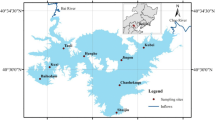
Abstract
Since a few decades, Lake Taihu, one of the largest fresh water lakes in China, has suffered from eutrophication problems, with total P and N level values up to 0.15 mg P/l and 2.5 mg N/l. To show the evident role of P sediment–water exchange in the lake, annual P budgets of Lake Taihu were set up for the period 1998–2000. Reliable water budgets could be derived as a basis for the subsequent P mass budgets. For the latter, the P accumulation rates by the sediment, as a ‘fitting term’ of the P mass budgets, were found to be between 1000 and 1060 × 103 kg P/yr (= 1.2 mg P/m2 day). This P accumulation amounts to around 65% of the total P inputs into the lake; it represents both physico–chemical processes (adsorption/precipitation, etc.) as well as physical sedimentation of particulate matter. No significant seasonal trends in the P sediment–water exchange were observed here. The particulate P profiles in the upper sediment layers of the lake indicate that, especially for the relatively-polluted north-western sub-lakes, the sediment P uptake capacity has now gradually been depleted. Restoration measures, such as sediment dredging in the NW sub-lakes, will be necessary to improve the Lake Taihu water quality in the coming years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Berner (1980) Early Diagenesis Princeton University Press Princeton 241
P.C.M. Boers O. Hese (1988) ArticleTitlePhosphorus release from the peaty sediments of the Loosdrecht Lakes (The Netherlands) Journal for Geographical Review. 22 355–363 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXitV2ktb0%3D
W. Calmano P. Roeters T. Vellinga (1998) ArticleTitleContaminated sediments Water Science and Technology. 37 IssueID6–7 453
T.H.L. Claassen (1979) ArticleTitleGlobale fosfaatbalans van Frieslands boezem (Overall phosphorus balance of the polder waters in the province of Friesland) (in Dutch) H2O 12 6–10
D.G. Cooke E.B. Welch S.A. Peterson P.N. Newroth (1993) Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs EditionNumber2 Lewis publishers Boca Raton 548
P.J. Dillon H.E. Evans (1993) ArticleTitleA comparison of phosphorus retention in lakes determined from mass balance and sediment core calculations Water Research 27 659–668 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXisVShurg%3D
S.L. Dingman (2002) Physical Hydrology Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River
A.D. Eaton L.S. Clesceri A.E. Greenberg (Eds) (1995) Standards Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater APHA Washington
B. Gumbo H.S.A. Savenije P. Kelderman (2003) The Phosphorus Calculator: A Planning Tool for Closing Nutrient Cycles in Urban Eco-systems Proceedings ECOSAN Conference Lübeck Germany 741–748
L. Håkanson M. Jansson (1983) Principles of Lake Sedimentology Springer-Verlag. Berlin 316
P. Kelderman (1980) ArticleTitlePhosphate budget and sediment-water exchange in Lake Grevelingen (SW Netherlands) Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 14 229–238 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXkvVGqtLo%3D
P. Kelderman (1984) ArticleTitleSediment-water exchange in Lake Grevelingen under different environmental conditions Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 18 286–311 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhtVWruw%3D%3D
P. Kelderman W.M.E. Drossaert Min Zhang L.C. Okonkwo I.A. Clarisse (2000) ArticleTitlePollution assessment of the canal sediments in Delft (The Netherlands) Water Research 34 936–944 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXntVKhtA%3D%3D
C.P. Mainstone K. Schofield (1996) ArticleTitleAgricultural management for nonpoint pollution control, with particular reference to the UK European Water Pollution Control 6 21–30 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXptF2qsQ%3D%3D
R.G. Perkins G.J.C. Underwood (2001) ArticleTitleThe potential for phosphorus release across the sediment-water interface in an eutrophic reservoir dosed with ferric sulphate Water Research 35 1399–1406 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXhs1Sqtro%3D Occurrence Handle11317886
P.B. Roeters (1998) ArticleTitleLarge scale treatment of contaminated sediments in The Netherlands, the feasibility study Water Science and Technology 37 IssueID6–7 291–298 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktFemtro%3D
V. Ruban P. Pardo G. Rauret H. Muntau P. Quevauviller (2001) ArticleTitleSelection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment Journal for Environmental Monitoring 1 51–56
H. Sas (1989) Lake Restoration by Reduction of Nutrient Loading Academia Verlag Richarz Sankt Augustin 497
M. Søndergaard J.P. Jensen E. Jeppesen (1999) ArticleTitleInternal phosphorus loading in shallow Danish lakes Hydrobiologia 408 IssueID409 145–152
W.M. Stigliani P.R. Jaffé S. Anderberg (1993) ArticleTitleHeavy metal pollution in the Rhine basin Environmental Science and Technology 27 787–793
InstitutionalAuthorNameTBA (2000) Atlas of Ecology and Environment of the Taihu Lake TBA Shanghai
Zhu Wei. (2002). Phosphorus exchange between sediment and overlying water in Lake Taihu (China P.R.). UNESCO-IHE MSc thesis WERM 02–19, 77 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelderman, P., Wei, Z. & Maessen, M. Water and mass budgets for estimating phosphorus sediment–water exchange in Lake Taihu (China P. R.). Hydrobiologia 544, 167–175 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0542-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0542-5