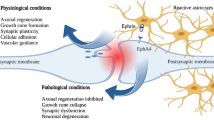
Abstract
Nogo-A protein consists of two main extracellular domains: Nogo-66 (rat amino acid [aa] 1019–1083) and Nogo-A-Δ20 (extracellular, active 180 amino acid Nogo-A region), which serve as strong inhibitors of axon regeneration in the adult CNS (Central Nervous System). Although receptors S1PR2 and HSPGs have been identified as Nogo-A-Δ20 binding proteins, it remains at present elusive whether other receptors directly interacting with Nogo-A-Δ20 exist, and decrease cell death. On the other hand, the key roles of EphA4 in the regulation of glioblastoma, axon regeneration and NSCs (Neural Stem Cells) proliferation or differentiation are well understood, but little is known the relationship between EphA4 and Nogo-A-Δ20 in NSCs apoptosis. Thus, we aim to determine whether Nogo-A-Δ20 can bind to EphA4 and affect survival of NSCs. Here, we discover that EphA4, belonging to a member of erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular (Eph) receptors family, could be acting as a high affinity ligand for Nogo-A-Δ20. Trans-membrane protein of EphA4 is needed for Nogo-A-Δ20-triggered inhibition of NSCs apoptosis, which are mediated by balancing p38 inactivation and JNK MAPK pathway activation. Finally, we predict at the atomic level that essential residues Lys-205, Ile-190, Pro-194 in Nogo-A-Δ20 and EphA4 residues Gln-390, Asn-425, Pro-426 might play critical roles in Nogo-A-Δ20/EphA4 binding via molecular docking.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- NSCs:
-
Neural stem cells
- DHC:
-
Dehydrocorydaline chloride
- SP:
-
SP600125
- Rhy:
-
Rhynchophylline
- GADPH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- SCI:
-
Control group: Con. spinal cord injury
References
Ahmed AI, Shtaya AB, Zaben MJ, Owens EV, Kiecker C, Gray WP (2012) Endogenous GFAP-positive neural stem/progenitor cells in the postnatal mouse cortex are activated following traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 29(5):828–842. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.1923
Antrobus R, Borner GH (2011) Improved elution conditions for native co-immunoprecipitation. PLoS ONE 6(3):e18218. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018218
Aoki M, Yamashita T, Tohyama M (2004) EphA receptors direct the differentiation of mammalian neural precursor cells through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 279(31):32643–32650
Bartlow P, Uechi GT, Cardamone JJ Jr, Sultana T, Fruchtl M, Beitle RR, Ataai MM (2011) Identification of native Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) proteins that bind to immobilized metal affinity chromatography under high imidazole conditions and use of 2D-DIGE to evaluate contamination pools with respect to recombinant protein expression level. Protein Expr Purif 78(2):216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2011.04.021
Bowden TA, Aricescu AR, Nettleship JE, Siebold C, Rahman-Huq N, Owens RJ, Stuart DI, Jones EY (2009) Structural plasticity of eph receptor A4 facilitates cross-class ephrin signaling. Structure 17(10):1386–1397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2009.07.018
Chang L, Karin M (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410(6824):37–40
Chong ZS, Ohnishi S, Yusa K, Wright GJ (2018) Pooled extracellular receptor-ligand interaction screening using CRISPR activation. Genome Biol 19(1):205. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-018-1581-3
Colell A, Green DR, Ricci JE (2009) Novel roles for GAPDH in cell death and carcinogenesis. Cell Death Differ 16(12):1573–1581. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.137
Darling TK, Lamb TJ (2019) Emerging roles for Eph receptors and Ephrin ligands in immunity. Front Immunol 10:1473. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01473
Depaepe V, Suarez-Gonzalez N, Dufour A, Passante L, Gorski JA, Jones KR, Ledent C, Vanderhaeghen P (2005) Ephrin signalling controls brain size by regulating apoptosis of neural progenitors. Nature 435(7046):1244–1250
Deschesnes RG, Huot J, Valerie K, Landry J (2001) Involvement of p38 in apoptosis-associated membrane blebbing and nuclear condensation. Mol Biol Cell 12(6):1569–1582
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP (2008) JNK signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene 27(48):6245–6251. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.301
Dhanasekaran DN, Reddy EP (2017) JNK-signaling: A multiplexing hub in programmed cell death. Genes Cancer 8(9–10):682–694. https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.155
Fu AKY, Hung K-W, Huang H, Gu S, Shen Y, Cheng EYL, Ip FCF, Huang X, Fu W-Y, Ip NY (2014) Blockade of EphA4 signaling ameliorates hippocampal synaptic dysfunctions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(27):9959–9964. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405803111
Fukai J, Yokote H, Yamanaka R, Arao T, Nishio K, Itakura T (2008) EphA4 promotes cell proliferation and migration through a novel EphA4-FGFR1 signaling pathway in the human glioma U251 cell line. Mol Cancer Ther 7(9):2768–2778. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2263
Furne C, Ricard J, Cabrera JR, Pays L, Bethea JR, Mehlen P, Liebl DJ (2009) EphrinB3 is an anti-apoptotic ligand that inhibits the dependence receptor functions of EphA4 receptors during adult neurogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793(2):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.09.009
Goldshmit Y, Galea MP, Wise G, Bartlett PF, Turnley AM (2004) Axonal regeneration and lack of astrocytic gliosis in EphA4-deficient mice. J Neurosci 24(45):10064–10073
Goldshmit Y, McLenachan S, Turnley A (2006) Roles of Eph receptors and ephrins in the normal and damaged adult CNS. Brain Res Rev 52(2):327–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.04.006
Gu S, Fu W-Y, Fu AKY, Tong EPS, Ip FCF, Huang X, Ip NY (2018) Identification of new EphA4 inhibitors by virtual screening of FDA-approved drugs. Sci Rep 8(1):7377. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25790-1
Gururajan M, Chui R, Karuppannan AK, Ke J, Jennings CD, Bondada S (2005) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is required for survival and proliferation of B-lymphoma cells. Blood 106(4):1382–1391
Hara Y, Nomura T, Yoshizaki K, Frisén J, Osumi N (2010) Impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and vascular formation in ephrin-A5-deficient mice. Stem Cells 28(5):974–983. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.427
Huang TY, Zhao Y, Jiang L-L, Li X, Liu Y, Sun Y, Piña-Crespo JC, Zhu B, Masliah E, Willnow TE, Pasquale EB, Xu H (2017) SORLA attenuates EphA4 signaling and amyloid β-induced neurodegeneration. J Exp Med 214(12):3669–3685. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20171413
Huebner EA, Kim BG, Duffy PJ, Brown RH, Strittmatter SM (2011) A multi-domain fragment of Nogo-A protein is a potent inhibitor of cortical axon regeneration via Nogo receptor 1. J Biol Chem 286(20):18026–18036. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.208108
Ishitani R, Sunaga K, Hirano A, Saunders P, Katsube N, Chuang DM (1996) Evidence that glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is involved in age-induced apoptosis in mature cerebellar neurons in culture. J Neurochem 66(3):928–935
Ishitani R, Tajima H, Takata H, Tsuchiya K, Kuwae T, Yamada M, Takahashi H, Tatton NA, Katsube N (2003) Proapoptotic protein glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: a possible site of action of antiapoptotic drugs. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27(2):291–301
Joly S, Jordi N, Schwab ME, Pernet V (2014) The Ephrin receptor EphA4 restricts axonal sprouting and enhances branching in the injured mouse optic nerve. Eur J Neurosci 40(7):3021–3031. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12677
Kay BK, Williamson MP, Sudol M (2000) The importance of being proline: the interaction of proline-rich motifs in signaling proteins with their cognate domains. FASEB J 14(2):231–241
Kempf A, Boda E, Kwok JCF, Fritz R, Grande V, Kaelin AM, Ristic Z, Schmandke A, Schmandke A, Tews B (2017) Control of cell shape, neurite outgrowth, and migration by a Nogo-A/HSPG interaction. Dev Cell 43(1):24–34
Kempf A, Tews B, Arzt ME, Weinmann O, Schwab ME (2014) The sphingolipid receptor S1PR2 is a receptor for Nogo-A repressing synaptic plasticity. PLoS Biol 12(1):e1001763
Khodosevich K, Watanabe Y, Monyer H (2011) EphA4 preserves postnatal and adult neural stem cells in an undifferentiated state in vivo. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 8):1268–1279. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.076059
Kwon H, Young PG, Squire CJ, Baker EN (2017) Engineering a Lys-Asn isopeptide bond into an immunoglobulin-like protein domain enhances its stability. Sci Rep 7(1):42753. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42753
Lamberto I, Lechtenberg BC, Olson EJ, Mace PD, Dawson PE, Riedl SJ, Pasquale EB (2014) Development and structural analysis of a nanomolar cyclic peptide antagonist for the EphA4 receptor. ACS Chem Biol 9(12):2787–2795. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb500677x
Liebscher T, Schnell L, Schnell D, Scholl J, Schneider R, Gullo M, Fouad K, Mir A, Rausch M, Kindler D, Hamers FP, Schwab ME (2005) Nogo-A antibody improves regeneration and locomotion of spinal cord-injured rats. Ann Neurol 58(5):706–719. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.20627
Lisabeth EM, Falivelli G, Pasquale EB (2013) Eph receptor signaling and ephrins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009159
Liu B, Fang M, Lu Y, Lu Y, Mills GB, Fan Z (2001) Involvement of JNK-mediated pathway in EGF-mediated protection against paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in SiHa human cervical cancer cells. Br J Cancer 85(2):303–311
Mi YJ, Hou B, Liao QM, Ma Y, Luo Q, Dai YK, Ju G, Jin WL (2012) Amino-Nogo-A antagonizes reactive oxygen species generation and protects immature primary cortical neurons from oxidative toxicity. Cell Death Differ 19(7):1175–1186. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.206
Miao H, Wei BR, Peehl DM, Li Q, Alexandrou T, Schelling JR, Rhim JS, Sedor JR, Burnett E, Wang B (2001) Activation of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits the Ras/MAPK pathway. Nat Cell Biol 3(5):527–530
Morrison DK (2012) MAP kinase pathways. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a011254
Murai KK, Nguyen LN, Koolpe M, McLennan R, Krull CE, Pasquale EB (2003) Targeting the EphA4 receptor in the nervous system with biologically active peptides. Mol Cell Neurosci 24(4):1000–1011
Noberini R, Koolpe M, Peddibhotla S, Dahl R, Su Y, Cosford NDP, Roth GP, Pasquale EB (2008) Small molecules can selectively inhibit ephrin binding to the EphA4 and EphA2 receptors. J Biol Chem 283(43):29461–29472. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M804103200
Oertle T, van der Haar ME, Bandtlow CE, Robeva A, Burfeind P, Buss A, Huber AB, Simonen M, Schnell L, Brösamle C, Kaupmann K, Vallon R, Schwab ME (2003) Nogo-A inhibits neurite outgrowth and cell spreading with three discrete regions. J Neurosci 23(13):5393–5406
Park JM, Greten FR, Li Z-W, Karin M (2002) Macrophage apoptosis by anthrax lethal factor through p38 MAP kinase inhibition. Science 297(5589):2048–2051
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22(2):153–183
Posch A (2014) Sample preparation guidelines for two-dimensional electrophoresis. Arch Physiol Biochem 120(5):192–197. https://doi.org/10.3109/13813455.2014.955031
Ramasamy S, Yu F, Yuan HY, Srivats H, Dawe GS, Ahmed S (2014) NogoR1 and PirB signaling stimulates neural stem cell survival and proliferation. Stem Cells 32(6):1636–1648
Sarkar D, Su Z-Z, Lebedeva IV, Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Valerie K, Dent P, Fisher PB (2002) mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(15):10054–10059
Saunders PA, Chen RW, Chuang DM (1999) Nuclear translocation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase isoforms during neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 72(3):925–932
Sawa A, Khan AA, Hester LD, Snyder SH (1997) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: nuclear translocation participates in neuronal and nonneuronal cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(21):11669–11674
Schwab ME (2010) Functions of Nogo proteins and their receptors in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(12):799–811
Shu Y, Xiao B, Wu Q, Liu T, Du Y, Tang H, Chen S, Feng L, Long L, Li Y (2016) The Ephrin-A5/EphA4 interaction modulates neurogenesis and angiogenesis by the p-Akt and p-ERK pathways in a mouse model of TLE. Mol Neurobiol 53(1):561–576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9020-2
Spanevello MD, Tajouri SI, Mirciov C, Kurniawan N, Pearse MJ, Fabri LJ, Owczarek CM, Hardy MP, Bradford RA, Ramunno ML, Turnley AM, Ruitenberg MJ, Boyd AW, Bartlett PF (2013) Acute delivery of EphA4-Fc improves functional recovery after contusive spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 30(12):1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2012.2729
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang Q, He C, Pan H (2014) p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Lett 344(2):174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.11.019
Tagami S, Eguchi Y, Kinoshita M, Takeda M, Tsujimoto Y (2000) A novel protein, RTN-XS, interacts with both Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 on endoplasmic reticulum and reduces their anti-apoptotic activity. 19 (50):5736–5746
Vargas LM, Leal N, Estrada LD, González A, Serrano F, Araya K, Gysling K, Inestrosa NC, Pasquale EB, Alvarez AR (2014) EphA4 activation of c-Abl mediates synaptic loss and LTP blockade caused by amyloid-β oligomers. PLoS ONE 9
Wada T, Penninger JM Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 23 (16):2838–2849
Wada T, Penninger JM (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in apoptosis regulation. Oncogene 23(16):2838–2849
Wagner EF, Nebreda AR (2009) Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):537–549. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2694
Wang J-L, Wang J-J, Cai Z-N, Xu C-J (2018) The effect of curcumin on the differentiation, apoptosis and cell cycle of neural stem cells is mediated through inhibiting autophagy by the modulation of Atg7 and p62. Int J Mol Med 42(5):2481–2488. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3847
Wang J-L, Xu C-J (2020) Astrocytes autophagy in aging and neurodegenerative disorders. Biomed Pharmacother 122:109691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109691
Wang J-L, Zhao L, Li M-Q, Chen W-G, Xu C-J (2020) A sensitive and reversible staining of proteins on blot membranes. Anal Biochem 592:113579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113579
Wang L, Wei F-X, Cen J-S, Ping S-N, Li Z-Q, Chen N-N, Cui S-B, Wan Y, Liu S-Y (2014) Early administration of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist promotes survival of transplanted neural stem cells and axon myelination after spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.05.038
Xu C-J, Wang J-L, Jin W-L (2015) The neural stem cell microenvironment: focusing on axon guidance molecules and myelin-associated factors. J Mol Neurosci 56(4):887–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0538-1
Xu C-J, Wang J-L, Jing P, Min L (2019) Tph2 genetic ablation contributes to senile plaque load and Astrogliosis in APP/PS1 Mice. Curr Alzheimer Res 16(3):219–232. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205016666190301110110
Xu C, Zhi J, Zhao W, Zhang L, Li D (2012) Comparative analysis of the role of JNK signaling pathway in regulating cell proliferation and apoptosis of rat liver regeneration and rat acute hepatic failure. Genetika 48(8):909–917
Xu CJ, Xu L, Huang LD, Li Y, Yu PP, Hang Q, Xu XM, Lu PH (2011) Combined NgR vaccination and neural stem cell transplantation promote functional recovery after spinal cord injury in adult rats. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 37(2):135–155. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2990.2010.01117.x
Xu K, Tzvetkova-Robev D, Xu Y, Goldgur Y, Chan Y-P, Himanen JP, Nikolov DB (2013) Insights into Eph receptor tyrosine kinase activation from crystal structures of the EphA4 ectodomain and its complex with ephrin-A5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(36):14634–14639. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1311000110
Xu L, Xu C-j, Lü H-Z, Wang Y-X, Li Y, Lu P-H (2010) Long-term fate of allogeneic neural stem cells following transplantation into injured spinal cord. Stem Cell Rev Rep 6(1):121–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-009-9104-y
Xue X, Wang B, Du W, Zhang C, Song Y, Cai Y, Cen D, Wang L, Xiong Y, Jiang P, Zhu S, Zhao KN, Zhang L (2016) Generation of affibody molecules specific for HPV16 E7 recognition. Oncotarget 7(45):73995–74005. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12174
Yeung Y-G, Stanley ER (2009) A solution for stripping antibodies from polyvinylidene fluoride immunoblots for multiple reprobing. Anal Biochem 389(1):89–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2009.03.017
Yiu G, He Z (2006) Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(8):617–627
Zhang C, Wu J-M, Liao M, Wang J-L, Xu C-J (2016) The ROCK/GGTase Pathway Are Essential to the Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells Mediated by Simvastatin. J Mol Neurosci 60(4):474–485
Zhang YQ, Sarge KD (2008) Sumoylation of amyloid precursor protein negatively regulates Abeta aggregate levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374(4):673–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.07.109
Acknowledgements
SWISS-MODEL is available from https://swissmodel.expasy.org/interactive software. ZDOCK is available from http://zdock.umassmed.edu/. Additionally, we must thank Dr Wei Lin, Jin of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for giving us suggestions of experimental design and Professor Li Fang, Zhang of Wenzhou Medical University for technical assistance in protein purification.
Funding
The study was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY18H090013) and Wenzhou Municipal Science & Technology Bureau Fund (Grant No. Y20180094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-LW: Formal analysis, writing original draft. W-GC: formal analysis. C-JX: formal analysis, writing—original draft. J-JZ performed partial WB.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2021_9960_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig.S1 Overall diagram of interaction between Nogo-A-Δ20 with EphA4. Cartoon structure of α-helix represents Nogo-A-Δ20. Brown sticks indicate residues of binding sites located in EphA4 ecodomain. LBD: ephrins ligand-binding domain. Fn1 and Fn2: 2 fibronectin-type-3 domains. (TIF 3768 kb)
10735_2021_9960_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Fig.S2 EphA4 knockdown inhibits anti-apoptosis functions of Nogo-A-△20 in NSCs. (A) NSCs were transfected with ctl-small interfering RNA (sictl) and EphA4-siRNA for 48 h, EphA4 expression at the protein were decreased compared with negative control (sictl) (n = 3, t-test,**p < 0.01 vs sictl). (B) After transfection for 48 h as described in (A), Nogo-A-Δ20 was added into culture medium for another 24h, supernatants of cell lysates were collected and blotted with proapoptotic proteins antibody: cleaved-PARP and caspase 3. (n = 3, ANOVA, **p < 0.01 vs con, ##p < 0.01 vs sictl). siRNA, small interfering RNA; siEphA4, EphA4 siRNA; siCtl, scramble siRNA. Quantification by densitometric scans was presented by apoptotic-related antibody/β-actin. Data were normalized to β-actin. n=3, Mean±S.D. **P < 0.01 vs siCtl group or control group, ##P < 0.01 vs. Nogo-A-Δ20+ siCtl group. Data were normalized to that of siCtl. (TIF 1108 kb)
10735_2021_9960_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Fig.S3 Effects of DHC and SP on NSCs apoptosis in vitro. NSCs were treated with 10 μM SP (A) and 10 μM DHC (B) for 48 h, cell extracts were collected and pro-apoptotic members like caspase 8, cleaved-PARP and p53 were detected by Western blotting. Representative data of three individual samples in SP group (C-E) and DHC group (F-H) were through statistical analysis of t-test. *P < 0.05 vs control group. Data were normalized to that of Control. NS: no significant difference. (TIF 620 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, JL., Chen, WG., Zhang, JJ. et al. Nogo-A-Δ20/EphA4 interaction antagonizes apoptosis of neural stem cells by integrating p38 and JNK MAPK signaling. J Mol Histol 52, 521–537 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09960-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09960-6