Abstract
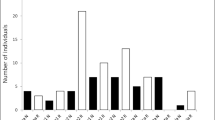
The use of artificial habitats as tool for management and conservation of lentic freshwater ecosystems has been most studied in North America, with dominance of Centrarchidae fish. Contrary to north temperate ecosystems, Cichlidae species appear to be prevalent on artificial habitats in Neotropical reservoirs. Currently, due to the rapid expansion of non-native fish introductions globally, these two fish families are increasingly expected to coexist in the same environments. This study aimed to test experimentally the use of artificial habitats by fish in two Neotropical reservoirs between: (i) kind of habitats, (ii) Cichlidae and Centrarchidae, (iii) native and non-native species, and (iv) size classes. The results showed a higher number of individuals and species in pipes and rocks habitats. The dominance of Cichlidae over Centrarchidae in pipes, rocks and control habitats suggests a kind of partitioning between these groups. Native Cichlidae (< 80 mm) were predominant in pipes whereas native and non-native species seemed to share tree and rock habitats. Artificial habitats can potentially increase local abundance and diversity of fish species, however, it is essential to consider the species’ origin (i.e. native or non-native) associated with each kind of artificial habitat in order to prevent invasive species from benefiting of artificial structures deployment in freshwater systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho, A. A., L. C. Gomes, S. M. Thomaz & N. S. Hahn, 2004. The Upper Paraná River and its floodplain: main characteristics and perspectives for management and conservation. In Thomaz, S. M., A. A. Agostinho & N. S. Hah (eds), The Upper Paraná River and its Floodplain: Physical Aspects, Ecology and Conservation. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden: 381–393.
Agostinho, A. A., L. C. Gomes & F. M. Pelicice, 2007. Ecologia e Manejo de Recursos Pesqueiros em Reservatórios do Brasil. EDUEM, Maringá.
Anderson, M. J., R. N. Gorley & K. R. Clarke, 2008. PERMANOVA + for Primer: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods. Primer-E, Plymouth.
Andreoli, C. V., C. Hoppen, E. S. Pegorini & O. Dalarmi, 2003. A crise da água e os mananciais de abastecimento. In Andreoli, C. V. (ed.), Mananciais de Abastecimento: Planejamento e Gestão. Curitiba, Sanepar: 33–85.
Baumgartner, G., C. S. Pavanelli, D. Baumgartner, A. G. Bifi, T. Debona & V. A. Frana, 2012. Peixes do baixo rio Iguaçu. Maringá, EDUEM.
Bezerra, L. A. V., V. M. Ribeiro, M. O. Freitas, L. Kaufman, A. A. Padial & J. R. S. Vitule, 2019. Benthification, biotic homogenization behind the trophic downgrading in altered ecosystems. Ecosphere 10(6):
Bolding, B., S. Bonar & M. Divens, 2004. Use of artificial structure to enhance angler benefits in lakes, ponds, and reservoirs: a literature review. Reviews in Fisheries Science 12: 75–96.
Braga, R. R., L. Gómez-Aparicio, T. Heger, J. R. S. Vitule & J. M. Jeschke, 2018. Structuring evidence for invasional meltdown: broad support but with biases and gaps. Biological Invasions 20: 923–936.
Bray, J. R. & J. T. Curtis, 1957. An ordination of the upland forest community of southern Wisconsin. Ecological Monographs 27: 325–349.
Brito, M. F. G., V. S. Daga & J. R. S. Vitule, 2020. Fisheries and biotic homogenization of freshwater fish in the Brazilian semiarid region. Hydrobiologia 847: 3877–3895.
Cambray, J. A., 2003. Impact on indigenous species biodiversity caused by the globalisation of alien recreational freshwater fisheries. Hydrobiologia 500: 217–230.
Chakrabarty, P., 2004. Cichlid biogeography: comment and review. Fish and Fisheries 5: 97–119.
Charvet, P., T. V. T. Occhi, L. Faria, B. Carvalho, C. R. Pedroso, L. Carneiro, M. Freitas, M. Petrers-Junior & J. R. S. Vitule, 2021. Tilapia farming threatens Brazil’s water. Science 371(6527): 356.
Clarke, K. R. & R. N. Gorley, 2006. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth.
Clavero, M. & V. Hermoso, 2011. Reservoirs promote the taxonomic homogenization of fish communities within river basins. Biodiversity and Conservation 20: 41–57.
Daga, V. S., S. Skóra, A. A. Padial, V. Abilhoa, E. A. Guniane & J. R. S. Vitule, 2015. Homogenization dynamics of the fish assemblages in Neotropical reservoirs: comparing the roles of introduced species and their vectors. Hydrobiologia 746: 327–347.
Daga, V. S., T. Debona, V. Abilhoa, E. A. Gubiani & J. R. S. Vitule, 2016. Non-native fish invasions of a Neotropical ecoregion with high endemism: a review of the Iguaçu River. Aquatic Invasions 11: 209–223.
Daga, V. S., J. D. Olden, E. A. Gubiani, P. A. Piana, A. A. Padial & J. R. S. Vitule, 2020. Scale-dependent patterns of fish faunal homogenization in Neotropical reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 847: 3759–3772.
Daugherty, D. J., M. T. Driscoll, D. E. Ashe & J. W. Schlechte, 2014. Effects of structural and spatiotemporal factors on fish use of artificial habitat in a Texas reservoir. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 34: 453–462.
Dias, R. M., A. G. Oliveira, M. T. Baumgartner, M. A. Angulo-Valencia & A. A. Agostinho, 2020. Functional erosion and trait loss in fish assemblages from Neotropical reservoirs: The man beyond the environment. Fish and Fisheries. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12524.
Ellender, B. R. & O. L. F. Weyl, 2014. A review of current knowledge, risk and ecological impacts associated with non-native freshwater fish introductions in South Africa. Aquatic Invasions 9: 117–132.
FEOW, 2018. Freshwater ecoregions of the World. http://www.feow.org. Accessed 02 May 2019
Frehse, F. A., R. R. Braga, G. A. Nocera & J. R. S. Vitule, 2016. Nonnative species and invasion biology in a megadiverse country: Scientometric analysis and ecological interactions in Brazil. Biological Invasions 18: 3713–3725.
Freitas, C. E. C. & M. Petrere-Jr, 2001. Influence of artificial reefs on fish assemblage of the Barra Bonita Reservoir (São Paulo, Brazil). Lakes and Reservoirs 6: 273–278.
Freitas, C. E. C., M. Petrere & W. Barrella, 2005. Natural and artificially-induced habitat complexity and freshwater fish species composition. Fisheries Management and Ecology 12: 63–67.
Garcia, D. A. Z., A. D. A. Costa, G. L. A. Leme & M. S. Orsi, 2014. Biology of black bass Micropterus salmoides (Lacepède, 1802) fifty years after the introduction in a small drainage of the Upper Paraná River basin, Brazil. Biodiversitas 15: 180–185.
Godoy, M. P., 1954. Observações sobre a adaptação do “Black bass” (Micropterus salmoides) em Pirassununga, Estado de São Paulo. Revista Brasileira de Biologia 14: 32–38.
Gois, K. S., R. R. Antonio, L. C. Gomes, F. M. Pelicice & A. A. Agostinho, 2012. The role of submerged trees in structuring fish assemblages in reservoirs: two case studies in South America. Hydrobiologia 685: 109–119.
Gozlan, R. E., J. R. Britton, I. Cowx & G. H. Copp, 2010. Current knowledge on non-native freshwater fish introductions. Journal of Fish Biology 76: 751–786.
Graham, R. J., 1992. Visually estimating fish density at artificial structures in Lake Anna, Virginia. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 12: 204–212.
Johnson, D. L. & W. E. Lynch Jr., 1992. Panfish use of and angler success at evergreen tree, brush, and stake-bed structures. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 12: 222–229.
Johnson, P. T. J., J. D. Olden & M. J. V. Zanden, 2008. Dam invaders: impoundments facilitate biological invasions into freshwaters. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 6: 357–363.
Johnson, P. T. J., J. D. Olden, C. T. Solomon & M. J. V. Zanden, 2009. Interactions among invaders: community and ecosystem effects of multiple invasive species in an experimental aquatic system. Oecologia 159: 161–170.
Lowe-Mcconnell, R. L., 1991. Fish Communities in Tropical Freshwaters. Longman, London: 337p.
Magnelia, S. J., M. J. DeJesus, J. W. Schlechte, G. C. Cummings & J. L. Duty, 2008. Comparison of plastic pipe and juniper tree fish attractors in a central Texas reservoir. Proceedings of the Annual Conference Southeastern Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies 62: 183–188.
Matsuzaki, S. S., T. Sasaki & M. Akasaka, 2013. Consequences of the introduction of exotic and translocated species and future extirpations on the functional diversity of freshwater fish assemblages. Global Ecology and Biogeography 22: 1071–1082.
Mineur, F., E. J. Cook, D. Minchin, K. Bohn, A. MacLeod & C. A. Maggs, 2012. Changing coasts: marine aliens and artificial structures. In Gibson, R. N., R. J. A. Atkinson, J. D. M. Gordon & R. N. Hughes (eds), Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Vol. 50., CRC Press Abingdon, GB: 189–234.
Near, T. J. & J. B. Koppelman, 2009. Species diversity, phylogeny and phylogeography of Centrarchidae. In Near, T. J. & J. B. Koppelman (eds), Centrarchid Fishes: Diversity, Biology and Conservation. Wiley-Blackwell, London: 1–38.
Oliveira, I. S., V. M. Ribeiro, E. R. Pereira & J. R. S. Vitule, 2016. Predation on native anurans by invasive vertebrates in the Atlantic Rain Forest, Brazil. Oecologia Australis 20(3): 70–74.
Padial, A. A., J. R. S. Vitule & J. D. Olden, 2020. Preface: aquatic homogenocene—understanding the era of biological re-shuffling in aquatic ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 847: 3705–3709.
Pereira, F. W. & J. R. S. Vitule, 2019. The largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides (Lacepède, 1802): impacts of a powerful freshwater fish predator outside of its native range. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 29(3): 639–652.
Ribeiro, V. M., R. R. Braga, V. Abilhoa & J. R. S. Vitule, 2015. Evaluation of three capture techniques for invasive Micropterus salmoides (Lacépède, 1802) in a Neotropical reservoir: implications for population control and management. Journal Applied Ichthyology 31: 1127–1129.
Rogers, K. B. & E. P. Bergersen, 1999. Utility of synthetic structures for concentrating adult northern pike and largemouth bass. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 19: 1054–1065.
Rold, R. E., T. S. McComish & D. E. Van Meter, 1996. A comparison of cedar trees and fabricated polypropylene modules of fish attractors in a strip mine impoundment. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 16: 223–227.
Rosenberg, D. M., P. McCully & C. M. Pringle, 2000. Global-scale environmental effects of hydrological alterations: introduction. BioScience 50: 746–751.
Santos, L. N., F. G. Araújo & D. S. Brotto, 2008. Artificial structures as tools for fish habitat rehabilitation in a neotropical reservoir. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18: 896–908.
Santos, L. N., G. Garcia-Berthou, A. A. Agostinho & J. G. Latini, 2011. Fish colonization of artificial reefs in a large Neotropical reservoir: material type and successional changes. Ecological Applications 21: 251–262.
Tonella, L. H., O. B. Vitorino Junior, D. P. Lima-Junior, L. C. Gomes, F. M. Pelicice & A. A. Agostinho, 2020. Extemporaneous environmental legislation: an analysis of the conflicts underlying Law 3824/1960 on coarse wood removal in Brazilian artificial reservoirs. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 32:
Vitule, J. R. S., C. A. Freire & D. Simberlof, 2009. Introduction of non-native freshwater fish can certainly be bad. Fish and Fisheries 10: 98–108.
Vitule, J. R. S., F. Skóra & V. Abilhoa, 2012. Homogenization of freshwater fish faunas after the elimination of a natural barrier by a dam in Neotropics. Diversity and Distributions 18: 111–120.
Vitule, J. R. S., T. V. T. Occhi, B. Kang, S. Matsuzaki, L. A. Bezerra, V. S. Daga, L. Faria, F. A. Frehse, F. Walter & A. A. Padial, 2019. Intra-country introductions unraveling global hotspots of alien fish species. Biodiversity and Conservation 28: 3037–3043.
Walters, D. A., W. E. Lynch & D. L. Johnson, 1991. How depth and interstice size of artificial structures influence fish attraction. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 11: 319–329.
Wills, T. C., M. T. Bremigan & D. B. Hayes, 2004. Variable effects of habitat enhancement structures across species and habitats in Michigan reservoirs. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 133: 399–411.
Zarfl, C., A. Lumsdon, J. Berlekamp, L. Tydecks & K. Tockner, 2015. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquatic Sciences 77(1): 161–170.
Acknowledgements
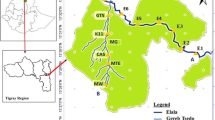
We are grateful to Acquanauta Diving Center (Curitiba) and its divers’ team for all support during artificial habitats deployment and the supply of diving equipment during the sampling period, especial thanks to R. Alberti, R. R. Braga and H. Laufer. We are also grateful to N. L. L. Frehse, B. K. Nakagawa and G. E. Yamassaki for all the support during the field campaigns. We thank L. Strictar and P. Charvet for comments and suggestions in the manuscript, T. Occhi for help with analyses, and L. Carneiro for help with Fig. 1. We thank the Sanitation Company of Paraná (SANEPAR) for providing research permits in the reservoirs. We also thank CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nivel Superior) for the scholarship provided to FAF, and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) for research grants provided to JRSV (Process Numbers: 310850/2012-6; 303776/2015-3). OLFW acknowledges support by the National Research Foundation – South African Research Chairs Initiative of the Department of Science and Technology (Grant No. 110507).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare
Ethical statement
In the present study, individuals were not handled or collected, thus guidelines for the care and use of animals were not necessary.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guest editors: Katya E. Kovalenko, Fernando M. Pelicice, Lee B. Kats, Jonne Kotta & Sidinei M. Thomaz / Aquatic Invasive Species III
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Frehse, F.d., Weyl, O.L.F. & Vitule, J.R.S. Differential use of artificial habitats by native and non-native fish species in Neotropical reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 848, 2355–2367 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04564-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04564-3