at preventing the onset of adolescent aggressive behavior.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abela, J. R., Brozina, K., & Haigh, E. P. (2002). An examination of the response styles theory of depression in third- and sixth-grade children: A short-term longitudinal study. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 515–527.
Adrian, C., & Hammen, C. (1993). Stress exposure and stress generation in children of depressed mothers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 61(2), 354–359.
Arbuckle, J. L. (2005). AMOS 6.0 user’s guide. Chicago: SPSS, Inc.
Attar, B. K., Guerra, N. G., & Tolin, P. H. (1994). Neighborhood disadvantage, stressful life events, and adjustment in urban elementary-school children. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 23, 391–400.
Baumeister, R. F., Bratslavsky, E., Muraven, M., & Tice, D. M. (1998). Ego depletion: Is the self a limited resource? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74, 1252–1265.
Baumeister, R. F., DeWall, C. N., Ciarocco, N. J., & Twenge, J. M. (2005). Social exclusion impairs self-regulation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 88, 589–604.
Bohnert, A. M., Crnic, K. A., & Lim, K. G. (2003). Emotional competence and aggressive behavior in school-age children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 31, 79–91.
Broderick, P. C., & Korteland, C. (2004). A prospective study of rumination and depression in early adolescence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 9, 383–394.
Camodeca, M., & Goossens, F. A. (2005). Aggression, social cognitions, anger and sadness in bullies and victims. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46, 186–197.
Cicchetti, D., & Toth, S. L. (2005). Child maltreatment. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 1, 409–438.
Coddington, D. R. (1972). The significance of life events as etiologic factors in the diseases of children: A study of normal population. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 16, 205–213.
Coie, J. D., Lochman, J. E., Terry, R., & Hyman, C. (1992). Predicting early adolescent disorder from childhood aggression and peer rejection. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60, 783–792.
Cole, P. M., Zahn-Waxler, C., & Smith, D. (1994). Expressive control during a disappointment: Variations related to preschoolers’ problem behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 30, 835–846.
Connecticut Department of Education. (2006). Strategic school profile 2005–2006: New Britain public schools. Hartford, CT: Connecticut Department of Education.
Crick, N. R., & Bigbee, M. A. (1998). Relational and over forms of peer victimization: A multiinformant approach. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 66(2), 337–347.
Crick, N. R., & Dodge, K. A. (1996). Social information-processing mechanisms in reactive and proactive aggression. Child Development, 67(3), 993–1002.
Deater-Deckard, K., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Pettit, G. S. (1998). Multiple risk factors in the development of externalizing behavior problems: Group and individual differences. Development and Psychopathology, 10(3), 469–493.
DeRosier, M. E. (2004). Building relationships and combating bullying: Effectiveness of a school-based social skills group intervention. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33, 196–201.
DeRosier, M. E., & Marcus, S. R. (2005). Building friendships and com- bating bullying: Effectiveness of S. S. GRIN at one-year follow-up. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34, 140–150.
Denham, S. A. (1998). Emotional development in young children. New York: Guilford Press.
Dodge, K. A. (1993). Social-cognitive mechanisms in the development of conduct disorder and depression. Annual Review of Psychology, 44, 559–584.
Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Pettit, G. S. (1990). Mechanisms in the cycle of violence. Science, 250, 1678–1683.
Dodge, K. A., Lansford, J. E., Burks, V. S., Bates, J. E., Pettit, G. S., Fontaine, R., et al. (2003). Peer rejection and social information- processing factors in the development of aggressive behavior in children. Child Development, 74, 374–393.
Dodge, K. A., Pettit, G. S., Bates, J. E., & Valente, E. (1995). Social information-processing patterns partially mediate the effect of early physical abuse on later conduct problems. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 104, 632–643.
Esienberg, N., Fabes, R. A., Nyman, M., et al. (1994). The relations of emotionality and regulation to children’s anger-related reactions. Child Development, 65(1), 109–128.
Eisenberg, N., & Spinard, T. L. (2004). Emotion related regulation: Sharpening the definition. Child Development, 75(2), 334–339.
Eisenberg, N., Guthrie, I. K., Fabes, R. A., Reiser, M., Murphy, B. C., Holmgren, R., et al. (1997). The relations of regulation and emotionality to resiliency and competent social functioning in elementary school children. Child Development, 68, 295–311.
Fredrickson, B. L. (2000). Extracting meaning from past affective experiences: The importance of peaks, ends, and specific emotions. Cognition and Emotion, 14, 577–606.
Garber, J., Quiggle, N. L., Panak, W., & Dodge, K. A. (1991). Depression and aggression in children: Comorbidity, specificity, and social cognitive processing. In D. Cicchetti & S. L. Toth (Eds.), Internalizing and externalizing expressions of dysfunction (pp. 225–264). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Grant, K. E., Compas, B. E., Stuhlmacher, A., Thurm, A. E., McMahon, S., & Halpert, J. (2003). Stressors and child and adolescent psychopathology: Moving from markers to mechanisms of risk. Psychological Bulletin, 129, 447–466.
Grant, K. E., Compas, B. E., Thurm, A. E., McMahon, S., & Gipson, P. (2004). Stressors and child and adolescent psychopathology: Measurement issues and prospective effects. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 33, 412–425.
Gross, J. J. (1998). Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: Divergent consequences for expression, experience, and physiology. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 24, 224–237.
Gross, J. J. (2001). Emotion regulation in adulthood: Timing is everything. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 10, 214–219.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85, 348–362.
Guerra, N. G., Huesmann, L. R., & Spindler, A. (2003). Community violence exposure, social cognition, and aggression among urban elementary school children. Child Development, 74(5), 1561–1576.
Hammen, C. (2008). Stress exposure and stress generation in adolescent depression. In S. Nolen-Hoeksema & L. M. Hilt (Eds.), Handbook of Depression in Adolescents. New York: Lawrence Erlabaum.
Inzlicht, M., McKay, L., & Aronson, J. (2006). Stigma as ego depletion: How being the target of prejudice affects self-control. Psychological Science, 17, 262–269.
Kazdin, A. E., Siegal, T. C., & Bass, D. (1992). Cognitive problem-solving skills training and parent management training in the treatment of antisocial behavior in children. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 60(5), 733–747.
Kishton, J. M., & Wadaman, K. F. (1994). Unidimensional versus domain representative parceling of questionnaire items: An empirical example. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 54, 757–765.
Kovacs, M., Sherrill, J., George, C. J., Pollack, M., Tumuluru, R. V., & Ho, V. (2006). Contextual emotion-regulation therapy for childhood depression: Description and pilot testing of a new intervention. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 45, 892–903.
Lansford, J. E., Malone, P. S., Dodge, K. A., Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (2010). Developmental cascades of peer rejection, social information processing biases, and aggression during middle childhood. Development and Psychopathology, 22, 593–602.
Larson, R., & Ham, M. (1993). Stress and “storm and stress” in early adolescence: The relationship of negative events with dysphoric affect. Developmental Psychology, 29, 130–140.
Little, T. D., Cunningham, W. A., Shahar, G., & Widaman, K. F. (2002). To parcel or not to parcel: Examining the question, weighing the evidence. Structural Equation Modeling, 9, 151–173.
Mahady Wilton, M. M., Craig, W. M., & Pepler, D. J. (2000). Emotional regulation and display in classroom victims of bullying: Characteristic expressions of affect, coping styles and relevant contextual factors. Social Development, 9, 226–245.
MacKinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., Hoffman, J. M., West, S. G., & Sheets, V. (2002). A comparison of methods to test mediation and other intervening variable effects. Psychological Methods, 7, 83–104.
Maxwell, S. E., & Cole, D. A. (2007). Bias in cross-sectional analyses of longitudinal mediation. Psychological Methods, 12, 23–44.
McLaughlin, K. A., & Hatzenbuehler, M. L. (2009). Mechanisms linking stressful life events and mental health problems in a prospective, community-based sample of adolescents. Journal of Adolescent Health, 44, 153–160.
McLaughlin, K. A., Hatzenbuehler, M. L., & Hilt, L. M. (2009). Emotion dysregulation as a mechanism linking peer victimization to internalizing symptoms in adolescents. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 77, 894–904.
McLaughlin, K. A., Hatzenbuehler, M. L., Mennin, D. S., & Nolen-Hoeksema, S. (2011). Emotion dysregulation and adolescent psychopathology: A prospective study. Behavior Research and Therapy, 49, 544–554.
Miller-Johnson, S., Coie, J. D., Maumary-Gremaud, A., Bierman, K., & Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2002). Peer rejection and aggression and early starter models of conduct disorder. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30(3), 217–230.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Hilt, L. (2009). Gender differences in depression. In I. H. Gotlib & C. L. Hammen (Eds.), Handbook of Depression (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Morrow, J. (1991). A prospective study of depression and posttraumatic stress symptoms after a natural disaster: The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61, 115–121.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., Wisco, B. E., & Lyubomirsky, S. (2008). Rethinking rumination. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 3, 400–424.
Peled, M., & Moretti, M. M. (2007). Rumination on anger and sadness in adolescence: Fueling fury and deepening despair. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 36, 66–75.
Peled, M., & Moretti, M. M. (2010). Ruminating on rumination: Are rumination on anger and sadness differentially related to aggression and depressed mood? Journal of Psychopathology and Behavior Assessment, 32, 108–107.
Penza-Clyve, S., & Zeman, J. (2002). Initial validation of the emotion expression scale for children (EESC). Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 31, 540–547.
Prinstein, M. J., Cheah, C. S. L., & Guyer, A. E. (2005). Peer victimization, cue interpretation, and internalizing symptoms: Preliminary concurrent and longitudinal findings for children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 34(1), 11–24.
Prinstein, M. J., & La Greca, A. M. (2004). Childhood peer rejection and aggression as predictors of girls’ externalizing and health risk behaviors: A 6-year longitudinal study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72(1), 103–112.
Olweus, D. (1994). Bullying at school: Long-term outcomes for the victims and an effective school-based intervention program. In L. R. Huesmann (Ed.), Aggressive behavior: Current perspectives (pp. 97–130). New York: Plenum Press.
Prinstein, M. J., Boergers, J., & Vernberg, E. M. (2001). Overt and relational aggression in adolescents: Social-psychological adjustment of aggressors and victims. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 30, 479–491.
Quiggle, N. L., Garber, J., Panak, W. F., & Dodge, K. A. (1992). Social information processing in aggressive and depressed children. Child Development, 63, 1305–1320.
Repetti, R. L., Taylor, S. E., & Seeman, T. E. (2002). Risky families: Family social environments and the mental and physical health of offspring. Psychological Bulletin, 128, 330–336.
Rudolph, K. D., & Hammen, C. (1999). Age and gender as determinants of stress exposure, generation, and reactions in youngsters: A transactional perspective. Child Development, 70(3), 660–677.
Rudolph, K. D., Hammen, C., Burge, D., Lindberg, N., Herzberg, D., & Daley, S. (2000). Toward an interpersonal life-stress model of depression: The developmental context of stress generation. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 215–234.
Schwartz, D., Dodge, K. A., & Coie, J. D. (1993). The emergence of chronic peer victimization in boys’ play groups. Child Development, 64, 1755–1772.
Shields, A., & Cicchetti, D. (1998). Reactive aggression among maltreated children: The contributions of attention and emotion dysregulation. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 27, 381–395.
Shih, J. H., Eberhart, N. K., Hammen, C. L., & Brennan, P. A. (2006). Differential exposure and reactivity to interpersonal stress predict sex differences in adolescent depression. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 35(1), 103–115.
Silk, J. S., Steinberg, L., & Morris, A. S. (2003). Adolescents’ emotion regulation in daily life: Links to depressive symptoms and problem behaviors. Child Development, 74, 1869–1880.
Sim, L., & Zeman, J. (2005). Emotion regulation factors as mediators between body dissatisfaction and bulimic symptoms in early adolescent girls. Journal of Early Adolescence, 25, 478–496.
Sobel, M. E. (1982). Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. In S. Leinhart (Ed.), Sociological method- ology (pp. 290–312). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Southam-Gerow, M. A., & Kendall, P. C. (2000). A preliminary study of the emotional understanding of youth referred for treatment of anxiety disorders. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 29, 319–327.
Stone, A. A., Schwartz, J. E., Neale, J. M., Shiffman, S., Marco, C. A., Hickcox, M., et al. (1998). A comparison of coping assessed by ecological momentary assessment and retrospective recall. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74, 1670–1680.
Stucke, T. S., & Baumeister, R. F. (2006). Ego depletion and aggressive behavior: Is the inhibition of the self a limited resource? European Journal of Social Psychology, 36, 1–13.
Suveg, C., Kendall, P. C., Comer, J. S., & Robin, J. (2006). Emotion-focused cognitive- behavioral therapy for anxious youth: A multiple-baseline evaluation. Journal of Contemporary Psychotherapy, 36, 77–85.
Tate, D. C., Repucci, N. D., & Mulvey, E. P. (1995). Violent juvenile delinquents: Treatment effectiveness and implications for future action. American Psychologist, 50(9), 777–781.
Trosper, S. E., Buzzella, B. A., Bennett, S. M., & Ehrenreich, J. T. (2009). Emotion regulation in youth with emotional disorders: Implications for a unified treatment approach. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 12, 234–254.
Thompson, R. A. (1994). Emotion regulation: A theme in search of definition. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 59, 25–52.
Vernberg, E. M., Fonagy, P., & Twemlow, S. (2000). Preliminary report of the Topeka Peaceful Schools Project. Topeka, KS: Menninger Clinic.
Weiss, B., Dodge, K. A., Bates, J. E., & Pettit, G. S. (1992). Some consequences of early harsh discipline: Child aggression and a maladaptive social information processing style. Child Development, 63(6), 1321–1335.
Zeman, J., Shipman, K., & Penza-Clyve, S. (2001). Development and initial validation of the Children’s Sadness Management Scale. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 25, 187–205.
Zeman, J., Shipman, K., & Suveg, C. (2002). Anger and sadness regulation: Predictions to internalizing and externalizing symptoms in children. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 31, 393–398.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herts, K.L., McLaughlin, K.A. & Hatzenbuehler, M.L. Emotion Dysregulation as a Mechanism Linking Stress Exposure to Adolescent Aggressive Behavior. J Abnorm Child Psychol 40, 1111–1122 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9629-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-012-9629-4