Abstract
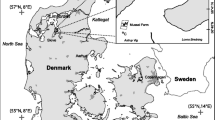
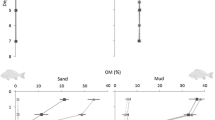
Fluxes of oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus were determined in two areas of the Sacca di Goro lagoon, at a site influenced by the farming of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis and a control site. Mussel farming induced intense biodeposition of organic matter to the underlying sediments, which stimulated sediment oxygen demand, and inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus regeneration rates compared to the nearby control station. Overall benthic fluxes (–11.4 ± 6.5 mmol O2 m−2 h−1; 1.59 ± 0.47 mmol NH +4 m−2 h−1 and 94 ± 42 μmol PO 3−4 m−2 h−1) at the mussel farm are amongst the highest ever recorded for an aquaculture impacted area and question the belief that farming of filter-feeding bivalves has inherently lower impacts than finfish farming. In situ incubations of intact mussel ropes demonstrated that the mussel rope community was an enormous sink for oxygen and particulate organic matter, and an equally large source of dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphate to the water column. Overall, a one meter square area of␣mussel farm (mussel ropes and underlying sediment) was estimated to have an oxygen demand of 46.8 mmol m2 h−1 and to regenerate inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus at rates of 8.5 and 0.3 mmol m2 h−1, with the mussel ropes accounting for between 70 and more than 90% of the overall oxygen and nutrient fluxes. Even taking into account that within the farmed area of the Sacca di Goro lagoon, there are 15–20 m−2 of open water for each one covered with mussel ropes, the mussel ropes would account for a large and often dominant part of overall oxygen and nutrient fluxes. These results demonstrate that it is essential to take into account the activity of the cultivated organisms and their epiphytic community when assessing the impacts of shellfish farming. Overall, whilst grazing by the mussel rope community could act as a top-down control on the phytoplankton, most of the ingested organic matter is rapidly recycled to the water column as inorganic nutrients, which would be expected to stimulate phytoplankton growth. Consequently, the net effect of the mussel farming on phytoplankton dynamics, may be to increase phytoplankton turnover and overall production, rather than to limit phytoplankton biomass.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.P.H.A., 1975. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewaters, 14th edn. A.P.H.A., Washington, USA, 1193 pp
M. J. Atkinson S. V. Smith (1983) ArticleTitleC:N:P ratios of benthic marine plants Limnology and Oceanography 28 568–574
C. Barranquet E. Alliot M. R. Plante-Cuny (1994) ArticleTitleBenthic microphytic activity at two mediterranean shellfish cultivation sites with references to benthic fluxes Oceanologica Acta 17 211–221
M. Bartoli D. Nizzoli P. Viaroli E. Turolla G. Castaldelli E. A. Fano R. Rossi (2001) ArticleTitleImpact of Tapes philippinarum farming on nutrient dynamics and benthic respiration in the Sacca di Goro Hydrobiologia 455 203–212 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1011910422400
D. Baudinet E. Alliot B. Berland C. Grenz M. R. Plante-Cuny R. Plante C. Salen-Picard (1990) ArticleTitleIncidence of mussel culture on biogeochemical fluxes at the sediment-water interface Hydrobiologia 207 187–196 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00041456
R. A. Berner (1984) ArticleTitleSedimentary pyrite formation: an update Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 48 605–615 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(84)90089-9
T. H. Blackburn N. D. Blackburn (1993) ArticleTitleRates of microbial processes in sediments Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 344 49–58
T. H. Blackburn B. A. Lund M. D. Krom (1988) ArticleTitleC- and N-mineralization in the sediments of earthen marine fishponds Marine Ecology Progress Series 44 221–227
G. Boucher R. Boucher-Rodoni (1988) ArticleTitleIn situ measurement of respiratory metabolism and nitrogen fluxes at the interface of oyster beds Marine Ecology Progress Series 44 229–238
C. E. Bower T. Holm-Hansen (1980) ArticleTitleA salicylate-hypoclorite method for determining ammonia in seawater Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 37 794–798
J. Castel P. Caumette R. Herbert (1996) ArticleTitleEutrophication gradients in coastal lagoons as exemplified by the Bassin d’Arcachon and Etang du Prévost Hydrobiologia 329 ix–xxviii Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00034542
J. D. Cline (1969) ArticleTitleSpectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulphide in natural waters Limnology and Oceanography 14 454–459
P. B. Christensen S. Rysgaard N. P. Sloth T. Dalsgaard S. Schwaeter (2000) ArticleTitleSediment mineralization, nutrient fluxes, denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in an estuarine fjord with sea cage trout farms Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21 73–84
P. B. Christensen R. N. Glud T. Dalsgaard P. Gillespie (2003) ArticleTitleImpacts of longline mussel farming on oxygen and nitrogen dynamics and biological communities of coastal sediments Aquaculture 218 567–588 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00587-2
J. E. Cloern (2001) ArticleTitleOur evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem Marine Ecology Progress Series 210 223–253
B. Dahlbäck L. H. A. H. Gunnarsson (1981) ArticleTitleSedimentation and sulfate reduction under a mussel culture Marine Biology 63 269–275 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00395996
R. Dame J. Spurrier T. Wolaver (1989) ArticleTitleCarbon, nitrogen and phosphorus processing by an oyster reef Marine Ecology Progress Series 54 249–256
A. Zwaan Particlede J. M. F. Babarro M. Monari O. Cattani (2002) ArticleTitleAnoxic survival potential of bivalves: (arte)facts Comparative Biochemistry And Physiology Part A 131 615–624 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1095-6433(01)00513-X
FAO, 2003. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2002. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation, Rome
H. Fossing B. B. Jorgensen (1989) ArticleTitleMeasurement of bacterial sulphate reduction in sediment: evaluation of a single-step chromium reduction method Biogeochemistry 8 205–222 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00002889
H. L. Golterman (1995) ArticleTitleThe role of the iron hydroxide–phosphate–sulphide system in the phosphate exchange between sediments and water Hydrobiologia 297 43–54 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00033500
G. Graf R. Rosenberg (1997) ArticleTitleBioresuspension and biodeposition: a review Journal of Marine Systems 11 269–278 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0924-7963(96)00126-1
J. Grant A. Hatcher D. B. Scott P. Pocklington C. T. Shafer G. V. Winters (1995) ArticleTitleA multidisciplinary approach to evaluating impacts of shellfish aquaculture on benthic communities Estuaries 18 124–144
Grenz, C., 1989. Quantification et destinee de la biodeposition en zones de production conchylicole intensive en mediterranee. Thése de doctorate. Université Aix-Marseille II, France, 152 pp
B. T. Hargrave D. E. Duplisea E. Pfeiffer D. J. Wildish (1993) ArticleTitleSeasonal changes in benthic fluxes of dissolved oxygen and ammonium associated with marine cultured Atlantic salmon Marine Ecology Progress Series 96 249–257
A. Hatcher J. Grant B. Schofield (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of suspended mussel culture (Mytillus spp.) on sedimentation, benthic respiration and sediment dynamics in a coastal bay Marine Ecology Progress Series 115 219–235
S. K. Heijs R. Azzoni G. Giordani H. M. Jonkers D. Nizzoli P. Viaroli H. Gemerden ParticleVan (2000) ArticleTitleSulphide-induced release of phosphate from sediments of coastal lagoons and the possible relation to the disappearance of Ruppia sp Aquatic Microbial Ecology 23 85–95
M. Holmer E. Kristensen (1992) ArticleTitleImpact of marine fish cage farming on metabolism and sulfate reduction of underlying sediments Marine Ecology Progress Series 80 191–201
M. Holmer N. Marbá J. Terrados C. Duarte M. D. Fortes (2002) ArticleTitleImpacts of milkfish (Chanos chanos) aquaculture on carbon and nutrient fluxes in the Bolinao area, Philippines Marine Pollution Bulletin 44 685–696 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00048-6 Occurrence Handle12222893
E. Jamarillo C. Bertran A. Bravo (1992) ArticleTitleMussel biodeposition in an estuary in southern Chile Marine Ecology Progress Series 82 85–94
B. B. Jørgensen (1977) ArticleTitleBacterial sulfate reduction within reduced microniches of oxidized marine sediments Marine Biology 41 7–17 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00390576
B. B. Jørgensen (1982) ArticleTitleMineralization of organic matter in the sea bed – the role of sulfate reduction Nature 296 643–645 Occurrence Handle10.1038/296643a0
M. J. Kaiser I. Laing S. D. Utting G. M. Burnell (1998) ArticleTitleEnvironmental impacts of bivalve mariculture Journal of Shellfish Research 17 59–66
H. F. Kaspar P. A. Gillespie I. C. Boyer A. L. MacKenzie (1985) ArticleTitleEffects of mussel aquaculture on the nitrogen cycle and benthic communities in Kenepuru Sound, Marlborough Sounds, New Zealand Marine Biology 85 127–136 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00397431
G.W. Luther (1991) ArticleTitlePyrite synthesis via polysulphide compounds Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 55 2839–2839 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(91)90449-F
N. Mazouni J. C. Gaertner J. M. Deslous Paoli (2001) ArticleTitleComposition of biofouling communities on suspended oyster cultures: an in situ study of their interactions with the water column Marine Ecology Progress Series 214 93–102
MacAlister, E., 1999. Forward study of community aquaculture. Summary report, 60 pp
R. L. Naylor R. J. Goldburg J. H. Primavera (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of aquaculture on world fish supplies Nature 405 1017–1024
Y. Nakamura F. Kerciku (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of filter-feeding bivalves on the distribution of water quality and nutrient cycling in a eutrophic coastal lagoon Journal of Marine Systems 26 209–221 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0924-7963(00)00055-5
C. B. Officer T. J. Smayda R. Mann (1982) ArticleTitleBenthic Filter Feeding: A Natural Eutrophication Control Marine Ecology Progress Series 9 203–210
Rana, K. J., 1988. Global overview of production and production trends. FAO Fisheries Circular No 886, Rev. FAO, Rome, 188 pp
Redfield, A. C., B. H. Ketchum & F. A. Richards, 1963. The influence of organisms on the composition of seawater. In Hill, M.N., (ed.), The Sea. Vol. II: 26–77
C. P. Slomp S. J. Gaast ParticleVan der W. Raaphorst ParticleVan (1996) ArticleTitlePhosphate adsorption in oxidised marine sediments Chemical Geology 107 477–480 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0009-2541(93)90235-B
P. N. Sloth H. Blackburn L. S. Hansen N. Risgaard-Peterson B. A. Lomstein (1995) ArticleTitleNitrogen cycling in sediments with different organic loading Marine Ecology Progress Series 116 163–170
I. Sorokin O. Giovanardi F. Pranovi P. I. Sorokin (1999) ArticleTitleNeed for restricting bivalve culture in the southern basin of the Lagoon of Venice Hydrobiologia 400 141–148 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003707231839
J. M. Sornin M. Feulillet M. Heral J. C. Fardeu (1986) ArticleTitleInfluence des cultures D’huitres Crassostrea gigas sur le cycle du phosphore en zone intertidale: role de la biodeposition Oceanologica Acta 9 313–322
D. Soto G. Mena (1999) ArticleTitleFilter feeding by the freshwater mussel, Diplodon chilensis, as a biocontrol of salmon farming eutrophication Aquaculture 171 65–81 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00420-7
Sokal, R. R. & F. J. Rolf, 1995. Biometry. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York
S. Thode Andersen B. B. Jørgensen (1989) ArticleTitleSulfate reduction and formation of 35S-labelled FeS, FeS2 and So in coastal marine sediments Limnology and Oceanography 34 793–806
J. M. Tiedj (1987) Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium A. J. B. Zehender (Eds) Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms Wiley New York 179–244
Valderrama, J. C., 1977. Methods used by the Hydrographic Department of National Board of Fisheries, Sweden. In Grasshof, K. (ed.), Report of the Baltic Intercalibraton Workshop. Annex, Interim Commission for the Protection of the Environment of the Baltic Sea: 13–40
P. Viaroli R. Azzoni M. Bartoli G. Giordani L. Tajé (2001) Evolution of the trophic conditions and dystrophic outbreaks in the Sacca di Goro lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea) F. M. Faranda L. Guglielmo G. Spezie (Eds) Structure and Processes in the Mediterranean Ecosystems Springer Verlag Italia Milano 443–451
D. T. Welsh G. Castadelli (2004) ArticleTitleBacterial nitrification activity directly associated with isolated benthic marine animals Marine Biology 144 1029–1037 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00227-003-1252-z
D. T. Welsh G. Castadelli M. Bartoli D. Poli R. Wit Particlede M. Careri P. Viaroli (2001) ArticleTitleDenitrification in an intertidal seagrass meadow, a comparison of 15N-isotope and acetylene block techniques; Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium as a source of N2O Marine Biology 139 1029–1036 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002270100672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nizzoli, D., Welsh, D.T., Bartoli, M. et al. Impacts of mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) farming on oxygen consumption and nutrient recycling in a eutrophic coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 550, 183–198 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4378-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4378-9