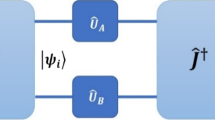
Abstract
Quantum systems are easily influenced by ambient environments. Decoherence is generated by system interaction with external environment. In this paper, we analyse the effects of decoherence on quantum games with Eisert-Wilkens-Lewenstein (EWL) (Eisert et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(15), 3077 1999) and Marinatto-Weber (MW) (Marinatto and Weber, Phys. Lett. A 272, 291 2000) schemes. Firstly, referring to the analytical approach that was introduced by Eisert et al. (Phys. Rev. Lett. 83(15), 3077 1999), we analyse the effects of decoherence on quantum Chicken game by considering different traditional noisy channels. We investigate the Nash equilibria and changes of payoff in specific two-parameter strategy set for maximally entangled initial states. We find that the Nash equilibria are different in different noisy channels. Since Unruh effect produces a decoherence-like effect and can be perceived as a quantum noise channel (Omkar et al., arXiv:1408.1477v1), with the same two parameter strategy set, we investigate the influences of decoherence generated by the Unruh effect on three-player quantum Prisoners’ Dilemma, the non-zero sum symmetric multiplayer quantum game both for unentangled and entangled initial states. We discuss the effect of the acceleration of noninertial frames on the the game’s properties such as payoffs, symmetry, Nash equilibrium, Pareto optimal, dominant strategy, etc. Finally, we study the decoherent influences of correlated noise and Unruh effect on quantum Stackelberg duopoly for entangled and unentangled initial states with the depolarizing channel. Our investigations show that under the influence of correlated depolarizing channel and acceleration in noninertial frame, some critical points exist for an unentangled initial state at which firms get equal payoffs and the game becomes a follower advantage game. It is shown that the game is always a leader advantage game for a maximally entangled initial state and there appear some points at which the payoffs become zero.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Myerson, R.B.: Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict. MIT Press, Cambridge (1991)
Meyer, D.A.: Quantum strategies. Phys. Rev. Lett 82, 1052 (1999)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M., Lewenstein, M.: Quantum games and guantum strategies. Phy. Rev. Lett 83(15), 3077 (1999)
Marinatto, L., Weber, T.: A quantum approach to static games of complete information. Phys. Lett. A 272, 291 (2000)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Quantum version of the Monty Hall problem. Phys. Rev. A 65, 062318 (2002)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M.: Quantum games. J. Mod. Opt 47, 2543 (2000)
Flitney, A.P., Ng, J., Abbott, D: Quantum Parrondo’s games. Physica A 314, 35 (2002)
Iqbal, A., Toor, A.H.: Quantum cooperative games. Phys. Lett. A 293, 103 (2002)
Situ, H.Z.: A quantum approach to play asymmetric coordination games. Quant. Inf. Process 13, 591–599 (2014)
Situ, H.Z.: Quantum Bayesian game with symmetric and asymmetric information. Quant. Inf. Process. 14, 1827–1840 (2015)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Advantage of a quantum player over a classical one in 2 ×. quantum games. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 459, 2463–2474 (2003)
Ichikawa, T., Tsutsui, I.: Duality, phase structures, and dilemmas in symmetric quantum games. Ann. Phys. 322, 531 (2007)
Ichikawa, T., Tsutsui, I., Cheon, T.J.: Quantum game theory based on the Schmidt decomposition. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 41, 135303 (2008)
Khan, S., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Quantum Model of Bertrand Duopoly. Chin. Phys. Lett. 27, 080302 (2010)
Flitney, A.P., Abbott, D.: Quantum games with decoherence. J. Phys. A 38, 449 (2005)
Chen, L.K., Ang, H., Kiang, D., Kwek, L.C., Lo, C.F.: Quantum prisoner dilemma under decoherence. Phys. Lett. A 316, 317 (2003)
Chen, J.L., Kwek, L.C., Oh, C.H.: Noisy quantum game. Phys. Rev. A 65, 052320 (2002)
Khan, S., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Quantum Parrondo’s games under decoherence. Int. J. Theor. Phys 49, 31–41 (2010)
Ramzan, M.: Three-player quantum Kolkata restaurant problem under decoherence. Quantum Inf. Process 12, 577–586 (2013)
Zhu, X., Kuang, L.M.: Quantum Stackelberg duopoly game in depolarizing channel. Commun. Theor. Phys 49, 111 (2008)
Zhu, X., Kuang, L.M.: The influence of entanglement and decoherence on the quantum Stackelberg duopoly game. J. Phys. A Math. Theor 40, 7729 (2007)
Omkar, S., Subhashish, B., Srikanth, R., Ashutosh, K.A.: The Unruh effect interpreted as a quantum noise channel. arXiv:1408.1477v1
Ling, Y., He, S., Qiu, W., Zhang, H.: Quantum entanglement of electromagnetic field in non-inertial reference frames. J. Phys. A Math. Theor 40, 9025–9032 (2007)
Pan, Q., Jing, J.: Degradation of nonmaximal entanglement of scalar and dirac fields in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. A 77, 024302 (2008)
Khan, S., Khan, M.K.: Open quantum systems in noninertial frames. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 44, 045305 (2011)
Wang, J., Jing, J.: Quantum decoherence in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. A 82, 032324 (2010)
Wang, J., Jing, J., Fan, H.: Quantum discord and measurement-induced disturbance in the background of dilaton black holes. Phys. Rev. D 90, 025032 (2014)
Khan, S., Khan, M.K.: Quantum Stackelberg Duopoly in a noninertial frame. Chin. Phys. Lett. 28, 070202 (2011)
Khan, S., Khan, M.K.: Relativistic quantum games in noninertial frames. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 44, 355302 (2011)
Goudarzi, H., Beyrami, S.: Effect of uniform acceleration on multiplayer quantum game. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 45, 225301 (2012)
Khan, S., Khan, M.K.: Noisy relativistic quantum games in noninertial frames. Quantum Inf. Process 12, 1351–1363 (2013)
Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Noise effects in a three-player prisoner’s dilemma quantum game. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 41, 435302 (2008)
Nawaz, A., Toor, A.H.: Quantum games with correlated noise. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen 39, 9321 (2006)
Ramzan, M., Nawaz, A., Toor, A.H., Khan, M.K.: The effect of quantum memory on quantum games. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 41, 055307 (2008)
Khan, S., Ramzan, M., Khan, M.K.: Quantum Stackelberg duopoly in the presence of correlated noise. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 43, 375301 (2010)
Benjamin, S.C., Hayden, P.M.: Comment on “Quantum games and quantum strategies”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 069801 (2001)
Eisert, J., Wilkens, M., Lewenstein, M.: Comment on “Quantum games and quantum strategies”-reply. Phy. Rev. Lett. 87, 069802 (2001)
Flitney, A.P., Hollenberg, L.C.L.: Nash equilibria in quantum games with generalized two-parameter strategies. Phys. Lett. A 363, 381 (2007)
Prevedel, R., Stefanov, A., Walther, P., Zeilinger, A.: Experimental realization of a quantum game on a one-way quantum computer. New J. Phys. 9, 205 (2007)
Nielson, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Du, J., Li, H., Xu, X., Zhou, X., Han, R.: Entanglement enhanced multiplayer quantum games. Phys. Lett. A 302, 229–233 (2002)
Alsing, P.M., Fuentes-Schuller, I., Mann, R.B., Tessier, T.E.: Entanglement of Dirac fields in noninertial frames. Phys. Rev. A 74, 032326 (2006)
Davies, P.C.W.: Scalar production in Schwarzschild and Rindler metrics. J. Phys. A: Math. Gen 8, 609 (1975)
Takagi, S.: Vacuum noise and stress induced by uniform acceleration. Hawking-Unruh effect in Rindler manifold of arbitrary dimension. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl 88, 1 (1986)
Gibbons, R.: Game Theory for Applied Economists. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1992)
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the anonymous referees for valuable suggestions to improve the quality of the paper. This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61272058, 61073054), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (No. 10251027501000004), and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20100171110042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Qiu, D. Quantum Games under Decoherence. Int J Theor Phys 55, 965–992 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-015-2741-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-015-2741-9