Abstract
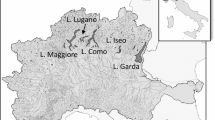
Winter air and spring surface water temperatures, spring epilimnetic phosphorus, and hypolimnetic oxygen in the deep lakes south of the Alps (Garda, Iseo, Como, Lugano, and Maggiore) showed a high degree of temporal coherence. The common temporal patterns were originating from the effects caused by winter climate, and from corresponding synchronisms in the interannual variations in the extent of the spring water renewal and replenishment of nutrients. In turn, the sequence of linked causal events was triggered by two atmospheric modes of variability relevant for the Mediterranean region, i.e. the East Atlantic pattern (EA) and the Eastern Mediterranean Pattern (EMP). In contrast, there were no significant relationships of air and water temperatures with the North Atlantic Oscillation. In oligotrophic lakes, which were characterised by weak vertical nutrient gradients, the spring replenishment of P was negligible and difficult to detect (Maggiore), or detectable but of minor importance (Garda and Como) compared to that measured in more enriched lakes (Iseo and Lugano). The applicability of EA and EMP in the study of the impact of climate on aquatic ecosystems will require to be tested by expanding the number, typology, and geographical location of water bodies in the Alpine and Mediterranean regions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeschbach-Hertig, W., C. P. Holzner, M. Hofer, M. Simona, A. Barbieri & R. Kipfer, 2007. A time series of environmental tracer data from deep, meromictic Lake Lugano, Switzerland. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 257–273.
Ambrosetti, W. & L. Barbanti, 1992. Physical limnology in Italy: an historical overview. Memorie dell’Istituto italiano di Idriobiologia 50: 37–59.
Ambrosetti, W. & L. Barbanti, 1999. Deep water warming in lakes: an indicator of climatic change. Journal of Limnology 58: 1–9.
Ambrosetti, W., L. Barbanti & E. A. Carrara, 2010. Mechanisms of hypolimnion erosion in a deep lake (Lago Maggiore, N. Italy). Journal of Limnology 69: 3–14.
Arvola, L., G. George, D. M. Livingstone, M. Järvinen, T. Blenckner, M. T. Dokulil, E. Jennings, C. N. Aonghusa, P. Nõges, T. Nõges & G. A. Weyhenmeyer, 2010. The impact of the changing climate on the thermal characteristics of lakes. In George, G. (ed.), The impact of climate change on European lakes. Springer, Dordrecht.
Barbieri, A. & M. Simona, 1997. Evoluzione trofica recente del Lago di Lugano in relazione agli interventi di risanamento. Documenta Istituto italiano di Idrobiologia 61: 73–91.
Blenckner, T., 2005. A conceptual model of climate-related effects on lake ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 533: 1–14.
CIPAIS: Commissione Internazionale per la Protezione delle Acque Italo-Svizzere, 2006. Stato limnologico del Lago di Lugano: Circolazione invernale 2005–2006. Bolletino dei Laghi Maggiore e Lugano 7.
Dokulil, M. T., A. Jagsch, G. D. George, O. Anneville, T. Jankowsky, B. Wahl, B. Lenhart, T. Blenckner & K. Teubner, 2006. Twenty years of spatially coherent deepwater warming in lakes across Europe related to the North Atlantic Oscillation. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 2787–2793.
EEA: European Environment Agency, 2010. Climate change impacts on water quality and biodiversity. Background Report for EEA European Environment State and Outlook Report 2010. The European Topic Centre on Water (ETC/W), Water Technical Report 1/2010. 68 pp. http://icm.eionet.europa.eu/.
George, G. (ed.), 2010. The impact of climate change on European lakes. Springer, Dordrecht.
Hatzaki, M., H. A. Flocas, D. N. Asimakopoulosa & P. Maheras, 2007. The eastern Mediterranean teleconnection pattern: identification and definition. International Journal of Climatology 27: 727–737.
Hatzaki, M., H. A. Flocas, C. Giannakopoulos & P. Maheras, 2009. The impact of the eastern Mediterranean teleconnection pattern on the Mediterranean climate. Journal of Climate 22: 977–992.
Hatzaki, M., H. A. Flocas, C. Oikonomou & C. Giannakopoulos, 2010. Future changes in the relationship of precipitation intensity in Eastern Mediterranean with large scale circulation. Advances in Geosciences 23: 31–36.
Holzner, C. P., W. Aeschbach-Hertig, M. Simona, M. Veronesi, D. M. Imboden & R. Kipfer, 2009. Exceptional mixing events in meromictic Lake Lugano (Switzerland/Italy), studied using environmental tracers. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 1113–1124.
Hurrell, J. W., Y. Kushnir, G. Ottersen & M. Visbeck (eds), 2003. The North Atlantic Oscillation. Climatic significance and environmental impact. Geophysical Monograph, Vol. 134. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC: 1–279.
Hurrell, J. W., Y. Kushnir & M. Visbeck, 2001. The North Atlantic oscillation. Science 291: 603–605.
Josey, S. A., S. Somot & M. Tsimplis, 2011. Impacts of atmospheric modes of variability on Mediterranean sea surface heat exchange. Journal of Geophysical Research 116: C02032.
Livingstone, D. & J. Padisák, 2007. Large-scale coherence in the response of lake surface-water temperatures to synoptic-scale climate forcing during summer. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 896–902.
Luterbacher, J. & E. Xoplaki, 2003. 500-Year winter temperature and precipitation variability over the Mediterranean area and its connection to the large-scale atmospheric circulation. In H. J. Bolle (ed.), Mediterranean climate—variability and trends. Springer, Berlin: 133–153.
Manca, M., N. Cavicchioni & G. Morabito, 2000. First observations on the effect of complete overturn of Lake Maggiore on plankton and primary production. International Review of Hydrobiology 85: 209–222.
Mooij, W. M., S. Hülsmann, L. N. De Senerpont Domis, B. A. Nolet, P. L. E. Bodelier, P. C. M. Boers, M. L. Dionisio Pires, H. J. Gons, B. W. Ibelings, R. Noordhuis, R. Portielje, K. Wolfstein & E. H. R. R. Lammens, 2005. The impact of climate change on lakes in the Netherlands: a review. Aquatic Ecology 39: 381–400.
Morabito, G., A. Oggioni & M. Austoni, 2012. Resource ratio and human impact: how diatom assemblages in Lake Maggiore responded to oligotrophication and climatic variability. Hydrobiologia 698: 47–60.
Mosello, R., M. Bianchi, H. Geiss, A. Marchetto, G. Serrini, G. Serrini lanza, G. A. Tartari, & H. Muntau, 1995. AQUACON-MedBas Subproject 6. Acid rain analysis. Intercomparison 1/94. Documenta Istituto italiano di Idrobiologia 54: 44 pp.
Mosello, R., A. Calderoni & R. de Bernardi, 1997. Le indagini sulla evoluzione dei laghi profondi sudalpini svolte dal C.N.R. Istituto italiano di Idrobiologia, Documenta Istituto italiano di Idrobiologia 61: 19–32.
Mosello, R., W. Ambrosetti, S. Arisci, R. Bettinetti, F. Buzzi, A. Calderoni, E. Carrara, R. De Bernardi, S. Galassi, L. Garibaldi, B. Leoni, M. Manca, A. Marchetto, G. Morabito, A. Oggioni, R. Pagnotta, D. Ricci, M. Rogora, N. Salmaso, M. Simona, G. Tartari, M. Veronesi & P. Volta, 2010. Evoluzione recente della qualità delle acque dei laghi profondi sudalpini (Maggiore, Lugano, Como, Iseo e Garda) in risposta alle pressioni antropiche e alle variazioni climatiche. Biologia Ambientale 24: 167–177.
Naselli-Flores, L. & R. Barone, 2012. Phytoplankton dynamics in permanent and temporary Mediterranean waters: is the game hard to play because of hydrological disturbance? Hydrobiologia 698: 147–159.
Nõges, T., 2009. Relationships between morphometry, geographic location and water quality parameters of European lakes. Hydrobiologia 633: 33–43.
Ohlendorf, C., C. Bigler, G. -H. Goudsmit, G. Lemcke, D. M. Livingstone, A. F. Lotter, B. Müller & M. Sturm, 2000. Causes and effects of long periods of ice cover on a remote high Alpine lake. Journal of Limnology 59: 65–80.
Pinheiro, J. C. & D. M. Bates, 2000. Mixed-effects models in S and S-Plus. Springer, New York.
Porter, K. G., P. A. Saunders, K. A. Haberyan, A. E. Macubbin, T. T. Jacobsen & R. E. Hodson, 1996. Annual cycle of autotrophic and heterotrophic production in a small, monomictic Piedmont lake (Lake Oglethorpe): analog for the effects of climatic warming on dimictic lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 1041–1051.
Poveda, G., D. M. Álvarez & Ó. A. Rueda, 2011. Hydro-climatic variability over the Andes of Colombia associated with ENSO: a review of climatic processes and their impact on one of the Earth’s most important biodiversity hotspots. Climate Dynamics 36: 2233–2249.
R Core Team, 2013. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. [http://www.R-project.org/].
Reynolds, C. S., 1987. Cyanobacterial water-bloom. Advances in Botanical Research 13: 67–143.
Reynolds, C. S. & A. E. Walsby, 1975. Water-blooms. Biological Reviews 50: 437–481.
Salmaso, N., 2012. Influence of atmospheric modes of variability on the limnological characteristics of a deep lake south of the Alps. Climate Research 51: 125–133.
Salmaso, N. & L. Cerasino, 2012. Long-term trends and fine year-to-year tuning of phytoplankton in large lakes are ruled by eutrophication and atmospheric modes of variability. Hydrobiologia 698: 17–28.
Salmaso, N. & F. Decet, 1997. Seasonal and interannual changes of chemical characteristics and phytoplankton in a mountain lake of the eastern Italian Alps (Lake Calaita, Trentino). Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie 82: 15–31.
Salmaso, N. & F. Decet, 1998. Interactions of physical, chemical and biological processes affecting the seasonality of mineral composition and nutrient cycling in the water column of a deep subalpine lake (Lake Garda, Northern Italy). Archiv für Hydrobiologie 142: 385–414.
Salmaso, N., F. Decet, S. Consolaro & P. Cordella, 1999. Caratteristiche chimiche e situazione trofica del Lago di Garda nel corso dell’episodio di mescolamento delle acque della primavera del 1999. Acqua Aria 9: 83–89.
Salmaso, N., R. Mosello, L. Garibaldi, F. Decet, M. C. Brizzio & P. Cordella, 2003. Vertical mixing as a determinant of trophic status in deep lakes: a case study from two lakes south of the Alps (Lake Garda and Lake Iseo). Journal of Limnology 62(suppl. 1): 33–41.
Simona, M., 2003. Winter and spring mixing depths affect the trophic status and composition of phytoplankton in the northern meromictic basin of Lake Lugano. Journal of Limnology 62: 190–206.
Sokal, R. R. & F. J. Rohlf, 1995. Biometry, 3rd ed. WH Freeman, New York.
Stenseth, N. C., G. Ottersen, G. W. Hurrell, A. Mysterud, M. Lima, K. -S. Chan, N. G. Yoccoz & B. Ådlandsvik, 2003. Studying climate effects on ecology through the use of climate indices: the North Atlantic Oscillation, El Niño Southern Oscillation and beyond. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 270: 2087–2096.
Straile, D., 2002. North Atlantic Oscillation synchronizes food-web interactions in central European lakes. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 269: 391–395.
Straile, D., D. M. Livingstone, G. A. Weyhenmeyer & D. G. George, 2003. The response of freshwater ecosystems to climate variability associated with the North Atlantic Oscillation. In Hurrell, J. W., Y. Kushnir, G. Ottersen & M. Visbeck (eds), The North Atlantic Oscillation. Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact. American Geophisical Union, Washington, DC: 263–279.
Toreti, A., F. Desiato, G. Fioravanti & W. Perconti, 2010. Seasonal temperatures over Italy and their relationship with low-frequency atmospheric circulation patterns. Climatic Change 99: 211–227.
Wang, J., X. Bai, G. Leshkevich, M. Colton, A. Clites & B. Lofgren, 2010. Severe Ice Cover on Great Lakes During Winter 2008–2009, Eos Transactions. American Geophisical Union 91: 41.
Wetzel, R., 2001. Limnology. Lake and river ecosystems. 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego.
Wetzel, R. & G. E. Likens, 1991. Limnological Analyses, 2nd ed. Springer, New York.
Winder, M. & U. Sommer, 2012. Phytoplankton response to a changing climate. Hydrobiologia 698: 5–16.
Zanchettin, D., P. Traverso & M. Tomasino, 2008. Po River discharges: a preliminary analysis of a 200-year time series. Climatic Change 89: 411–433.
Zuur, A., E. N. Ieno, N. J. Walker, A. A. Saveliev & G. M. Smith, 2009. Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, New York.
Acknowledgements
In Lake Garda the research was funded in part by the Veneto Region, ARPAV and the EU Central Europe Programme (EULAKES Project, 2CE243P3). Studies on lakes Maggiore and Lugano were funded by the CIPAIS (International Commission for the Protection of Waters between Italy and Switzerland). This study was made in the framework of the LTER (Long Term Ecological Research) Italian network, site “Southern Alpine lakes”, IT08-000-A (http://www.lteritalia.it/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: D. Straile, D. Gerdeaux, D. M. Livingstone, P. Nõges, F. Peeters & K.-O. Rothhaupt / European Large Lakes III. Large lakes under changing environmental conditions
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salmaso, N., Buzzi, F., Cerasino, L. et al. Influence of atmospheric modes of variability on the limnological characteristics of large lakes south of the Alps: a new emerging paradigm. Hydrobiologia 731, 31–48 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1659-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1659-6