Abstract
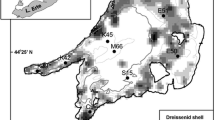
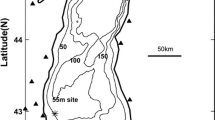
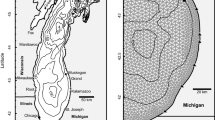
Dreissenid mussels have been hypothesized to cause selective decreases of phytoplankton in nearshore areas (nearshore shunt hypothesis) as well as the near-complete loss of the offshore phytoplankton spring bloom in some Laurentian Great Lakes. To evaluate whether mussels can reasonably be expected to mediate such changes, we extended the three-dimensional hydrodynamic-ecological model (ELCOM-CAEDYM) to include mussels as a state variable and applied it to Lake Erie (USA-Canada). Mussel-mediated decreases in mean phytoplankton biomass were highly sensitive to the assigned mussel population size in each basin. In the relatively deep east basin, mussels were predicted to decrease phytoplankton in both nearshore and offshore zones, even during periods of thermal stratification but especially during the spring phytoplankton maximum. Spatially, impacts were associated with mussel distributions but could be strong even in areas without high mussel biomass, consistent with advection from areas of higher mussel biomass. The results supported the nearshore shunt hypothesis that mussel impacts on phytoplankton should be greater in nearshore than offshore waters and also supported suggestions about the emerging importance of deep water offshore mussels. The results of this study provide an important insight into ecological role of mussels in lowering plankton productivity in some world’s largest lakes.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, J. D., M. R. Loewen & P. F. Hamblin, 2001. Benthic pelagic coupling over a zebra mussel reef in western Lake Erie. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 892–904.
Arhonditsis, G. B. & M. T. Brett, 2004. Evaluation of the current state of mechanistic aquatic biogeochemical modeling. Marine Ecology Progress Series 271: 13–26.
Arnott, D. L. & M. J. Vanni, 1996. Nitrogen and phosphorus recycling by the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in the western basin of Lake Erie. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 53: 646–659.
Barbiero, R. P. & M. L. Tuchman, 2004. Long-term dreissenid impacts in water clarity in Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research 30: 557–565.
Barbiero, R. P., D. C. Rockwell, G. J. Warren & M. L. Tuchman, 2006. Changes in spring phytoplankton communities and nutrient dynamics in the eastern basin of Lake Erie since the invasion of Dreissena spp. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 63: 1549–1563.
Barbiero, R. P., B. M. Lesht & G. J. Warren, 2012. Convergence of trophic state and the lower food web in Lakes Huron, Michigan and Superior. Journal of Great Lakes Research 38: 368–380.
Bierman, V. J. Jr., J. Kaur, J. V. DePinto, T. J. Feist & D. W. Dilks, 2005. Modeling the role of zebra mussels in the proliferation of blue-green algae in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31: 32–55.
Bocaniov, S. A. & R. E. H. Smith, 2009. Plankton metabolic balance at the margins of very large lakes: temporal variability and evidence for dominance of autochthonous processes. Freshwater Biology 54: 345–362.
Boegman, L., M. R. Loewen, P. F. Hamblin & D. A. Culver, 2008a. Vertical mixing and weak stratification over zebra mussel colonies in western Lake Erie. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 1093–1110.
Boegman, L., M. R. Loewen, D. A. Culver, P. F. Hamblin & M. M. Charlton, 2008b. Spatial–dynamic modeling of algal biomass in Lake Erie: relative impacts of dreissenid mussels and nutrient loads. Journal of Environmental Engineering 134: 456–468.
Charlton, M. N., M. N. LeSage & J. E. Milne, 1999. Lake Erie in transition: the 1990’s. In Munawar, M., T. Edsall & I. F. Munawar (eds), State of Lake Erie: Past. Present and Future. Ecovision World Monograph series. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden: 97–123.
Conroy, J. D., D. D. Kane, D. M. Dolan, W. J. Edward, M. N. Charlton & D. A. Culver, 2005a. Temporal trends in Lake Erie plankton biomass: roles of external phosphorus loading and dreissenid mussels. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31(Suppl. 2): 89–110.
Conroy, J. D., W. J. Edwards, R. A. Pontius, D. D. Kane, H. Y. Zhang, J. F. Shea, J. N. Richey & D. A. Culver, 2005b. Soluble nitrogen and phosphorus excretion of exotic freshwater mussels (Dreissena sp.): potential impacts for nutrient remineralisation in western Lake Erie. Freshwater Biology 50: 1146–1162.
Depew, D. C., S. J. Guildford & R. E. H. Smith, 2006. Nearshore-offshore comparison of chlorophyll-a and phytoplankton production in the dreissenid-colonized eastern basin of Lake Erie. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 63: 1115–1129.
Evans, M. A., G. A. Fahnenstiel & D. Scavia, 2011. Incidental oligotrophication of North American Great Lakes. Environmental Science and Technology 45: 3297–3303.
Fahnenstiel, G. L., T. B. Bridgeman, G. A. Lang, M. J. McCormick & T. F. Nalepa, 1995. Phytoplankton productivity in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron: effects of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) colonization. Journal of Great Lakes Research 21: 465–475.
Fahnenstiel, G. L., S. Pothoven, H. Vanderploeg, D. Klarer, T. Nalepa & D. Scavia, 2010. Recent changes in primary production and phytoplankton in the offshore region of southeastern Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 36(Suppl. 3): 20–29.
Fishman, D. B., S. A. Adlerstein, H. A. Vanderploeg, G. L. Fahnenstiel & D. Scavia, 2009. Causes of phytoplankton changes in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron, during the zebra mussel invasion. Journal of Great Lakes Research 35: 482–495.
Gergs, R., K. Rinke & K.-O. Rothhaupt, 2009. Zebra mussels mediate benthic–pelagic coupling by biodeposition and changing detrital stoichiometry. Freshwater Biology 54: 1379–1391.
Gergs, R., J. Grey & K.-O. Rothhaupt, 2011. Temporal variations in zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) density structure the benthic food web and community composition. Biological Invasions 13: 2727–2738.
Ghadouani, A. & R. E. H. Smith, 2005. Phytoplankton distribution in Lake Erie as assessed by a new in situ spectrofluorometric technique. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31(Suppl. 2): 154–167.
Goedkoop, W., R. Naddafi & U. Grandin, 2011. Retention of N and P by zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) and its quantitative role in the nutrient budget of eutrophic Lake Ekoln, Sweden. Biological Invasions 13: 1077–1086.
Gupta, H. V., S. Sorooshian & P. O. Yapo, 1999. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: comparison with multilevel expert calibration. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering 4(2): 135–143.
Haltuch, M. E. & Berkman, P. A. 1998. The Lake Erie Geographic Information System: Bathymetry, Substrates and Mussels. Ohio State University, Ohio SeaGrant College Program, Publication number OHSU-GS-20.
Haltuch, M. A., P. A. Berkman & D. W. Garton, 2000. Geographic information system (GIS) analysis of an ecosystem invasion: exotic mussels in Lake Erie. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1778–1787.
Hecky, R. E., R. E. H. Smith, D. R. Barton, S. J. Guildford, W. D. Taylor, M. N. Charlton & T. Howell, 2004. The nearshore phosphorus shunt: a consequence of ecosystem engineering by dreissenids in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 61: 1285–1293.
Higgins, S. N. & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2010. What a difference a species makes: a meta-analysis of dreissenid mussel impacts on freshwater ecosystems. Ecological Monographs 80: 179–196.
Higgins, S. M., M. J. VanderZanden, L. N. Joppa & Y. Vadeboncoeur, 2011. The effects of dreissenid invasions on chlorophyll and the chlorophyll:total phosphorus ratio in north temperate lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 68: 319–329.
Hipsey, M. R. & D. P. Hamilton, 2008. Computational aquatic ecosystems dynamics model: CAEDYM v3 Science Manual. Centre for Water Research Report, University of Western Australia.
Hodges, B. R., J. Imberger, A. Saggio & K. Winters, 2000. Modeling basin scale waves in a stratified lake. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1603–1620.
Holland, P. R. & A. Kay, 2003. A review of the physics and ecological implications of the thermal bar circulation. Limnologica 33: 153–162.
Jarvis, P., J. Dow, R. Dermott & R. Bonnell, 2000. Zebra (Dreissena polymorpha) and quagga mussel (Dreissena bugensis) distribution and density in Lake Erie, 1992–1998. Canadian Technical Report of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences No. 2304, Burlington, Ontario, Canada: 46 pp.
Karatayev, A. Y., L. E. Burlakova & D. K. Padilla, 1997. The effects of Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas) invasion on aquatic communities in Eastern Europe. Journal of Shellfish Research 16: 187–203.
Laval, B., J. Imberger, B. R. Hodges & R. Stocker, 2003. Modeling circulation in lakes: spatial and temporal variations. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 983–994.
Leon, L. F., J. Imberger, R. E. H. Smith, D. Lam & W. Schertzer, 2005. Modeling as a tool for nutrient management in Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31: 309–318.
Leon, L. F., R. E. H. Smith, M. R. Hipsey, S. A. Bocaniov, S. N. Higgins, R. E. Hecky, J. P. Antenucci, J. A. Imberger & S. J. Guildford, 2011. Application of a 3D hydrodynamic-biological model for seasonal and spatial dynamics of water quality and phytoplankton in Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research 37: 41–53.
MacIsaac, H. J., O. E. Johansson, J. Ye, W. G. Sprules, J. H. Leach, J. A. McCorquodale & I. A. Grigorovich, 1999. Filtering impacts of an introduced bivalve (Dreissena polymorpha) in a shallow lake: application of a hydrodynamic model. Ecosystems 2: 338–350.
Makarewicz, J. C., T. W. Lewis & P. Bertram, 1999. Phytoplankton composition and biomass in the offshore waters of Lake Erie: pre- and post-Dreissena introduction (1983–1993). Journal of Great Lakes Research 25: 135–148.
Malkin, S. Y., G. M. Silsbe, R. E. H. Smith & E. T. Howell, 2012. A deep chlorophyll maximum nourishes benthic filter feeders in the coastal zone of a large clear lake. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 735–748.
McMahon, R. F., 1996. The physiological ecology of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, in North America and Europe. American Zoologist 36: 339–363.
Millie, D. F., G. L. Fahnenstiel, J. D. Bressie, R. J. Pigg, R. R. Rediske, D. M. Klarer, P. A. Tester & R. W. Litaker, 2009. Late summer phytoplankton in western Lake Erie (Laurentian Great Lakes): bloom distributions, toxicity and environmental influences. Aquatic Ecology 43: 915–934.
Moriasi, D. N., J. G. Arnold, M. W. Van Liew, R. L. Bingner, R. D. Harmel & T. L. Veith, 2007. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the ASABE 50: 885–900.
Naddafi, R., K. Pettersson & P. Eklöv, 2007. The effect of seasonal variation in selective feeding by zebra mussels (Dreissenia polymorpha) on phytoplankton community composition. Freshwater Biology 52: 823–842.
Naddafi, R., K. Pettersson & P. Eklöv, 2008. Effects of the zebra mussel, an exotic freshwater species, on seston stoichiometry. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 1973–1987.
Naddafi, R., P. Eklöv & K. Pettersson, 2009. Stoichiometric constraints do not limit successful invaders: zebra mussels in Swedish lakes. PLoS ONE 4(4): e5345.
Naddafi, R., K. Pettersson & P. Eklöv, 2010. Predation and physical environment structure the density and population size structure of zebra mussels. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 29: 444–453.
Naddafi, R., T. Blenckner, P. Eklöv & K. Pettersson, 2011. Physical and chemical properties determine zebra mussel invasion success in lakes. Hydrobiologia 669: 227–236.
Nalepa, T. F., D. L. Fanslow & S. A. Pothoven, 2010. Recent changes in density, biomass, recruitment, size structure and nutritional state of Dreissena populations in southern Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 36(Suppl. 3): 5–19.
Nicholls, K. H., G. J. Hopkins & S. J. Standke, 1999. Reduced chlorophyll to phosphorus ratios in nearshore Great Lakes waters coincide with the establishment of dreissenid mussels. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56: 153–161.
Noonburg, E. G., B. J. Shuter & P. A. Abrams, 2003. Indirect effects of zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) on the planktonic food web. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60: 1353–1368.
North, R. L., R. E. H. Smith, R. E. Hecky, D. C. Depew, L. F. Leon, M. N. Charlton & S. J. Guildford, 2012. Distribution of seston and nutrient concentrations in the eastern basin of Lake Erie pre- and post-dreissenid mussel invasion. Journal of Great Lakes Research 38: 463–476.
Patterson, M. W. R., J. H. Ciborowski & D. R. Barton, 2005. The distribution and abundance of Dreissena species (Dreissenidae) in Lake Erie, 2002. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31(Suppl. 2): 223–237.
Radach, G. & A. Moll, 2006. Review of three-dimensional ecological modelling related to the North Sea shelf system. Part II: Model validation and data needs. Oceanography and Marine Biology – An Annual Review 44: 1–60.
Rao, Y. R. & D. J. Schwab, 2007. Transport and mixing between the coastal and offshore waters in the Great Lakes: a review. Journal of Great Lakes Research 33: 202–218.
Smith, R. E. H., V. P. Hiriart-Baer, S. N. Higgins, S. J. Guildford & M. N. Charlton, 2005. Planktonic primary production in the offshore waters of dreissenid-infested Lake Erie in 1996. Journal of Great Lakes Research 31: 50–62.
Spillman, C. M., D. P. Hamilton, M. R. Hipsey & J. Imberger, 2008. A spatially resolved model of seasonal variations in phytoplankton and clam (Tapes philippinarum) biomass in Barbamarco Lagoon, Italy. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 79: 187–203.
Spillman, C. M., D. P. Hamilton & J. Imberger, 2009. Management strategies to optimise sustainable clam (Tapes philippinarum) harvest in Barbamarco Lagoon, Italy. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 81: 267–278.
Vanderploeg, H. A., J. R. Liebig, W. W. Carmichael, M. A. Agy, T. H. Johengen, G. L. Fahnenstiel & T. F. Nalepa, 2001. Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) selective filtration promoted toxic Microcystis blooms in Saginaw Bay (Lake Huron) and Lake Erie. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 58: 1208–1221.
Vanderploeg, H. A., T. H. Johengen & J. R. Leibig, 2009. Feedback between zebra mussel selective feeding and algal composition affects mussel condition: did the regime changer pay a price for its success? Freshwater Biology 54: 47–63.
Vanderploeg, H. A., J. R. Liebig, T. F. Nalepa, G. L. Fahnenstiel & S. A. Pothoven, 2010. Dreissena and the disappearance of the spring phytoplankton bloom in Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 36(Suppl. 3): 50–59.
Walz, N., 1978. The energy balance of the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha Pallas in laboratory experiments and in Lake Constance. I. Pattern of activity, feeding and assimilation efficiency. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, Supplement 55: 83–105.
Werner, S., M. Mörtl, H.-G. Bauer & K.-O. Rothhaupt, 2005. Strong impact of wintering waterbirds on zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) populations at Lake Constance, Germany. Freshwater Biology 50: 1412–1426.
White, B. & K. Matsumoto, 2012. Causal mechanisms of the deep chlorophyll maximum in Lake Superior: a numerical modeling investigation. Journal of Great Lakes Research 38: 504–513.
Yu, N. & D. A. Culver, 1999. Estimating the effective clearance rate and refiltration by zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, in a stratified reservoir. Freshwater Biology 41: 481–492.
Zhang, H., D. A. Culver & L. Boegman, 2008. A two-dimensional ecological model of Lake Erie: application to estimate dreissenid impacts on large lake plankton populations. Ecological Modelling 214: 219–241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: D. Straile, D. Gerdeaux, D. M. Livingstone, P. Nõges, F. Peeters & K.-O. Rothhaupt / European Large Lakes III. Large lakes under changing environmental conditions
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bocaniov, S.A., Smith, R.E.H., Spillman, C.M. et al. The nearshore shunt and the decline of the phytoplankton spring bloom in the Laurentian Great Lakes: insights from a three-dimensional lake model. Hydrobiologia 731, 151–172 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1642-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1642-2