Abstract
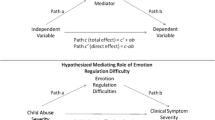
Mental health outcomes vary among maltreated youth, and the factors that impact variance need further investigation. The current study examined how maltreatment characteristics (age at onset, cumulative perpetrators, and cumulative types) and difficulties with emotion regulation (ER) predicted trauma-relevant symptoms among a community-recruited sample of female adolescents with histories of exposure to violence (N = 115; M(SD) age = 15.96 (1.56) years). To predict each trauma-relevant symptom (i.e. anger, anxiety, depression, dissociation, and posttraumatic stress (PTS)), a hierarchical two-step regression was conducted. For Step 1, maltreatment characteristics, taken together, predicted variance in four of five symptoms: anger, anxiety, dissociation, and posttraumatic stress (PTS). Above and beyond variance accounted for by maltreatment characteristics, age at onset predicted variance in anger, anxiety, and PTS symptoms. For Step 2, ER difficulties predicted variance in all symptoms. Findings highlight the need for further research about how maltreatment histories impact subsequent mental health. Results also suggest that ER difficulties should be increasingly considered in models of posttraumatic distress among maltreated youth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alink, L. A., Cicchetti, D., Kim, J., & Rogosch, F. A. (2009). Mediating and moderating processes in the relation between maltreatment and psychopathology: Mother-child relationship quality and emotion regulation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology An Official Publication of the International Society for Research in Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 37(6), 831–843.
Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A., & Brown, G. K. (1996). Manual for the beck depression inventory-II. San Antonio: Psychological Corporation.
Beers, S. R., & De Bellis, M. D. (2002). Neuropsychological function in children with maltreatment-related posttraumatic stress disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(3), 483–486.
Brassard, M. R., Hart, S. N., & Hardy, D. B. (1993). The psychological maltreatment rating scales. Child Abuse & Neglect, 17(6), 715–729.
Briere, J. (1996). Trauma Symptom Checklist for Children (TSCC), professional manual. Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Cicchetti, D., Rogosch, F. A., Gunnar, M. R., & Toth, S. L. (2010). The differential impacts of early physical and sexual abuse and internalizing problems on daytime cortisol rhythm in school-aged children. Child Development, 81(1), 252–269.
Cohen, J. A., Deblinger, E., Mannarino, A. P., & Steer, R. A. (2004). A multisite, randomized controlled trial for children with sexual abuse-related PTSD symptoms. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 43(4), 393–402.
Cole, P. M., Michel, M. K., & Teti, L. O. (1994). The development of emotion regulation and dysregulation: a clinical perspective. In N. A. Fox (Ed.), the development of emotion regulation: biological and behavioral considerations. Monographs of the society for re- search in child development, 59 (Serial No. 240), 73–100.
Collishaw, S., Pickles, A., Messer, J., Rutter, M., Shearer, C., & Maughan, B. (2007). Resilience to adult psychopathology following childhood maltreatment: evidence from a community sample. Child Abuse & Neglect, 31(3), 211–229.
Cook, A., Spinazzola, J., Ford, J., Lanktree, C., Blaustein, M., Cloitre, M., & van der Kolk, B. (2005). Complex trauma in children and adolescents. Psychiatric Annals, 35, 390–398.
DePrince, A. P., Combs, M. D., & Shanahan, M. (2009). Automatic relationship–harm associations and interpersonal trauma involving close others. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 33(2), 163–171.
Finkelhor, D., Ormrod, R. K., & Turner, H. A. (2007). Polyvictimization and trauma in a national longitudinal cohort. Development and Psychopathology, 19(1), 149–166.
Finkelhor, D., Turner, H., Ormrod, R., & Hamby, S. L. (2009). Violence, abuse, and crime exposure in a national sample of children and youth. Pediatrics, 124(5), 1411–1423.
Ford, J., Racusin, R., Ellis, C., Daviss, W. B., Reiser, J., Fleischer, A., & Thomas, J. (2000). Child maltreatment, other trauma exposure, and posttraumatic symptoms among children with oppositional defiant & attention deficit hyperactivity disorders. Child Maltreatment, 5, 205–217.
Ford, J. D., Racusin, R., Rogers, K., Ellis, C., Schiffman, J., Ribbe, D., et al. (2002). Traumatic Events Screening Inventory for Children (TESI-C) version 8.4. White River Junction: National Center for PTSD and Dartmouth Child Psychiatry Research Group.
Freyd, J. J. (1996). Betrayal trauma: the logic of forgetting childhood abuse. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Garner, P. W., & Spears, F. M. (2000). Emotion regulation in low-income preschoolers. Social Development, 9(2), 246–264.
Gratz, K. L., & Roemer, L. (2004). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation and dysregulation: development, factor structure, and initial validation of the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 26(1), 41–54.
Gratz, K. L., Rosenthal, M. Z., Tull, M. T., Lejuez, C. W., & Gunderson, J. G. (2006). An experimental investigation of emotion dysregulation in borderline personality disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 115(4), 850–855.
Gross, J. J., & Thompson, R. A. (2007). Emotion regulation: conceptual foundations. In J. J. Gross & J. J. Gross (Eds.), Handbook of emotion regulation (pp. 3–24). New York: Guilford Press.
Grothe, K. B., Dutton, G. R., Jones, G. N., Bodenlos, J., Ancona, M., & Brantley, P. J. (2005). Validation of the beck depression inventory-II in a low-income african american sample of medical outpatients. Psychological Assessment, 17(1), 110–114.
Gunnar, M. R., & Vasquez, D. M. (2001). Low cortisol and a flattening of expected daytime rhythm: potential indices of risk in human development. Development and Psychopathology, 13, 515–538.
Hamby, S., Finkelhor, D., Turner, H., & Ormrod, R. (2010). The overlap of witnessing partner violence with child maltreatment and other victimizations in a nationally representative survey of youth. Child Abuse & Neglect, 34(10), 734–741.
Higgins, D. J. (2004). The importance of degree versus type of maltreatment: a cluster analysis of child abuse types. Journal of Psychology Interdisciplinary and Applied, 138(4), 303–324.
Higgins, D. J., & McCabe, M. P. (2001). Multiple forms of child abuse and neglect: adult retrospective reports. Aggression and Violent Behavior A Review Journal, 6, 547–578.
Higgins, D. J., & McCabe, M. P. (2000). Multi-type maltreatment and the long-term adjustment of adults. Child Abuse Review, 9, 6–18.
Jonson-Reid, M., Drake, B., Chung, S., & Way, I. (2003). Cross-type recidivism among child maltreatment victims and perpetrators. Child Abuse & Neglect, 27(8), 899–917.
Kaplow, J., & Widom, C. S. (2007). Age of onset of child maltreatment predicts long-term mental health outcomes. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 116, 176–187.
Kaplow, J., Dodge, K., Amaya-Jackson, L., & Saxe, G. (2005). Pathways to PTSD, part II: sexually abused children. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(7), 1305–1310.
Keiley, M., Howe, T., Dodge, K., Bates, J., & Pettit, G. (2001). The timing of child physical maltreatment: a cross-domain growth analysis of impact on adolescent externalizing and internalizing problems. Development and Psychopathology, 13(4), 891–912.
Kim, J., & Cicchetti, D. (2010). Longitudinal pathways linking child maltreatment, emotion regulation, peer relations, and psychopathology. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 51(6), 706–716.
Lilly, M. M., & Hong Phylice Lim, B. (2012). Shared pathogeneses of posttrauma pathologies: attachment, emotion regulation, and cognitions. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 0(0), 1–12.
Linehan, M. M. (1993). Cognitive-behavioral treatment of borderline personality disorder. New York: Guilford Press.
Maccoby, E. E. (1983). Social-emotional development and response to stressors. In M. Rutter & N. Garnezy (Eds.), Stress, coping, and development in children (pp. 217–234). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Mulvihill, D. (2005). The health impact of childhood trauma: an interdisciplinary review, 1997–2003. Issues in Comprehensive Pediatric Nursing, 28, 115–136.
Neumann, A., van Lier, P. C., Gratz, K. L., & Koot, H. M. (2010). Multidimensional assessment of emotion regulation difficulties in adolescents using the difficulties in emotion regulation scale. Assessment, 17(1), 138–149.
Nolen-Hoeksema, S., & Aldao, A. (2011). Gender and age differences in emotion regulation strategies and their relationship to depressive symptoms. Personality and Individual Differences, 51(6), 704–708.
Ohan, J., Myers, K., & Collett, B. (2002). Ten-year review of rating scales. IV: scales assessing trauma and its effects. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(12), 1401–1422.
Perfect, M. M., Tharinger, D. J., Keith, T. Z., & Lyle-Lahroud, T. (2011). Relations between Minnesota multiphasic personality inventory–a scales and rorschach variables with the scope and severity of maltreatment among adolescents. Journal of Personality Assessment, 93(6), 582–591.
Repetti, R., Taylor, S., & Seeman, T. (2002). Risky families: family social environments and the mental and physical health of offspring. Psychological Bulletin, 128(2), 330–366.
Ribbe, D. (1996). Psychometric review of Traumatic Event Screening Instrument for Children (TESI-C). In B. H. Stamm (Ed.), Measurement of stress, trauma, and adaptation (pp. 386–387). Lutherville: Sidran Press.
Saunders, B. E. (2003). Understanding children exposed to violence: toward an integration of overlapping fields. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 18(4), 356–376.
Shipman, K., Zeman, J., Penza, S., & Champion, K. (2000). Emotion management skills in sexually maltreated and nonmaltreated girls: a developmental psychopathology perspective. Development and Psychopathology, 12, 47–62.
Sirles, E., Smith, J., & Kusama, H. (1989). Psychiatric status of intrafamilial child sexual abuse victims. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 28(2), 225–229.
Soenke, M., Hahn, K. S., Tull, M. T., & Gratz, K. L. (2010). Exploring the relationship between child abuse and analogue generalized anxiety disorder: the mediating role of emotion dysregulation. Cognitive Therapy and Research, 34(5), 401–412.
Thornberry, T. P., Henry, K. L., Ireland, T. O., & Smith, C. A. (2010). The causal impact of childhood-limited maltreatment and adolescent maltreatment on early adult adjustment. Journal of Adolescent Health, 46(4), 359–365.
Trickett, P. K., Noll, J. G., & Putnam, F. W. (2011). The impact of sexual abuse on female development: lessons from a multigenerational, longitudinal research study. Development and Psychopathology, 23(2), 453–476.
Tull, M. T., Barnett, H. M., McMillan, E. S., & Roemer, L. (2007). A preliminary investigation of the relationship between emotion regulation difficulties and posttraumatic stress symptoms. Behavior Therapy, 38, 303–313.
Watts-English, T., Fortson, B. L., Gibler, N., Hooper, S. R., & DeBellis, M. D. (2006). The psychobiology of maltreatment in childhood. Journal of Social Issues, 62(4), 717–736.
Weinberg, A., & Klonsky, E. D. (2009). Measurement of emotion dysregulation in adolescents. Psychological Assessment, 21(4), 616–621.
Zeman, J., & Garber, J. (1996). Display rules for anger, sadness, and pain: it depends on who is watching. Child Development, 67(3), 957–973.
Zeman, J., Klimes-Dougan, B., Cassano, M., & Adrian, M. (2007). Measurement issues in emotion research with children and adolescents. Clinical Psychology Science and Practice, 14(4), 377–401.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to current and former members of the Traumatic Stress Studies Group at the University of Denver. The National Institute of Justice grant, 2009-MU-MU-0025, awarded to Anne P. DePrince, PhD, supported this research. This research was carried out in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) for experiments involving humans. This project was supported by a PROF Award from the University of Denver and Award No. 2009-MU-MU-0025 from the National Institute of Justice Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice. The opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Department of Justice or the National Institute of Justice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundermann, J.M., DePrince, A.P. Maltreatment Characteristics and Emotion Regulation (ER) Difficulties as Predictors of Mental Health Symptoms: Results from a Community-Recruited Sample of Female Adolescents. J Fam Viol 30, 329–338 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-014-9656-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-014-9656-8