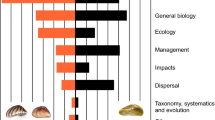
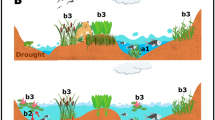
Abstract
Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from ecosystems. Freshwater mussels perform many important functions in aquatic ecosystems, which can in turn be framed as the ecosystem services that they contribute to or provide. These include supporting services such as nutrient recycling and storage, structural habitat, substrate and food web modification, and use as environmental monitors; regulating services such as water purification (biofiltration); and provisioning and cultural services including use as a food source, as tools and jewelry, and for spiritual enhancement. Mussel-provided ecosystem services are declining because of large declines in mussel abundance. Mussel propagation could be used to restore populations of common mussel species and their ecosystem services. We need much more quantification of the economic, social, and ecological value and magnitude of ecosystem services provided by mussels, across species, habitats, and environmental conditions, and scaled up to whole watersheds. In addition, we need tools that will allow us to value mussel ecosystem services in a way that is understandable to both the public and to policy makers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge, D. C., T. M. Fayle & N. Jackson, 2007. Freshwater mussel abundance predicts biodiversity in UK lowland rivers. Aquatic Conservation-Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 17: 554–564.
Allen, D. C. & C. C. Vaughn, 2010. Complex hydraulic and substrate variables limit freshwater mussel species richness and abundance. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 29: 383–394.
Allen, D. C. & C. C. Vaughn, 2011. Density-dependent biodiversity effects on physical habitat modification by freshwater bivalves. Ecology 92: 1013–1019.
Allen, D. C., C. C. Vaughn, J. F. Kelly, J. R. Cooper & M. H. Engel, 2012. Bottom-up biodiversity effects increase resource subsidy flux between ecosystems. Ecology 93: 2165–2174.
Allen, D. C., H. S. Galbraith, C. C. Vaughn & D. E. Spooner, 2013. A tale of two rivers: implications of water management practices for mussel biodiversity outcomes during droughts. Ambio 42: 881–891.
Allen, D. C., B. J. Cardinale & T. Wynn-Thompson, 2014. Toward a better integration of ecological principlesinto ecogeoscience research. BioScience 64: 444–454.
Atkinson, C. L., 2013. Razor-backed musk turtle (Sternotherus carinatus) diet across a gradient of invasion. Herpetological Conservation and Biology 8: 561–570.
Atkinson, C. L. & C. C. Vaughn, 2015. Biogeochemical hotspots: temporal and spatial scaling of the impact of freshwater mussels on ecosystem function. Freshwater Biology 60: 563–574.
Atkinson, C. L., C. C. Vaughn & K. J. Forshay, 2013a. Native mussels alter nutrient availability and reduce blue-green algae abundance. EPA Science Brief EPA/600/F13/231
Atkinson, C. L., C. C. Vaughn, K. J. Forshay & J. T. Cooper, 2013b. Aggregated filter-feeding consumers alter nutrient limitation: consequences for ecosystem and community dynamics. Ecology 94: 1359–1369.
Atkinson, C. L., A. D. Christian, D. E. Spooner & C. C. Vaughn, 2014a. Long-lived organisms provide an integrative footprint of agricultural land use. Ecological Applications 24: 375–384.
Atkinson, C. L., J. P. Julian & C. C. Vaughn, 2014b. Species and function lost: role of drought in structuring stream communities. Biological Conservation 176: 30–38.
Atkinson, C. L., J. F. Kelly & C. C. Vaughn, 2014c. Tracing consumer-derived nitrogen in riverine food webs. Ecosystems 17: 485–496.
Augspurger, T., F. J. Dwyer, C. G. Ingersoll & C. M. Kane, 2007. Advances and opportunities in assessing contaminant sensitivity of freshwater mussel (Unionidae) early life stages. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 26: 2025–2028.
Beck, M. W., R. D. Brumbaugh, L. Airoldi, A. Carranza, L. D. Coen, C. Crawford, O. Defeo, G. J. Edgar, B. Hancock, M. C. Kay, H. S. Lenihan, M. W. Luckenbach, C. L. Toropova, G. Zhang & X. Guo, 2011. Oyster reefs at risk and recommendations for conservation, restoration, and management. Bioscience 61: 107–116.
Beckett, D. C., B. W. Green & S. A. Thomas, 1996. Epizoic invertebrate communities on upper Mississippi River unionid bivalves. American Midland Naturalist 135: 102–114.
Black, B. A., J. B. Dunham, B. W. Blundon, M. F. Raggon & D. Zima, 2010. Spatial variability in growth-increment chronologies of long-lived freshwater mussels: Implications for climate impacts and reconstructions. Ecoscience 17: 240–250.
Blazejowski, B., G. Racki, P. Gieszcz, K. Malkowski, A. Kin & K. Krzywiecka, 2013. Comparative oxygen and carbon isotopic records of miocene and recent lacustrine unionid bivalves from Poland. Geological Quarterly 57: 113–122.
Bodis, E., B. Toth & R. Sousa, 2014. Massive mortality of invasive bivalves as a potential resource subsidy for the adjacent terrestrial food web. Hydrobiologia 735: 253–262.
Bolotov, I., I. Vikhrev, Y. Bespalaya, V. Artamonova, M. Gofarov, J. Kolosova, A. Kondakov, A. Makhrov Frolov, S. Tumpeesuwan, A. Lyubas, T. Romanis & K. Titova, 2014. Ecology and conservation of the Indochinese freshwater pearl mussel, Margaritifera laosensis (Lea, 18634) in the Nam Pe and Nam Long rivers, Northern Laos. Tropical Conservation Science 4: 706–719.
Brauman, K. A., G. C. Daily, T. K. Duarte & H. A. Mooney, 2007. The nature and value of ecosystem services: an overview highlighting hydrologic services. Annual Review of Environment and Resources. 32: 67–98.
Bril, J. S., J. J. Durst, B. M. Hurley, C. L. Just & T. J. Newton, 2014. Sensor data as a measure of native freshwater mussel impact on nitrate formation and food digestion in continuous-flow mesocosms. Freshwater Science 33: 417–424.
Brim Box, J., J. Howard, D. Wolf, C. O’Brien, D. Nez & D. Close, 2006. Freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionoida) of the Umatilla and Middle Fork John Day rivers in eastern Oregon. Northwest Science 80: 95–107.
Brown, M. E., M. Kowalewski, R. J. Neves, D. S. Cherry & M. E. Schreiber, 2005. Freshwater mussel shells as environmental chronicles: geochemical and taphonomic signatures of mercury-related extirpations in the North Fork Holston River, Virginia. Environmental Science & Technology 39: 1455–1462.
Brubaker, M., J. Bell & A. Rollin, 2009. Climate Change Effects on Traditional Inupiaq Food Cellars. Center for Climate and Health Alaska Native Health Consortium, CCH Bulletin No: 1.
Bruesewitz, D. A., J. L. Tank & S. K. Hamilton, 2009. Seasonal effects of zebra mussels on littoral nitrogen transformation rates in Gull Lake, Michigan, USA. Freshwater Biology 54: 1427–1443.
Castro, A. J., C. C. Vaughn, M. Garcia-Llorente, J. P. Julian & C. L. Atkinson, 2016a. Willingness to pay for ecosystem services among stakeholder groups in a south-central US watershed with regional conflict. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 142: 05016006.
Castro, A. J., C. C. Vaughn, J. P. Julian & M. Garcia-Llorente, 2016b. Social demand for ecosystem services and implications for watershed management. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 52: 209–221.
Choctaw Nation., 2016. http://www.choctawschool.com/home-side-menu/iti-fabvssa/traditional-uses-of-freshwater-mussels.asp
Chowdhury, G. W., A. Zieritz & D. C. Aldridge, 2016. Ecosystem engineering by mussels supports biodiversity and water clarity in a heavily polluted lake in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Freshwater Science 35: 188–199.
Christian, A. D., B. N. Smith, D. J. Berg, J. C. Smoot & R. H. Findley, 2004. Trophic position and potential food sources of 2 species of unionid bivalves (Mollusca: Unionidae) in 2 small Ohio streams. Journal of North American Benthological Society 23: 101–113.
Claassen, C., 2008. Shell symbolisms in pre-Columbian North America. In Antczak, A. & R. Cipriani (eds), Early Human Impacts on Megamolluscs. International Series 1865. British Archeological Reports, 232–236
Cope, W. G., R. B. Bringolf, D. B. Buchwalter, T. J. Newton, C. G. Ingersoll, N. Wang, T. Augspurger, F. J. Dwyer, M. C. Barnhart, R. J. Neves & E. Hammer, 2008. Differential exposure, duration, and sensitivity of unionoidean bivalve life stages to environmental contaminants. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 27: 451–462.
Daily, G. C., S. Alexander, P. R. Ehrlich, L. Goulder, J. Lubchenco, P. A. Matson, H. A. Mooney, S. Postel, S. H. Schneider, D. Tilman & G. M. Woodwell, 1997. Ecosystem services: benefits supplied to human societies by natural ecosystems. Issues in Ecology 2: 1–16.
Delong, M. D. & J. H. Thorp, 2009. Mollusc shell periostracum as an alternative to tissue in isotopic studies. Limnology and Oceanography-Methods 7: 436–441.
Dodds, W. K., J. S. Perkin & J. E. Gerken, 2013. Human impact on freshwater ecosystem services: a global perspective. Environmental Science & Technology 47: 9061–9068.
Du, B., S. P. Haddad, A. Luek, W. C. Scott, G. N. Saari, L. A. Kristofco, K. A. Connors, C. Rash, J. B. Rasmussen, C. K. Chambliss & B. W. Brooks, 2014. Bioaccumulation and trophic dilution of human pharmaceuticals across trophic positions of an effluent-dependent wadeable stream. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 369: 20140058.
Dunca, E., B. R. Schone & H. Mutvei, 2005. Freshwater bivalves tell of past climates: but how clearly do shells from polluted rivers speak. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology 228: 43–57.
Faust, C., D. Stallknecht, D. Swayne & J. Brown, 2009. Filter-feeding bivalves can remove avian influenza viruses from water and reduce infectivity. Proceedings of the Royal Society B-Biological Sciences 276: 3727–3735.
Francoeur, S. N., A. Pinowska, T. A. Clason, S. Makosky & R. L. Lowe, 2002. Unionid bivalve influence on benthic algal community composition in a Michigan Lake. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 17: 489–500.
Freshwater Mollusk Conservation Society, 2016. A national strategy for the conservation of native freshwater mollusks. Freshwater Mollusk Biology and Conservation 19: 1–21.
Fritts, A. K., J. T. Peterson, P. D. Hazelton & R. B. Bringolf, 2015. Evaluation of methods for assessing physiological biomarkers of stress in freshwater mussels. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 72: 1450–1459.
Fritts, A. K., M. W. Fritts, W. R. Haag, J. A. DeBower & A. F. Casper, 2017. Freshwater mussel shells (Unionidae) chronicle changes in a North American river over the past 1000 years. Science of the Total Environment 575: 199–206.
Galbraith, H. S., D. E. Spooner & C. C. Vaughn, 2010. Synergistic effects of regional climate patterns and local water management on freshwater mussel communities. Biological Conservation 143: 1175–1183.
Gangloff, M. M. & J. W. Feminella, 2007. Stream channel geomorphology influences mussel abundance in southern Appalachian streams, USA. Freshwater Biology 52: 64–74.
Geist, J., K. Auerswald & A. Boom, 2005. Stable carbon isotopes in freshwater mussel shells: environmental record or marker for metabolic activity? Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta 69: 3545–3554.
Goodchild, C. G., M. Frederich & S. I. Zeeman, 2015. AMP-activated protein kinase is a biomarker of energetic status in freshwater mussels exposed to municipal effluents. Science of the Total Environment 512: 201–209.
Goodchild, C. G., M. Frederich & S. I. Zeeman, 2016. Is altered behavior linked to cellular energy regulation in a freshwater mussel (Elliptio complanata) exposed to triclosan? Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C-Toxicology & Pharmacology 179: 150–157.
Grabowski, J. H., R. D. Brumbaugh, R. F. Conrad, A. G. Keeler, J. J. Opaluch, C. H. Peterson, M. F. Piehler, S. P. Powers & A. R. Smyth, 2012. Economic valuation of ecosystem services provided by oyster reefs. Bioscience 62: 900–909.
Green, R. H., S. M. Singh & R. C. Bailey, 1985. Bivalve molluscs as response systems for modeling spatial and temporal environmental patterns. The Science of the Total Environment 46: 147–169.
Gutierrez, J. L., C. G. Jones, D. L. Strayer & O. O. Iribane, 2003. Mollusks as ecosystem engineers: the role of shell production in aquatic habitats. Oikos 101: 79–90.
Haag, W. R., 2012. North American Freshwater Mussels: Ecology, Natural History and Conservation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Haag, W. R. & J. D. Williams, 2014. Biodiversity on the brink: an assessment of conservation strategies for North American freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 735: 45–60.
Hartmann, J. T., S. Beggel, K. Auerswald, B. C. Stoeckle & J. Geist, 2016. Establishing mussel behavior as a biomarker in ecotoxicology. Aquatic Toxicology 170: 279–288.
Hauser, L. W., 2015. Predicting episodic ammonium excretion by freshwater mussels via gape response and heart rate. PhD dissertation, University of Iowa.
Hoellein, T. J. & C. B. Zarnoch, 2014. Effect of eastern oysters (Crassostrea virginica) on sediment carbon and nitrogen dynamics in an urban estuary. Ecological Applications 24: 271–286.
Howard, J. K. & K. M. Cuffey, 2006. The functional role of native freshwater mussels in the fluvial benthic environment. Freshwater Biology 51: 460–474.
Humphries, P. & K. O. Winemiller, 2009. Historical impacts on river fauna, shifting baselines, and challenges for restoration. Bioscience 59: 673–684.
Ilarri, M. I., A. T. Souza, V. Modesto, L. Guilhermino & R. Sousa, 2015a. Differences in the macrozoobenthic fauna colonising empty bivalve shells before and after invasion by Corbicula fluminea. Marine and Freshwater Research 66: 549–558.
Ilarri, M. I., A. T. Souza & R. Souza, 2015b. Contrasting decay rates of freshwater bivalves’ shells: aquatic versus terrestrial habitats. Limnologica 51: 8–14.
Ismail, N. S., C. E. Muller, R. R. Morgan & R. G. Luthy, 2014. Uptake of contaminants of emerging concern by the bivalves Anodonta californiensis and Corbicula fluminea. Environmental Science & Technology 48: 9211–9219.
Ismail, N. S., H. Dodd, L. M. Sassoubre, A. J. Horne, A. B. Boehm & R. G. Luthy, 2015. Improvement of urban lake water quality by removal of Escherichia coli through the action of the bivalve Anodonta californiensis. Environmental Science & Technology 49: 1664–1672.
Izumi, T., K. Yagiti, S. Izumiyami, T. Endo & Y. Ituh, 2012. Depletion of Cryptosporidium parvaum oocysts from contaminated sewage using freshwater benthic pearl clams (Hyriopsis schlegeli). Applied and Environmental Microbiology 78: 7420–7428.
Jamil, A., K. Lajtha, S. Radan, G. Ruzsa, S. Cristofor & C. Postolache, 1999. Mussels as bioindicators of trace metal pollution in the Danube Delta of Romania. Hydrobiologia 392: 143–158.
Jasinska, E. J., G. G. Goss, P. L. Gillis, G. J. Van Der Kraak, J. Matsumoto, A. A. D. Machado, M. Giacomin, T. W. Moon, A. Massarsky, F. Gagne, M. R. Servos, J. Wilson, T. Sultana & C. D. Metcalfe, 2015. Assessment of biomarkers for contaminants of emerging concern on aquatic organisms downstream of a municipal wastewater discharge. Science of the Total Environment 530: 140–153.
Jiale, L. & L. Yingsen, 2009. http://agris.fao.org/agrisearch/search.do?recordID=US201301612025.
Kolarevic, S., M. Kracun-Kolarevic, J. Kostic, J. Slobodnik, I. Liska, Z. Gacic, M. Paunovic, J. Knezevic-Vukcevic & B. Vukovic-Gacic, 2016. Assessment of the genotoxic potential along the Danube River by application of the comet assay on haemocytes of freshwater mussels: the joint Danube Survey 3. Science of the Total Environment 540: 377–385.
Langlet, D., L. Y. Alleman, P. D. Plisnier, H. Hughes & L. Andre, 2007. Manganese content records seasonal upwelling in Lake Tanganyika mussels. Biogeosciences 4: 195–203.
Li, X. N., H. L. Song, W. Li, X. W. Lu & O. Nishimura, 2010. An integrated ecological floating-bed employing plant, freshwater clam and biofilm carrier for purification of eutrophic water. Ecological Engineering 36: 382–390.
Lopes-Lima, M., A. Teixeira, E. Froufe, A. Lopes, S. Varandas & R. Sousa, 2014. Biology and conservation of freshwater bivalves: past, present and future perspectives. Hydrobiologia 735: 1–13.
Lorenz, S., F. Gabel, N. Dobra & M. T. Pusch, 2013. Modelling the effects of recreational boating on self-purification activity provided by bivalve mollusks in a lowland river. Freshwater Science 32: 82–93.
Lydeard, C., R. H. Cowie, W. F. Ponder, A. E. Bogan, P. Bouchet, S. A. Clark, K. S. Cummings, T. J. Frest, O. Gargominy, D. G. Herbert, R. Hershler, K. E. Perez, B. Roth, M. Seddon, E. E. Strong & F. G. Thompson, 2004. The global decline of nonmarine mollusks. Bioscience 54: 321–330.
McDowell, W. G., W. H. McDowell & J. E. Byers, 2016. Mass mortality of a dominant invasive species in response to an extreme climate event: implications for ecosystem function. Limnology and Oceanography. doi:10.1002/lno.10384.
McKinney, R. A., J. L. Lake, M. A. Charpentier & S. Ryba, 2002. Using mussel isotope ratios to assess anthropogenic nitrogen inputs to freshwater ecosystems. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 74: 167–192.
Moore, J. W., 2006. Animal ecosystem engineers in streams. Bioscience 56: 237–246.
Newton, T. J. & M. R. Bartsch, 2007. Lethal and sublethal effects of ammonia to juvenile Lampsilis mussels (Unionidae) in sediment and water-only exposures. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 26: 2057–2065.
Newton, T. J. & W. G. Cope, 2007. Biomarker responses of unionid mussels to environmental contaminants. In Farris, J. L. & J. H. Van Hassel (eds.), Freshwater Bivalve Ecotoxicology. CRC Press, Boca Raton: 257–284.
Newton, T. J., S. J. Zigler, J. T. Rogala, B. R. Gray & M. Davis, 2011. Population assessment and potential functional roles of native mussels in the Upper Mississippi River. Aquatic Conservation-Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 21: 122–131.
Newton, T. J., C. C. Vaughn, D. E. Spooner & M. Arts, 2013. Profiles of biochemical tracers in unionid mussels across a broad geographic range. Journal of Shellfish Research 32: 497–507.
Novais, A., A. T. Souza, M. Ilarri, C. Pascoal & R. Sousa, 2015. From water to land: how an invasive clam may function as a resource pulse to terrestrial invertebrates. Science of the Total Environment 538: 664–671.
Othman, F., M. S. Islam, E. N. Sharifah, F. Shahrom-Harrison & A. Hassan, 2015. Biological control of streptococcal infection in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) using filter-feeding bivalve mussel Pilsbryoconcha exilis (Lea, 1838). Journal of Applied Ichthyology 31: 724–728.
Pigneur, L. M., E. Falisse, K. Roland, E. Everbecq, J. F. Deliege, J. S. Smitz, K. van Doninck & J. P. Descy, 2014. Impact of invasive Asian clams, Corbicula spp., on a large river ecosystem. Freshwater Biology 59: 573–583.
Rafferty, J. & E. Peacock, 2008. The spread of shell tempering in the Mississippi Black Prairie. Southeastern Archeology 27: 253–264.
Raikow, D. F. & S. K. Hamilton, 2001. Bivalve diets in a midwestern U.S. stream: a stable isotope enrichment study. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 513–522.
Ricciardi, A. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1999. Extinction rates of North American freshwater fauna. Conservation Biology 13: 1220–1222.
Rocha, T. L., T. Gomes, V. S. Sousa, N. C. Mestre & M. J. Bebianno, 2015. Ecotoxicological impact of engineered nanomaterials in bivalve molluscs: an overview. Marine Environmental Research 111: 74–88.
Ruffo, S. & P. M. Kareiva, 2009. Using science to assign value to nature. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7: 3–3.
Rypel, A. L., W. R. Haag & R. H. Findlay, 2009. Pervasive hydrologic effects on freshwater mussels and riparian trees in southeastern floodplain ecosystems. Wetlands 29: 497–504.
Sansom, B., 2013. The influence of mussels on fish populations. MS thesis, Department of Biology, University of Oklahoma.
Schone, B. R., E. Dunca, H. Mutvei & U. Norlund, 2004. A 217-year record of summer air temperature reconstructed from freshwater pearl mussels (M. margaritifera, Sweden). Quaternary Science Reviews 23: 1803–1816.
Soto, D. & G. Mena, 1999. Filter-feeding by the freshwater mussel, Diplodon chilensis, as a biocontrol of salmon farming eutrophication. Aquaculture 171: 65–81.
Sousa, R., S. Varandas, R. Cortes, A. Teixeira, M. Lopes-Lima, J. Machado & L. Guilhermino, 2012. Massive die-offs of freshwater bivalves as resource pulses. Annales De Limnologie-International Journal of Limnology 48: 105–112.
Southwick, R. I. & A. J. Loftus (eds), 2003. Investigation and Monetary Values of Fish and Freshwater Mussel Kills. American Fisheries Society Special Publication No. 30. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda
Spooner, D. E. & C. C. Vaughn, 2006. Context-dependent effects of freshwater mussels on the benthic community. Freshwater Biology 51: 1016–1024.
Spooner, D. E. & C. C. Vaughn, 2008. A trait-based approach to species’ roles in stream ecosystems: climate change, community structure, and material cycling. Oecologia 158: 307–317.
Spooner, D. E. & C. C. Vaughn, 2012. Species’ traits and environmental gradients interact to govern primary production in freshwater mussel communities. Oikos 121: 403–416.
Spooner, D. E., C. C. Vaughn & H. S. Galbraith, 2012. Species traits and environmental conditions govern the relationship between biodiversity effects across trophic levels. Oecologia 168: 533–548.
Spooner, D. E., P. C. Frost, H. Hillebrand, M. T. Arts, O. Puckrin & M. A. Xenopoulos, 2013. Nutrient loading associated with agriculture land use dampens the importance of consumer-mediated niche construction. Ecology Letters 16: 1115–1125.
Strayer, D. L., 1999. Use of flow refuges by unionid mussels in rivers. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18: 468–476.
Strayer, D. L., 2008. Freshwater Mussel Ecology: A Multifactor Approach to Distribution and Abundance. University of California Press, Berkeley.
Strayer, D. L., 2014. Understanding how nutrient cycles and freshwater mussels (Unionoida) affect one another. Hydrobiologia 735: 277–292.
Strayer, D. L. & H. M. Malcom, 2007. Shell decay rates of native and alien freshwater bivalves and implications for habitat engineering. Freshwater Biology 52: 1611–1617.
Strayer, D. L., N. F. Caraco, J. J. Cole, S. Findley & M. L. Pace, 1999. Transformation of freshwater ecosystems by bivalves. BioScience 49: 19–27.
Thorp, J. H., M. D. Delong, K. S. Greenwood & A. F. Casper, 1998. Isotopic analysis of three food web theories in constricted and floodplain regions of a large river. Oecologia 117: 551–563.
Trant, A. J., W. Nijland, K. M. Hoffman, D. L. Mathews, D. McLaren, T. A. Nelson & B. M. Starzomski, 2016. Intertidal resource use over millennia enhances forest productivity. Nature Communications. doi:10.1038/ncomms12491.
Turek, K. A. & T. J. Hoellein, 2015. The invasive Asian clam (Corbicula fluminea) increases sediment denitrification and ammonium flux in 2 streams in the midwestern USA. Freshwater Science 34: 472–484.
Tyrell, M. & D. J. Hornbach, 1998. Selective predation by muskrats on freshwater mussels in two Minnesota rivers. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 17: 301–310.
Vanden Byllaardt, J. & J. D. Ackerman, 2014. Hydrodynamic habitat influences suspension feeding by unionid mussels in freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater Biology 59: 1187–1196.
Vaughn, C. C., 2010. Biodiversity losses and ecosystem function in freshwaters: emerging conclusions and research directions. BioScience 60: 25–35.
Vaughn, C. C. & C. C. Hakenkamp, 2001. The functional role of burrowing bivalves in freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater Biology 46: 1431–1446.
Vaughn, C. C. & D. E. Spooner, 2006. Unionid mussels influence macroinvertebrate assemblage structure in streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 691–700.
Vaughn, C. C., K. B. Gido & D. E. Spooner, 2004. Ecosystem processes performed by unionid mussels in stream mesocosms: species roles and effects of abundance. Hydrobiologia 527: 35–47.
Vaughn, C. C., D. E. Spooner & H. S. Galbraith, 2007. Context-dependent species identity effects within a functional group of filter-feeding bivalves. Ecology 88: 1654–1662.
Vaughn, C. C., S. J. Nichols & D. E. Spooner, 2008. Community and foodweb ecology of freshwater mussels. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 27: 41–55.
Vaughn, C. C., C. L. Atkinson & J. P. Julian, 2015. Multiple droughts lead to long-term losses in mussel-provided ecosystem services. Ecology and Evolution 5: 1291–1305.
Wang, N., T. Augspurger, M. C. Barnhart, J. R. Bidwell, W. G. Cope, F. J. Dwyer, S. Geis, I. E. Greer, C. G. Ingersoll, C. M. Kane, T. W. May, R. J. Neves, T. J. Newton, A. D. Roberts & D. W. Whites, 2007. Intra- and interlaboratory variability in acute toxicity tests with glochidia and juveniles of freshwater mussels (Unionidae). Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 26: 2029–2035.
Welker, M. & N. Walz, 1998. Can mussels control the plankton in rivers? A planktological approachapplying a Langrangian sampling strategy. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 753–762.
Wen, Z. R., P. Xie & J. Xu, 2010. Mussel isotope signature as indicator of nutrient pollution in a freshwater eutrophic lake: species, spatial, and seasonal variability. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 163: 139–147.
Zieritz, A., M. Lopes-Lima, A. E. Bogan, R. Sousa, S. Walton, K. Rahim, J. J. Wilson, P. Y. Ng, E. Froufe & S. McGowan, 2016. Factors driving changes in freshwater mussel (Bivalvia, Unionida) diversity and distribution in Peninsular Malaysia. Science of the Total Environment 571: 1069–1078.
Zieritz, A., A. E. Bogan, O. Klishko, T. Kondo, U. Kovitvadhi, S. Kovitvadhi, J. H. Lee, M. Lopes-Lima, J. M. Pfeiffer, R. Sousa, D. V. Tu, I. Vikhrev, & D. T. Zanatta, 2017. Diversity, biogeography and conservation status of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia: Unionida) in East and Southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia (in press)
Zigler, S. J., T. J. Newton, J. J. Steuer, M. R. Bartsch & J. S. Sauer, 2008. Importance of physical and hydraulic characteristics to unionid mussels: a retrospective analysis in a reach of large river. Hydrobiologia 598: 343–360.
Zimmerman, G. F. & F. A. de Szalay, 2007. Influence of unionid mussels (Mollusca: Unionidae) on sediment stability: an artificial stream study. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 168: 299–306.
Acknowledgements
This article stems from a presentation at the Second International Conference on the Biology and Conservation of Freshwater Bivalves. I thank the conference organizers and participants, and Antonio Castro, Carla Atkinson, Daniel Spooner, Kiza Gates, Daniel Allen, Heather Galbraith, Brandon Sansom, Thomas Parr, Traci Popejoy, and Brent Tweedy for thoughtful conversations and comments. Antonio Castro assisted with Table 1 and Andy Vaughn drew the figures. Comments from Ronaldo Sousa and an anonymous reviewer improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Manuel P. M. Lopes-Lima, Ronaldo G. Sousa, Lyuba E. Burlakova, Alexander Y. Karatayev & Knut Mehler / Ecology and Conservation of Freshwater Bivalves
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaughn, C.C. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia 810, 15–27 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3139-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3139-x