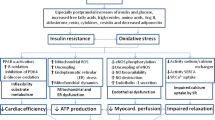
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome, associated with high rates of mortality, hospitalization, and impairment of quality of life. Obesity and type 2 diabetes are major cardiometabolic drivers, represented as distinct stages of adiposity- and dysglycemia-based chronic disease (ABCD, DBCD), respectively, and leading to cardiometabolic-based chronic disease (CMBCD). This review focuses on one aspect of the CMBCD model: how ABCD and DBCD influence genesis and progression of HF phenotypes. Specifically, the relationships of ABCD and DBCD stages with structural and functional heart disease, HF risk, and outcomes in overt HF are detailed. Also, evidence-based lifestyle, pharmacological, and procedural interventions that promote or reverse cardiac remodeling and outcomes in individuals at risk or with HF are discussed. In summary, driver-based chronic disease models for individuals at risk or with HF can expose prevention targets for more comprehensive interventions to improve clinical outcomes. Future randomized trials that investigate structured lifestyle, pharmacological, and procedural therapies specifically tailored for the CMBCD model are needed to develop personalized care plans to decrease HF susceptibility and improve outcomes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M et al (2021) 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 42(36):3599–3726
Aune D, Sen A, Norat T, Janszky I, Romundstad P, Tonstad S et al (2016) Body mass index, abdominal fatness, and heart failure incidence and mortality: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circulation 133(7):639–649
Ohkuma T, Komorita Y, Peters SAE, Woodward M (2019) Diabetes as a risk factor for heart failure in women and men: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 cohorts including 12 million individuals. Diabetologia 62(9):1550–1560
Hruby A, Hu FB (2015) The epidemiology of obesity: a big picture. Pharmacoeconomics 33(7):673–689
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N et al (2019) Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157:107843
Mechanick JI, Hurley DL, Garvey WT (2017) Adiposity-based chronic disease as a new diagnostic term: the american association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology position statement. Endocr Pract 23(3):372–378
Mechanick JI, Garber AJ, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Garvey WT (2018) Dysglycemia-based chronic disease: an american association of clinical endocrinologists position statement. Endocr Pract 24(11):995–1011
Mechanick JI, Farkouh ME, Newman JD, Garvey WT (2020) Cardiometabolic-based chronic disease, addressing knowledge and clinical practice gaps: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol 75(5):539–555
Mechanick JI, Farkouh ME, Newman JD, Garvey WT (2020) Cardiometabolic-based chronic disease, adiposity and dysglycemia drivers. J Am Coll Cardiol 75(5):525–538
Opio J, Croker E, Odongo GS, Attia J, Wynne K, McEvoy M (2020) Metabolically healthy overweight/obesity are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease in adults, even in the absence of metabolic risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Obes Rev 21(12):e13127
Khan SS, Shah SJ, Colangelo LA, Panjwani A, Liu K, Lewis CE et al (2018) Association of patterns of change in adiposity with diastolic function and systolic myocardial mechanics from early adulthood to middle age: the coronary artery risk development in young adults study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 31(12):1261-1269.e8
Reis JP, Allen N, Gibbs BB, Gidding SS, Lee JM, Lewis CE et al (2014) Association of the degree of adiposity and duration of obesity with measures of cardiac structure and function: the CARDIA study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 22(11):2434–2440
Selvaraj S, Martinez EE, Aguilar FG, Kim K-YA, Peng J, Sha J et al (2016) Association of central adiposity with adverse cardiac mechanics: findings from the hypertension genetic epidemiology network study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 9(6):e004396
Fontes-Carvalho R, Gonçalves A, Severo M, Lourenço P, Rocha Gonçalves F, Bettencourt P et al (2015) Direct, inflammation-mediated and blood-pressure-mediated effects of total and abdominal adiposity on diastolic function: EPIPorto study. Int J Cardiol 15(191):64–70
Levitan EB, Yang AZ, Wolk A, Mittleman MA (2009) Adiposity and incidence of heart failure hospitalization and mortality: a population-based prospective study. Circ Heart Fail 2(3):202–208
Reis JP, Allen N, Gunderson EP, Lee JM, Lewis CE, Loria CM et al (2015) Excess body mass index- and waist circumference-years and incident cardiovascular disease: the CARDIA study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 23(4):879–885
Iacobellis G (2015) Local and systemic effects of the multifaceted epicardial adipose tissue depot. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11(6):363–371
Koepp KE, Obokata M, Reddy YNV, Olson TP, Borlaug BA (2020) Hemodynamic and functional impact of epicardial adipose tissue in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail 8(8):657–666
Oikonomou EK, Antoniades C (2019) The role of adipose tissue in cardiovascular health and disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 16(2):83–99
Elsenberg E, McElhinney PA, Commandeur F, Chen X, Cadet S, Goeller M et al (2020) Deep learning-based quantification of epicardial adipose tissue volume and attenuation predicts major adverse cardiovascular events in asymptomatic subjects. circulation cardiovascular imaging [Internet]. [cited 2021 Sep 19];13(2). Available from: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih.ez24.periodicos.capes.gov.br/32063057/
Iacobellis G (2009) Epicardial and pericardial fat: close, but very different. Obesity (Silver Spring) 17(4):625; author reply 626–627
Kim J-S, Kim SW, Lee JS, Lee SK, Abbott R, Lee KY et al (2021) Association of pericardial adipose tissue with left ventricular structure and function: a region-specific effect?. Cardiovasc Diabetol 20(1):26
Schwenzer NF, Springer F, Schraml C, Stefan N, Machann J, Schick F (2009) Non-invasive assessment and quantification of liver steatosis by ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance. J Hepatol 51(3):433–445
Simon TG, Roelstraete B, Hagström H, Sundström J, Ludvigsson JF (2021) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and incident major adverse cardiovascular events: results from a nationwide histology cohort. Gut [Internet]. [cited 2021 Sep 19]; Available from: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih.ez24.periodicos.capes.gov.br/34489307/
Chiu LS, Pedley A, Massaro JM, Benjamin EJ, Mitchell GF, McManus DD et al (2020) The association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiac structure and function-framingham heart study. Liver international : official journal of the international association for the study of the liver [Internet]. Liver Int 40(10). Available from: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih.ez24.periodicos.capes.gov.br/32654390/
VanWagner LB, Wilcox JE, Ning H, Lewis CE, Carr JJ, Rinella ME et al (2020) Longitudinal association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with changes in myocardial structure and function: the CARDIA study. J Am Heart Assoc 9(4):e014279
Styczynski G, Kalinowski P, Michałowski Ł, Paluszkiewicz R, Ziarkiewicz-Wróblewska B, Zieniewicz K et al (2021) Cardiac morphology, function, and hemodynamics in patients with morbid obesity and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Am Heart Assoc 10(8):e017371
Lee Y, Kim KJ, eun Yoo M, Kim G, Yoon H, Jo K et al (2018) Association of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with subclinical myocardial dysfunction in non-cirrhotic patients. J Hepatol 68(4):764–772
Simon TG, Bamira DG, Chung RT, Weiner RB, Corey KE (2017) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is associated with cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. Obesity (Silver Spring) 25(8):1313–1316
Haykowsky MJ, Kouba EJ, Brubaker PH, Nicklas BJ, Eggebeen J, Kitzman DW (2014) Skeletal muscle composition and its relation to exercise intolerance in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Am J Cardiol 113(7):1211–1216
Kitzman DW, Nicklas B, Kraus WE, Lyles MF, Eggebeen J, Morgan TM et al (2014) Skeletal muscle abnormalities and exercise intolerance in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 306(9):H1364-1370
Molina AJA, Bharadwaj MS, Van Horn C, Nicklas BJ, Lyles MF, Eggebeen J et al (2016) Skeletal muscle mitochondrial content, oxidative capacity, and Mfn2 expression are reduced in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction and are related to exercise intolerance. JACC Heart Fail 4(8):636–645
Haykowsky MJ, Brubaker PH, John JM, Stewart KP, Morgan TM, Kitzman DW (2011) Determinants of exercise intolerance in elderly heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction. J Am Coll Cardiol 58(3):265–274
Costa RM, Neves KB, Tostes RC, Lobato NS (2018) Perivascular adipose tissue as a relevant fat depot for cardiovascular risk in obesity. Front Physiol 9:253
Chait A, den Hartigh LJ (2020) Adipose tissue distribution, inflammation and its metabolic consequences, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 25(7):22
Sebo ZL, Rendina-Ruedy E, Ables GP, Lindskog DM, Rodeheffer MS, Fazeli PK et al (2019) Bone marrow adiposity: basic and clinical implications. Endocr Rev 40(5):1187–1206
Singh RG, Yoon HD, Wu LM, Lu J, Plank LD, Petrov MS (2017) Ectopic fat accumulation in the pancreas and its clinical relevance: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Metabolism 69:1–13
D’Marco L, Puchades MJ, Panizo N, Romero-Parra M, Gandía L, Giménez-Civera E et al (2021) Cardiorenal fat: a cardiovascular risk factor with implications in chronic kidney disease. Front Med 8:733
Ha EE, Bauer RC (2018) Emerging roles for adipose tissue in cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 38(8):e137–e144
Narumi T, Watanabe T, Kadowaki S, Kinoshita D, Yokoyama M, Honda Y et al (2014) Impact of serum omentin-1 levels on cardiac prognosis in patients with heart failure. Cardiovasc Diabetol 23(13):84
Anthony SR, Guarnieri AR, Gozdiff A, Helsley RN, Phillip Owens A, Tranter M (2019) Mechanisms linking adipose tissue inflammation to cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Clin Sci (Lond) 133(22):2329–2344
Garvey WT, Mechanick JI (2020) Proposal for a scientifically-correct and medically-actionable disease classification system (ICD) for obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 28(3):484–492
Elagizi A, Carbone S, Lavie CJ, Mehra MR, Ventura HO (2020) Implications of obesity across the heart failure continuum. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 63(5):561–569
Karason K, Jamaly S (2020) Heart failure development in obesity: mechanistic pathways. Eur Heart J 41(36):3485
Bozkurt B, Coats AJ, Tsutsui H, Abdelhamid M, Adamopoulos S, Albert N et al (2021) Universal definition and classification of heart failure: a report of the heart failure society of america, heart failure association of the european society of cardiology, japanese heart failure society and writing committee of the universal definition of heart failure. J Card Fail S1071–9164(21):00050–00056
Carbone S, Lavie CJ, Elagizi A, Arena R, Ventura HO (2020) The impact of obesity in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin 16(1):71–80
Sharma A, Lavie CJ, Borer JS, Vallakati A, Goel S, Lopez-Jimenez F et al (2015) Meta-analysis of the relation of body mass index to all-cause and cardiovascular mortality and hospitalization in patients with chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 115(10):1428–1434
Clark AL, Fonarow GC, Horwich TB (2011) Waist circumference, body mass index, and survival in systolic heart failure: the obesity paradox revisited. J Card Fail 17(5):374–380
Streng KW, Voors AA, Hillege HL, Anker SD, Cleland JG, Dickstein K et al (2018) Waist-to-hip ratio and mortality in heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 20(9):1269–1277
Gao F, Wan J, Xu B, Wang X, Lin X, Wang P (2020) Trajectories of waist-to-hip ratio and adverse outcomes in heart failure with mid-range ejection fraction. Obes Facts 13(3):344–357
Tsujimoto T, Kajio H (2017) Abdominal obesity is associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality in patients with HFpEF. J Am Coll Cardiol 70(22):2739–2749
Mechanick JI (2013) “What if” being overweight was good for you?. Endocr Pract 19(1):166–168
Nagarajan V, Cauthen CA, Starling RC, Tang WHW (2013) Prognosis of morbid obesity patients with advanced heart failure. Congest Heart Fail 19(4):160–164
Myers J, Kokkinos P, Chan K, Dandekar E, Yilmaz B, Nagare A et al (2017) Cardiorespiratory fitness and reclassification of risk for incidence of heart failure: the veterans exercise testing study. Circ Heart Fail 6:e003780
Kokkinos P, Faselis C, Franklin B, Lavie CJ, Sidossis L, Moore H et al (2019) Cardiorespiratory fitness, body mass index and heart failure incidence. Eur J Heart Fail 21(4):436–444
Shah RV, Abbasi SA, Heydari B, Rickers C, Jacobs DR, Wang L et al (2013) Insulin resistance, subclinical left ventricular remodeling, and the obesity paradox: MESA (multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis). J Am Coll Cardiol 61(16):1698–1706
Fontes-Carvalho R, Ladeiras-Lopes R, Bettencourt P, Leite-Moreira A, Azevedo A (2015) Diastolic dysfunction in the diabetic continuum: association with insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13(14):4
Banerjee D, Biggs ML, Mercer L, Mukamal K, Kaplan R, Barzilay J et al (2013) Insulin resistance and risk of incident heart failure: cardiovascular health study. Circ Heart Fail 6(3):364–370
Vardeny O, Gupta DK, Claggett B, Burke S, Shah A, Loehr L et al (2013) Insulin resistance and incident heart failure the ARIC study (atherosclerosis risk in communities). JACC Heart Fail 1(6):531–536
Rooney MR, Rawlings AM, Pankow JS, Echouffo Tcheugui JB, Coresh J, Sharrett AR et al (2021) Risk of progression to diabetes among older adults with prediabetes. JAMA Intern Med 181(4):511–519
Michel A, Mando R, Waheed MA-A, Halalau A, Karabon P (2021) Prediabetes associated with an increase in major adverse cardiovascular events. J Am Coll Cardiol 77(18_Supplement_2):14–14
Cai X, Liu X, Sun L, He Y, Zheng S, Zhang Y et al (2021) Prediabetes and the risk of heart failure: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 23(8):1746–1753
Milwidsky A, Maor E, Kivity S, Berkovitch A, Zekry SB, Tenenbaum A et al (2015) Impaired fasting glucose and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in middle-age adults: a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 2971 subjects. Cardiovasc Diabetol 14(1):119
Fox ER, Sarpong DF, Cook JC, Samdarshi TE, Nagarajarao HS, Liebson PR et al (2011) The relation of diabetes, impaired fasting blood glucose, and insulin resistance to left ventricular structure and function in african americans. Diabetes Care 34(2):507–509
Stahrenberg R, Edelmann F, Mende M, Kockskämper A, Düngen HD, Scherer M et al (2010) Association of glucose metabolism with diastolic function along the diabetic continuum. Diabetologia 53(7):1331–1340
Mai L, Wen W, Qiu M, Liu X, Sun L, Zheng H et al (2021) Association between prediabetes and adverse outcomes in heart failure. Diabetes Obes Metab
Kodama S, Fujihara K, Horikawa C, Sato T, Iwanaga M, Yamada T et al (2020) Diabetes mellitus and risk of new-onset and recurrent heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ESC Heart Fail 7(5):2146–2174
Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Zhang S, Florido R, Hamo C, Pankow JS, Michos ED et al (2021) Duration of diabetes and incident heart failure: the ARIC (atherosclerosis risk in communities) study. JACC Heart Fail 9(8):594–603
Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C, Salomon C, Zuñiga FA (2018) Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17(1):122
Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE, Kaye D (2018) Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(3):339–351
Dunlay SM, Givertz MM, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Chan M, Desai AS et al (2019) Type 2 diabetes mellitus and heart failure: a scientific statement from the american heart association and the heart failure society of america: this statement does not represent an update of the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA heart failure guideline update. Circulation 140(7):e294-324
Roos CJ, Scholte AJ, Kharagjitsingh AV, Bax JJ, Delgado V (2014) Changes in multidirectional LV strain in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 2-year follow-up study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15(1):41–47
Dauriz M, Mantovani A, Bonapace S, Verlato G, Zoppini G, Bonora E et al (2017) Prognostic impact of diabetes on long-term survival outcomes in patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 40(11):1597–1605
Florea VG, Cohn JN (2014) The autonomic nervous system and heart failure. Circ Res 114(11):1815–1826
Vinik AI, Ziegler D (2007) Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation 115(3):387–397
Mancia G, Grassi G (2014) The autonomic nervous system and hypertension. Circ Res 114(11):1804–1814
Piccirillo G, Germanò G, Vitarelli A, Ragazzo M, di Carlo S, De Laurentis T et al (2006) Autonomic cardiovascular control and diastolic dysfunction in hypertensive subjects. Int J Cardiol 110(2):160–166
Grassi G, Seravalle G, Quarti-Trevano F, Dell’Oro R, Arenare F, Spaziani D et al (2009) Sympathetic and baroreflex cardiovascular control in hypertension-related left ventricular dysfunction. Hypertension 53(2):205–209
Babick A, Elimban V, Zieroth S, Dhalla NS (2013) Reversal of cardiac dysfunction and subcellular alterations by metoprolol in heart failure due to myocardial infarction. J Cell Physiol 228(10):2063–2070
Colucci WS (1998) The effects of norepinephrine on myocardial biology: implications for the therapy of heart failure. Clin Cardiol 21(12 Suppl 1):I20-24
Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, Buroker AB, Goldberger ZD, Hahn EJ et al (2019) 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the american college of cardiology/american heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 140(11):e596-646
Bays HE, Taub PR, Epstein E, Michos ED, Ferraro RA, Bailey AL et al (2021) Ten things to know about ten cardiovascular disease risk factors. Am J Prev Cardiol: 100149
Khan MS, Khan F, Fonarow GC, Sreenivasan J, Greene SJ, Khan SU et al (2021) Dietary interventions and nutritional supplements for heart failure: a systematic appraisal and evidence map. Eur J Heart Fail [Internet]. [cited 2021 Sep 13];n/a(n/a). Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ejhf.2278
Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, Butler J, Yancy CW, Fonarow GC (2015) Association of physical activity or fitness with incident heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Circ Heart Fail 8(5):853–861
Garvey WT, Mechanick JI, Brett EM, Garber AJ, Hurley DL, Jastreboff AM et al (2016) American association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology comprehensive clinical practice guidelines for medical care of patients with obesity. Endocr Pract 22(Suppl 3):1–203
Feldman AL, Griffin SJ, Ahern AL, Long GH, Weinehall L, Fhärm E et al (2017) Impact of weight maintenance and loss on diabetes risk and burden: a population-based study in 33,184 participants. BMC Public Health 17(1):170
Pandey A, Patel KV, Bahnson JL, Gaussoin SA, Martin CK, Balasubramanyam A et al (2020) Association of intensive lifestyle intervention, fitness, and body mass index with risk of heart failure in overweight or obese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 141(16):1295–1306
MacMahon SW, Wilcken DE, Macdonald GJ (1986) The effect of weight reduction on left ventricular mass. A randomized controlled trial in young, overweight hypertensive patients. N Engl J Med 314(6):334–339
Katzmarzyk PT, Martin CK, Newton RL, Apolzan JW, Arnold CL, Davis TC et al (2020) Weight loss in underserved patients - a cluster-randomized trial. N Engl J Med 383(10):909–918
Kane JA, Mehmood T, Munir I, Kamran H, Kariyanna PT, Zhyvotovska A et al (2019) Cardiovascular risk reduction associated with pharmacological weight loss: a meta-analysis. Int J Clin Res Trials 4(1):131
Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S, Davies M, Van Gaal LF, Lingvay I et al (2021) Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med 384(11):989
Mechanick JI, Apovian C, Brethauer S, Garvey WT, Joffe AM, Kim J et al (2019) Clinical practice guidelines for the perioperative nutrition, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of patients undergoing bariatric procedures - 2019 update: cosponsored by american association of clinical endocrinologists/american college of endocrinology, the obesity society, american society for metabolic & bariatric surgery, obesity medicine association, and american society of anesthesiologists - executive summary. Endocr Pract 25(12):1346–1359
Moussa O, Ardissino M, Heaton T, Tang A, Khan O, Ziprin P et al (2020) Effect of bariatric surgery on long-term cardiovascular outcomes: a nationwide nested cohort study. Eur Heart J 41(28):2660–2667
Garber AJ, Handelsman Y, Grunberger G, Einhorn D, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI et al (2020) Consensus statement by the american association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm – 2020 executive summary. Endocr Pract 26(1):107–139
Castagno D, Baird-Gunning J, Jhund PS, Biondi-Zoccai G, MacDonald MR, Petrie MC et al (2011) Intensive glycemic control has no impact on the risk of heart failure in type 2 diabetic patients: evidence from a 37,229 patient meta-analysis. Am Heart J 162(5):938-948.e2
Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, Bailey CJ, Ceriello A, Delgado V et al (2020) 2019 ESC guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J 41(2):255–323
McGuire DK, Shih WJ, Cosentino F, Charbonnel B, Cherney DZI, Dagogo-Jack S et al (2021) Association of SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA Cardiol 6(2):148–158
Kristensen SL, Rørth R, Jhund PS, Docherty KF, Sattar N, Preiss D et al (2019) Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 7(10):776–785
Zhang D-P, Xu L, Wang L-F, Wang H-J, Jiang F (2020) Effects of antidiabetic drugs on left ventricular function/dysfunction: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol 19(1):10
Haykowsky MJ, Liang Y, Pechter D, Jones LW, McAlister FA, Clark AM (2007) A meta-analysis of the effect of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling in heart failure patients: the benefit depends on the type of training performed. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(24):2329–2336
Kitzman DW, Brubaker P, Morgan T, Haykowsky M, Hundley G, Kraus WE et al (2016) Effect of caloric restriction or aerobic exercise training on peak oxygen consumption and quality of life in obese older patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 315(1):36–46
Taylor RS, Long L, Mordi IR, Madsen MT, Davies EJ, Dalal H et al (2019) Exercise-based rehabilitation for heart failure: cochrane systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis. JACC Heart Fail 7(8):691–705
Mahajan R, Stokes M, Elliott A, Munawar DA, Khokhar KB, Thiyagarajah A et al (2020) Complex interaction of obesity, intentional weight loss and heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart 106(1):58–68
Doumouras AG, Wong JA, Paterson JM, Lee Y, Sivapathasundaram B, Tarride J-E et al (2021) Bariatric surgery and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with obesity and cardiovascular disease: a population-based retrospective cohort study. Circulation 143(15):1468–1480
daSilva-deAbreu A, Alhafez BA, Curbelo-Pena Y, Lavie CJ, Ventura HO, Loro-Ferrer JF et al (2021) Bariatric surgery in patients with obesity and ventricular assist devices considered for heart transplantation: systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. J Card Fail 27(3):338–348
Zannad F, Ferreira JP, Pocock SJ, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G et al (2020) SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a meta-analysis of the EMPEROR-reduced and DAPA-HF trials. Lancet 396(10254):819–829
Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M et al (2021) Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 385(16):1451–1461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Mechanick has received honoraria for lectures and program development from Abbott Nutrition. Drs. Eduardo Correia, Letícia Barbetta, Antonio Jorge, and Evandro Mesquita have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira Correia, E.T., Mechanick, J.I., dos Santos Barbetta, L.M. et al. Cardiometabolic-based chronic disease: adiposity and dysglycemia drivers of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 28, 47–61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-022-10233-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-022-10233-x