Abstract.
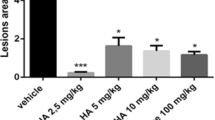
Paracetamol is regarded as a relatively safe drug in the gastro-duodenal region of humans but recent epidemiological investigations have suggested that at high doses there may be an increased risk of ulcers and bleeding. To investigate the possibility that inflammatory conditions and gastric acidity may play a role in potentiating development of gastric mucosal injury from paracetamol in rats (as noted previously with various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) we studied the gastric irritant effects of paracetamol and some phenolic and non-phenolic analgesics and antipyretics in rats with adjuvant or collagen II induced arthritis or zymosan-induced paw inflammation and given 1.0 ml hydrochloric acid (HCl) 0.1 M and/or an i. p. injection of the cholinomimetic, acetyl-β-methyl choline chloride 5.0 mg/kg. Gastric lesions were determined 2 h after oral administration of 100 or 250 mg/kg paracetamol or at therapeutically effective doses of the phenolic or non-phenolic analgesics/antipyretics. The results showed that gastric mucosal injury occurred with all these agents when given to animals that received all treatments so indicating there is an adverse synergy of these three factors, namely: (i) intrinsic disease; (ii) hyperacidity; and (iii) vagal stimulation for rapidly promoting gastric damage, both in the fundic as well as the antral mucosa, for producing gastric damage by paracetamol, as well as the other agents. Removing one of these three predisposing factors effectively blunts/abolishes expression of this paracetamol-induced gastrotoxity in rats. These three factors, without paracetamol, did not cause significant acute gastropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 4 February 2004; revised 9 January 2006; accepted 24 February 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rainsford, K.D., Whitehouse, M.W. Paracetamol [acetaminophen]-induced gastrotoxicity: revealed by induced hyperacidity in combination with acute or chronic inflammation. Inflammopharmacol 14, 150–154 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-006-1389-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-006-1389-8