Abstract
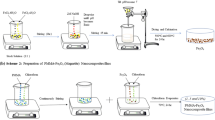
Mössbauer spectroscopy has been applied to study the structure and magnetostriction interdependence of metall/polymer composites with spatially oriented FeGa particles in a polymer matrix. Composites were synthesized combining modified polyurethane with nanocrystalline mechanosynthesized particles of magnetostrictive FeGa composition through polymerization to achieve a considerable magnetostrictive response. To increase magnetoelastic effects a spatial particle arrangement in the polymer matrix was generated. The magnetostrictive composition of the mechanosynthesized particles has been determined by Mössbauer spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and TEM at different stages of ball milling. The microstructure of the composites via the particle orientation in the polymer has been researched by SEM and Conversion Mössbauer spectroscopy with the registration of resonant X-rays. The spatial particle inhomogeneity and magnetic anisotropy have been analyzed in order to reveal the factors determining the functional properties of the manufactured composites. Three-fold enhancement of the magnetostrictive response for FeGa/polyurethane composites with non-standard magnetic anisotropy has been demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Kickelbick G., (ed.): Hybrid materials. Synthesis, Characterization, and Application, p. 498. Wiley-VCH (2006)
Nicolais, L., Carotenuto, G., (eds.): Metal-Polymer Nanocomposites, p. 320. Wiley (2005)
Balaz, P.: Mechanochemistry in Nanoscience and Minerals Engineering, p. 413. Springer (2008)
Lyakhov, N.Z., et al. (eds.): Mechanocomposites precursor for the creation of materials with new properties, p. 432. Novosibirsk. ISBN 978-5-7692-1108-9 (2010)
Kiseleva, T.Yu., Novakova, A.A., et al.: Iron-based amorphous magnetic phase formation in the course of Fe and Fe2O3 mechanical activation. Solid State Phenom 152–153, 25–28 (2009). doi:10.4028/3-908454-13-1.25
Kiseleva, T.Yu., Novakova, A.A., et al.: Mechanosynthesis of corundum ceramics/intermetallics nanocomposites. Advan. Mater. (in Russian) (6), 1–10 (2008)
Kiseleva, T.Yu., Grigorieva, T.F., et al.: Iron and Indium interactions during mechanical attrition. J. Alloy. Comp. 383, 94–97 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.04.015
Novakova, A.A., Khenkin, L.V., et al.: Formation of graphite encapsulated iron nanoparticles during mechanical activation and annealing analyzed by mössbauer spectroscopy. Hyperfine Interact. 189(1–3), 105–110 (2009). doi:10.1007/s10751-009-9934-7
Novakova, A.A., Grigorieva, T.F., et al.: Fe(In) solid solution formation during mechanical attrition. J. Alloy. Comp. 434–435, 455–458 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.08.102. (SPEC. ISS.)
Kiseleva, T.Yu., Novakova, A.A., et al.: Structural study of Fe-Al Structural study of Fe-Al nanomaterial produced by mechanical activation and self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Moscow University Phys. Bull. 63(1), 55–60 (2008). doi:10.1007/s11972-008-1011-8
Kiseleva, T., Novakova, A., et al.: Amorphous shell formarion on the Iron particles during mechanosynthesis in Fe2O3/Fe/(Ga,Al) mixtures. J. Solid State Phenom. 170, 139–143 (2011). doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.170.139
Kiseleva, T.Yu., Novakova, A.A., et al.: Mechanochemically induced formation of amorphous phase at oxide nanocomposite interfaces. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 217(1) (2010). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/217/1/012106
Polyakov, A.O., Kiseleva, T.Y., et al.: Step-by-step powder composite mechanosynthesis for functional nanoceramics. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 217(1) (2010). doi:10.1088/1742-6596/217/1/012081
Atulasimha, J., Flatau, A.B.: Topical review: A review of magnetostrictive iron-gallium alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 043001 (2011)
Rafique, S., Cullen, J.R., et al.: Magnetic anisotropy of FeGa alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 95(11), 6939–694 (2004)
Hristoforou, E., Ktena, A.: Magnetostriction and magnetostrictive materials. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 316, 372–378 (2007)
Okamoto, H.: The fe-ga (iron-gallium) system. Bull. Alloy Phase Diag. 11(6), 576–581 (1990). doi:10.1007/BF02841721
Clark, A.E., Wun-Gogle, M., et al.: Magnetostrictive properties of body-centered cubic Fe-Ga and Fe-Ga-Al alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 36, 3238–3240 (2000)
Cao, H., Gehring, P.M., et al.: Role of nanoscale precipitates on the enhanced magnetostriction of heat-treated galfenol (Fe1_xGax) alloys. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 127–201 (2009)
Dobrzański, L.A., Wydrzyńska, A., et al.: Magnetostrictive properties of epoxy-bonded Tb0, 3Dy 0, 7Fe1,9 composites. J. Adv. Mater. Res. 89–91, 633–638 (2010). doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.89-91.633
Rusakov, V.S.: Mössbauer Spectroscopy of Local-Inhomogeneous Systems, p. 430. Almaty Publ. (2000)
Grigor’eva, T.F., Kiseleva, T.Y., et al.: Study of the products of interaction between iron and gallium during mechanical activation. Phys. Metals Metallograph. 113(6), 575–582 (2012). doi:10.1134/S0031918X12060075
Gaudet, J.M., Hatchard, T.D., et al.: Properties of Fe-Ga based powders prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 320, 821–829 (2007)
Dunlap, R.A., McGraw, J.D., et al.: Mössbauer effect study of structural ordering in rapidly quenched Fe-Ga alloys. J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 305, 315–320 (2006)
Newkirk, L.R., Tsuei, C.C.: Mössbauer study of hyperfine magnetic interactions in fe-ga solid solutions. J. Phys. Rev. B 4(11), 4046–4053 (1971). doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.4.4046
Novakova, A.A., Smirnov, E.V., et al.: Magnetic anisotropy in Fe3O4—PVA nanocomposites as a result of Fe3O4-nanoparticles chains formation J. Magnet. Magnet. Mater. 300(1), e354–e356 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.10.119
Novakova, A.A., Agladze, O.V., et al: Detection of anisotropy effects in compact nanocrystalline iron. J. Surf. Invest. X-Ray Synchrot. Neutron Techniq. 16(12), 1863–1867 (2001). ISSN: 10274510
Reicher, Y.L., Stolbov, O.V.: Modelling of magnetostrictive strain in soft magnetic elastomer. Comput. Contin. Mech. 2(2), 85–95 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on the Applications of the Mössbauer Effect (ICAME 2013) held in Opatija, Croatia, 1–6 September 2013
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zholudev, S.I., Kiseleva, T.Y. Mössbauer study of new functional metal/polymer nanocomposites with spatially oriented FeGa particles. Hyperfine Interact 226, 375–382 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-013-0957-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-013-0957-8