Abstract
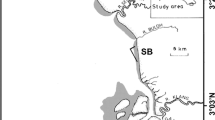
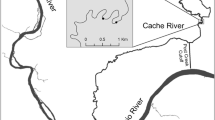
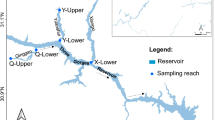
In shallow reservoirs, seasonal water drawdowns expose littoral areas and over time produce barren mudflats. When flooded, mudflats provide homogeneous substrates, turbid water, and eroding shorelines of limited ecological value. We hypothesized that in mudflats structurally complex habitats are occupied by more fish, smaller fish of a larger range in sizes, more species, and fish assemblages that are different from those in simpler habitats. We tested these hypotheses over two consecutive years with fish collections made in sites with varying structural complexity. Results indicated that structural complexity harbors more fish in transects and enclosures. Structural complexity did not influence median length, but length range increased with structural complexity. Average species richness increased with structural complexity. Fish assemblage composition changed as structural complexity increased. The ability of cover to provide survival, growth, and carrying capacity benefits is fundamental to programs aimed at increasing structural complexity. Results suggest observed effects on fish assemblages can lead to such benefits. Considering mudflats are a major component of reservoirs, expand as reservoirs age, and there is a potential to exert meaningful change on fish assemblages of impounded rivers by managing mudflats, we suggest additional attention is needed to develop practical habitat restoration options.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahams, C., 2006. Sustainable shorelines: the management and revegetation of drawdown zones. Journal of Practical Ecology and Conservation 6: 37–51.
Almany, G. R., 2004. Does increased habitat complexity reduce predation and competition in coral reef fish assemblages? Oikos 106: 275–284.
Anderson, M. J., 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology 26: 32–46.
Bao, Y., P. Gao & X. He, 2015. The water-level fluctuation zone of three Gorges reservoir—a unique geomorphological unit. Earth-Science Reviews 150: 14–24.
Bell, S. S., E. D. McCoy & H. R. Mushinsky (eds), 1991. Habitat Structure: The Physical Arrangement of Objects in Space. Chapman and Hall, London.
Bettoli, P. W. & M. J. Maceina, 1996. Sampling with toxicants. In Murphy, B. R. & D. W. Willis (eds), Fisheries Techniques, 2nd ed. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda: 303–333.
Beukers, J. S. & G. P. Jones, 1998. Habitat complexity modifies the impact of piscivores on a coral reef fish population. Oecologia 114: 50–59.
Bohnsack, J. A., 1991. Habitat Structure and the Design of Artificial Reefs. In Bell, S. S., E. D. McCoy & H. R. Mushinsky (eds), Habitat Structure: The Physical Arrangement of Objects in Space. Chapman and Hall, London: 412–426.
Bowen, K. L., N. K. Kaushik & A. M. Gordon, 1998. Macroinvertebrate communities and biofilm chlorophyll on woody debris in two Canadian oligotrophic lakes. Archive fur Hydrobiologia 141: 257–281.
Brickhill, M. J., S. Y. Lee & R. M. Connolly, 2005. Fishes associated with artificial reefs: attributing changes to attraction or production using novel approaches. Journal of Fish Biology 67(Supplement B): 53–71.
Carmignani, J. R. & A. H. Roy, 2017. Ecological impacts of winter water level drawdowns on lake littoral zones: a review. Aquatic Sciences 79: 803–824.
Coops, H., M. Beklioglu & T. L. Crisman, 2003. The role of water-level fluctuations in shallow lake ecosystems—workshop conclusions. Hydrobiologia 506–509: 23–27.
Davies-Colley, R. J. & D. G. Smith, 2001. Turbidity, suspended sediment, and water clarity: a review. Journal of American Water Resources Association 37: 1085–1101.
Dufrêne, M. & P. Legendre, 1997. Species assemblages and indicator species: the need for a flexible asymetrical approach. Ecological Monographs 67: 345–366.
Eklöv, P., 1997. Effects of habitat complexity and prey abundance on the spatial and temporal distributions of perch (Perca fluviatilis) and pike (Esox lucius). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 54: 1520–1531.
Fischer, J., D. B. Lindenmayer & A. D. Manning, 2006. Biodiversity, ecosystem function, and resilience: ten guiding principles for commodity production landscapes. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 4: 80–86.
Fowler, D. K. & D. A. Hammer, 1976. Techniques for establishing vegetation on reservoir inundation zones. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 31: 116–118.
Furey, P. C., R. N. Mordin & A. Mazumder, 2004. Water level drawdown affects physical and biogeochemical properties of littoral sediments of a reservoir and a natural lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 20: 280–295.
Gerwing, T. G., D. Drolet, D. J. Hamilton & M. A. Barbeau, 2016. Relative importance of biotic and abiotic forces on the composition and dynamics of a soft-sediment intertidal community. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0147098.
Gladfelter, W. B., J. C. Ogden & E. H. Gladfelter, 1980. Similarity and diversity among coral reef fish communities: a comparison between tropical western Atlantic (Virgin Islands) and tropical central Pacific (Marshal1 Islands) patch reefs. Ecology 61: 1156–1168.
Gois, K. S., R. R. Antonio, L. C. Gomes, F. M. Pelicice & A. A. Agostinho, 2008. The role of submerged trees in structuring fish assemblages in reservoirs: two case studies in South America. Hydrobiologia 685: 109–119.
Gotelli, N. J. & R. K. Colwell, 2011. Estimating Species Richness. In Magurran, A. E. & B. J. McGill (eds), Frontiers in Measuring Biodiversity. Oxford University Press, New York: 39–54.
Grenouillet, G., D. Pont & K. L. Seip, 2002. Abundance and species richness as a function of food resources and vegetation structure: juvenile fish assemblages in rivers. Ecography 25: 641–650.
Hellsten, S., J. Riihimäki, E. Alasaarela & R. Keränen, 1996. Experimental revegetation of the regulated lake Ontojärvi in northern Finland. Hydrobiologia 340: 339–343.
Hixon, M. A. & B. A. Menge, 1991. Species diversity: prey refuges modify the interactive effects of predation and competition. Theoretical Population Biology 39: 178–200.
Hoff, M. H, 1991. Effects of increased nesting cover on nesting and reproduction of smallmouth bass in northern Wisconsin lakes. In: D. C. Jackson, editor. Proceedings of the First International Smallmouth Bass Symposium. Mississippi State University, Starkville: 39–43.
Hunt, J. & C. A. Annett, 2002. Effects of habitat manipulation on reproductive success of individual largemouth bass in an Ozark reservoir. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 22: 1201–1208.
Kaufmann, P. R., D. V. Peck, S. G. Paulsen, C. W. Seeliger, R. M. Hughes, T. R. Whittier & N. C. Kamman, 2014. Lakeshore and littoral physical habitat structure in a national lakes assessment. Lake and Reservoir Management 30: 192–215.
Kennedy, R. H., 1999. Reservoir Design and Operation: Limnological Implications and Management Opportunities. In Tundisi, J. G. & M. Straskrabova (eds), Theoretical Reservoir Ecology and Its Applications. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden: 1–29.
Kostylev, V. E., J. Erlandsson, M. Y. Ming & G. A. Williams, 2005. The relative importance of habitat complexity and surface area in assessing biodiversity: fractal application on rocky shores. Ecological Complexity 2: 272–286.
Kovalenko, K. E., S. M. Thomaz & D. M. Warfe, 2012. Habitat complexity: approaches and future directions. Hydrobiologia 685: 1–17.
Li, B., X. Yuan, H. Xiao & Z. Chen, 2011. Design of the dike-pond system in the littoral zone of a tributary in the three Gorges reservoir, China. Ecological Engineering 37: 1718–1725.
Li, B., C. Du, X. Yuan, J. H. Martin Willison & H. Xiao, 2016. Suitability of Taxodium distichum for afforesting the littoral zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. PLoS ONE 11(1): e0146664.
Lingo, M. E. & S. T. Szedlmayer, 2006. The influence of habitat complexity on reef fish communities in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Environmental Biology of Fishes 76: 71–80.
Mellin, C., C. Huchery, M. J. Caley, M. G. Meekan & C. J. A. Bradshaw, 2010. Reef size and isolation determine the temporal stability of coral reef fish populations. Ecology 91: 3138–3145.
Miranda, L. E., 2017. Reservoir Fish Habitat Management. Lightning Press, Totowa: 306.
Miranda, L. E. & J. Boxrucker, 2009. Warmwater Fish in Large Standing Waters. In Bonar, S. A., W. A. Hubert & D. W. Willis (eds), Standard Methods for Sampling North American Freshwater Fishes. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda: 29–42.
Miranda, L. E. & D. J. Dembkowski, 2016. Evidence for serial discontinuity in the fish community of a heavily impounded river. River Research and Applications 32: 1187–1195.
Miranda, L. E. & W. D. Hubbard, 1994. Winter survival of age-0 largemouth bass relative to size, predators, and shelter. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 14: 790–796.
Miranda, L. E., S. L. Wigen & J. D. Dagel, 2014. Reservoir floodplains support distinct fish assemblages. River Research Applications 30: 338–346.
Moore, E. C. & K. A. Hovel, 2010. Relative influence of habitat complexity and proximity to patch edges on seagrass epifaunal communities. Oikos 119: 1299–1311.
New, T. & Z. Xie, 2008. Impacts of large dams on riparian vegetation: applying global experience to the case of China’s Three Gorges Dam. Biodiversity and Conservation 17: 3149–3163.
Petr, T, 2000. Interactions Between Fish and Aquatic Macrophytes in Inland Waters. A Review. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 396. Rome.
Pickering, H. & D. Whitmash, 1997. Artificial reefs and fisheries exploitation: a review of the ‘attraction versus production’ debate, the influence of design and its significance for policy. Fisheries Research 31: 39–59.
R Core Team. 2017. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-project.org/
Rountree, R. A., 1989. Association of fishes with fish aggregation devices: effect of structure size on fish abundance. Bulletin of Marine Science 44: 960–972.
Santos, L. N., F. G. Araújo & D. S. Brotto, 2008. Artificial structures as tools for fish habitat rehabilitation in a Neotropical reservoir. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18: 896–908.
Savino, J. F. & R. A. Stein, 1989. Behavior of fish predators and their prey: habitat choice between open water and dense vegetation. Environmental Biology of Fishes 24: 287–293.
Smokorowski, K. E. & T. C. Pratt, 2007. Effect of a change in physical structure and cover on fish and fish habitat in freshwater ecosystems—a review and meta-analysis. Environmental Review 15: 15–41.
Smokorowski, K. E., T. C. Pratt, W. G. Cole, L. J. McEachern & E. C. Mallory, 2006. Effects on periphyton and macroinvertebrates from removal of submerged wood in three Ontario lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 63: 2038–2049.
Tokeshi, M. & S. Arakaki, 2012. Habitat complexity in aquatic systems: fractals and beyond. Hydrobiologia 685: 27–47.
U. K. Brig (U. K. Biodiversity Reporting and Information Group), 2008. Intertidal Mudflats. In Maddock, A. & N. Chapman (eds), UK Biodiversity Action Plan Priority Habitat Descriptions. UK Biodiversity Reporting and Information Group, Peterborough: 31–32.
USFWS (U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service), 1988. A Study of Cutoff Bendways on the Tennessee-Tombigbee Waterway, 1987 Annual Report. U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Daphne.
Van Dam, A. A., M. E. Azim, M. C. M. Beveridge & M. C. J. Verdregen, 2002. The potential of fish production based on periphyton. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 12: 1–31.
Vogele, L. E. & W. C. Rainwater, 1975. Use of brush shelters as cover by spawning black bass (Micropterus) in bull shoals reservoir. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 104: 264–269.
Warfe, D. M. & L. A. Barmuta, 2004. Habitat structural complexity mediates the foraging success of multiple predator species. Oecologia 141: 171–178.
Whitlatch, R. B., 1982. The Ecology of New England Tidal Flats: A Community Profile. US Fish and Wildlife Service Biological Services Program, Washington, DC: 25.
Willis, S. C., K. O. Winemiller & H. Lopez-Fernandez, 2005. Habitat structural complexity and morphological diversity of fish assemblages in a Neotropical floodplain river. Oecologia 142: 284–295.
Wilson, J. H., 1973. Distribution patterns of mudflat vegetation in Iowa flood control reservoirs. PhD Dissertation. Iowa State University, Ames.
Yanovski, R., P. A. Nelson & A. Abelson, 2017. Structural complexity in coral reefs: examination of a novel evaluation tool on different spatial scales. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 5: 27.
Acknowledgements
Funding was provided by the Mississippi Department of Wildlife, Fisheries and Parks and Reservoir Fisheries Habitat Partnership. We thank C. Gilliland, M. McNerney, B. Richardson, W. Tucker, and A. Shamaskin for assistance with field work; and J. Boxrucker, R. Ott, and D. Schumann for helpful reviews. This study was performed under the auspices of Mississippi State University’s IACUC protocol # 17-368. Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Eric Larson
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatcher, H.R., Miranda, L.E., Colvin, M.E. et al. Fish assemblages in a Mississippi reservoir mudflat with low structural complexity. Hydrobiologia 841, 163–175 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04019-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-04019-w