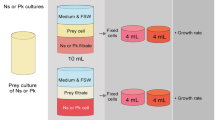
Abstract
For avoiding the unfavorable environmental conditions several aquatic microorganisms are capable of forming specialized resistance cells like akinets, hypnospores, statospores, etc. Recognition of the important role of cysts in the life cycles of dinoflagellates increased the need to study their role in the ecology of phytoplanktons, and this, combined with the knowledge of chemical and biological characteristics of the water, may lead to a better understanding of the spatial and temporal dynamics of dinoflagellates. This paper reports on the effects of temperature, nitrogen, and phosphorus on the percentage of encystment of the dinoflagellate Peridinum cinctum Stein. The phosphorus content of the medium affected encystment only at the highest temperature applied (22 °C). Nitrogen content and temperature were the most important factors controlling the encystment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson D. M., Kulis D. M. and Binder B. J. (1984). Sexuality and cyst formation in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax tamarensis cyst yield in batch cultures. Journal of Phycology 20(3): 418–425
Anderson D. M. and Lindquist N. L. (1985). Time-course measurements of phosphorus depletion and cyst formation in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax tamarensis Lebour. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 86(1): 1–13
Barry C., Smith I. and Persson A. (2004). Dinoflagellate cyst production in one-liter containers. Journal of Applied Phycology 16: 401–405
Binder B. J. and Anderson D. M. (1987). Physiological and environmental control of germination in Scrippsiella trochoidea (Dinophyceae) resting cysts. Journal of Phycology 23: 99–107
Cantonati M., Tardio M., Tolotti M. and Corradini F. (2003). Blooms of the dinoflagellate Glenodinium sanguineum obtained during enclosure experiments in Lake Tovel (N. Italy). Journal of Limnology 62(1): 79–87
Carefoot J. R. (1968). Culture and heterotrophy of the freshwater dinoflagellates Peridinium cintum fa. ovoplanum Lindemann. Journal of Phycology. 4: 129–131
Chapman A. D. and Pfiester L. A. (1995). The effect of temperature, irradiance and nitrogen on encystment and growth of the freshwater Dinoflagellates Peridinium cinctum and P. willei in culture (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology 31: 355–359
Chorus I. and Bartram J. (1999). Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. A Guide to their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management. E. & FN Spon, London and New York
Dale B. (1983). Dinoflagellate resting cysts: ‘bentic plankton’. In: Fryxel, G. A. (eds) Survival Strategies of Algae, pp 69–136. Cambridge University Press, New York
Demanche J. M., Lundy D. W. and Donaghay P. L. (1979). The rapid response of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum to changes in external and internal nutrient concentration. Marine Biology 53: 323–333
Dortch Q., Clayton J. R., Thoreson S. and Ahmed S. I. (1984). Species differences in accumulation of nitrogen pools in phytoplankton. Marine Biology 81: 237–250
Doucette G. J., Cembella A. D. and Boyer G. L. (1989). Cyst formation in the red tide dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense (Dinophyceae): effects of iron stress. Journal of Phycology 25: 721–731
Edmondson, W. T. (1972). Nutrients and phytoplankton in Lake Washington. In Likens, G. E. (ed), Nutrients and Eutrophication. 172–193
Endo T. and Nagata H. (1984). Resting and germination of cysts of Peridinium sp. (Dinophyceae) (in Japanese). Bulletin Plankton Societies of Japan 31: 23–33
Eppley R. W. and Renger E. H. (1974). Nitrogen assimilation of an oceanic diatom in nitrogen-limited continuous culture. Journal of Phycology 10: 15–23
Figueroa R. I. and Bravo I. (2005a). A study of the sexual reproduction and determination of mating type of Gymnodinium nolleri (Dinophyceae) in culture. Journal of Phycology 41(1): 74–83
Figueroa R. I. and Bravo I. (2005b). Sexual reproduction and two different encystment strategies of Lingulodium polyedrum (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology 41(2): 370–379
Flaim, G., G. Hansen, Ø. Moestrup, F. Corradini & B. Borghi, 2004. Reinterpretation of the reddening of Lake Tovel in the Italian Alps by dinoflagellates Glenodinium sanguineum. Phycologia 43(6): 737–743
Flaim G., Rott E., Corradini F., Toller G. and Borghi B. (2003). Long-term trends in species composition of dinoflagellates in Lake Tovel (Trentino, Italy). Hydrobiologia 502: 357–366
Fleming R. H. (1940). The composition of plankton and units for reporting population and production. Process of Pacific Sciences Congress 3: 526–540
Grigorszky I., Nagy S., Krienitz L., Kiss K. T., Mikó H. M., Tóth A., Borics G., Máthé C., Kiss B., Borbély G., Dévai G. and Padisák J. (2000). Seasonal succession of phytoplankton in a small eutrophic oxbow and some consideration to the PEG model. Verhandlungen Internationales Verein Limnologie 27: 152–156
Grigorszky I., Borics G., Padisák J., Tóthmérész B., Vasas G., Nagy S. and Borbély G. (2003a). Factors controlling the occurrence of Dinophyta species in Hungary. Hydrobiologia 506–507: 203–207
Grigorszky I., Padisák J., Borics G. and Schnitchen C. (2003b). Deep chlorophyll maximum by Ceratium hirundinella O.F.Müller (Bergh) in a shallow oxbow in Hungary. Hydrobiologia 506–507: 209–212
Hickel B. (1988). Sexual reproduction and life cycle of Ceratium furcoides (Dinophyceae) in situ in Lake Plüssee (F.R.G.). Hydrobiologia 161: 41–48
Huppert A., Blasius B. and Stone L. (2002). A model of phytoplankton blooms. American Naturalist 159: 156–171
Karlsson I. (1999). On the germination of the akinete-forming cynaobacterium Gloeotrichia echinulata, in Lake Erken, Sweden. Algological Studies 94: 175–180
Karlsson I. (2003). Benthic growth of Gloeotrichia echinulata, Cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 506–507: 189–193
Karsson-Elfgren I., Rydin E., Hyenstrand P. and Pettersson K. (2003). Recruitment and pelagic growth of Gloeotrichia echinulata. Journal of Phycology 39: 1050–1056
Ketchum, B. H., 1939. The development and restoration of deficiencies in the phosphorus and nitrogen composition of unicellular plants. Journal Cell Physiology, 373–381
Kida K., Park H. and Hayashi H. (1989). Occurence of freshwater red tide of Peridinium spp. in Lake Kizaki (in Japanese). Journal of Faculty of Science Shinshu University 24: 13–25
Moore D., O’Donohue M., Shaw G. and Critchley C. (2003). Potential triggers of akinete differentation in an Australian strain of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (AWT 205/1). Hydrobiologia 506–507: 175–180
Olli K. and Anderson D. M. (2002). High encystment success of the Dinoflagellate Scrippsiella cf. Lachrzmosa in culture experiments. Journal of Phycology 38: 145–156
Olli K., Neubert M. G. and Anderson D. M. (2004). Encystment probability and encystment rate: new terms to quantitatively describe formation of resting cysts in planktonic microbial populations. Marine Ecology 273: 43–48
Park H. and Hayashi H. (1992). Life cycle of Peridinium bipes f. occulatum (Dinophyceae) isolated from Lake Kizaki. Journal of Faculty of Science Shinshu University 27: 87–104
Park H. and Hayashi H. (1993). Role of encystment and excystment of Peridinium bipes f. oculatum (Dinophyceae) in freshwater red tides in Lake Kizaki, Japan. Journal of Phycology 29: 435–441
Perry M. J. (1976). Phosphate utilization by oceanic diatom in phosphorus limited chemostat culture and in the oligotrophic waters of the central North Pacific. Limnology and Oceanography. 21: 88–107
Pfiester L. A. (1975). Sexual reproduction of Peridinium cinctum f. ovoplanum (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology 11: 259–265
Pfiester L. A. (1976). Sexual reproduction of Peridinium willei (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology 12: 234–238
Pfiester L. A. (1977). Sexua reproduction of Peridinium gatunense (Dinophyceae). Journal of Phycology 13: 92–95
Pollingher U. (1986). Freshwater armored dinoflagellates: Growth, reproduction strategies and population dynamics. In: Sandgren, C. D. (eds) Growth and Reproductive Strategies of Freshwater Phytoplankton, pp 134–174. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rengefors K. and Anderson D. M. (1998). Environmental and endogenous regulation of cyst germination in two freshwater dinoflagellates. Journal of Phycology 34: 568–577
Rodhe W. (1948). Environmental requirements of freshwater plankton algae. Symbolae Botanicae Upsalienses 10: 1–49
Sako Y., Ishida T., Kadota H. and Hata Y. (1984). Sexual reproduction and cyst formation in the freshwater dinoflagellate Peridinium cunningtonii. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries 50: 743–750
Sako Y., Ishida Y., Kadota H. and Hata Y. (1985). Excystment in the freshwater dinoflagellate Peridinium cunningtonii. Bulletin Japanese Societies Sciences Fisheries. 51: 267–272
Sako Y., Ishida T., Nishijama T. and Hata Y. (1987). Sexual reproduction and cyst formation in the freshwater dinoflagellate Peridinium penardii. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53: 473–478
Sakshaug E. and Holm-Hansen O. (1977). Chemical composition of Skeletonema costatum and Pavlova (Monochrysis) lutheri as a function of nitrate-, phosphate- and iron-limited growth. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 29: 1–34
Schindler D. W. (1971). A hypothesis to explain differences and similarities among lakes in the experimental lakes area., Northwestern Ontario. Journal of the Fisheries research Board of Canada 28: 295–301
Serruya C. and Bermann T. (1975). Phosphorus, nitrogen and growth of algae in Lake Kinneret. Journal of Phycology 11: 155–162
Shafik H. M., Herodek S., Vörös L., Présing M. and Kiss K. T. (1997). Growth of Cyclotella meneghiniana Kutz. I. Effect of temperature, light and low rate nutrient supply. Annals of Limnology 33: 139–147
Spoehr H. A. and Miller H. W. (1949). The chemical composition of Chlorella; effect of environmental conditions. Plant Physiology 24: 120–149
(1973). Observations on vegetative reproduction and sexual life cycles of two freshwater dinoflagellates, Gymnodinium pseudopalustre Schiller and Woloszynskia apiculata sp. nov. British Phycolical Journal 8: 105–134
Susek E., Zonneveld K. A. F., Fischer G., Versteegh G. J. M. and Willems H. (2005). Organic-walled dinoflagellate cyst production in relation to upwelling intensity and lithogenic influx in the Cape Blanc region (off north-west Africa). Phycological Research 53: 97–112
Vollenweider R. A., 1968. Scientific fundamentals of eutrophication of lakes and flowing waters, with particular reference to nitrogen and phosphorus as factors in eutrophication. OECD Report technical Report. 159 pp
Watanabe M., Watanabe M. and Fukuyo Y. (1982). Encysment and excystment of red tide flagellates I. Introduction of encystment of Scrippsiella trochoidea. Research Report Natural Institute of Environmental Studies 30: 27–42
Wynne D. (1981). The role of phosphatases in the metabolism of Peridinium cinctum, from Lake Kinneret. Hydrobiologia. 81: 93–99
Zohary T., Pollingher U., Hadas O. and Hambright K. D. (1998). Bloom dynamics and sedimentation of Peridinium gatunense in Lake Kinneret. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 175–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grigorszky, I., Kiss, K.T., Béres, V. et al. The Effects of Temperature, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus on the Encystment of Peridinium cinctum, Stein (Dinophyta). Hydrobiologia 563, 527–535 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0037-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0037-z