Abstract
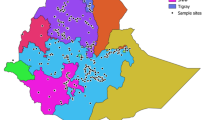
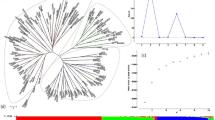
A barley core collection can be studied extensively and the derived information can be used to identify loci/genes for the genetic improvement of quantitative and qualitative traits. To assess genetic diversity, allelic variation and population structure of Egyptian barley, 134 barley genotypes collected from a different region along with 19 cultivated genotypes obtained from of the Egyptian Agricultural Research Center. All genotypes were analyzed with 261 polymorphic SSR and SNP alleles. The mean number of alleles per locus was 4 and PIC was 0.49, while the level of genetic diversity was 0.55 ranging from 0.03 to 0.82. The genotypes were assigned to three subpopulations that were consistent with their origins. The genetic variation within population was higher (51%) than among population at the molecular levels (FST = 0.491 when P < 0.10). The level of polymorphic variation was highest in subpopulations-II, due to collected from different regions with different ear-types thus, expected to contain more diversity than local genotypes in subpopulations-I and subpopulations-III. The structured study found that the 153 barley genotypes are in harmony with clustering approaches using the SSR and SNP genotypic data in a neighbor-joining tree and principal components analysis, which identified three subpopulations. These results demonstrated genetic diversity among the Egyptian barley genotypes can be applied to suggest approaches, such as association analysis, classical mapping population development, and parental line selection in breeding programs. Therefore, it is necessary to use the exotic genotypes as the genetic resources for developing new barley cultivars in Egypt.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaby RG (2015) Barley domestication: the end of a central dogma? Genome Biol 16:176. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0743-9
Anderson M, Reinbergs E (1985) “Barley breeding.” In: Rasmusson DC et al (ed) Barley. Agronomy monograph 26, American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, and Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, p 231–268
Anonymous (2008) Global strategy for the ex situ conservation and use of barley germplasm. p 1–65
Baum BR, Nevo E, Johnson DA, Beiles A (1997) Genetic diversity in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum C. Koch) in the Near East: a molecular analysis using Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 44:147–157. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008655023906
Bellucci E, Bitocchi E, Rau D, Nanni L, Ferradini N, Giardini A et al (2013) Population structure of barley landrace populations and gene-flow with modern varieties. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083891
Botstein D, White R, Skolnick M, Davis R (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Cronin JK, Bundock PC, Henry RJ, Nevo E (2007) Adaptive climatic molecular evolution in wild barley at the Isa defense locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:2773–2778. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611226104
Doebley JF, Gaut BS, Smith BD (2006) The molecular genetics of crop domestication. Cell 127:1309–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.006
Doyle JJDJLJJ, Doyle JJDJLJJ (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus (Madison) 12:13–15
Elakhdar A, Abd El-Sattar M, Amer K, Kumamaru T (2016a) Genetic diversity and association analysis among Egyptian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genotypes with different adaptations to saline conditions analyzed by SSR markers. AJCS 10:637–645. https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.2016.10.05.p7331
Elakhdar A, Abdelsattar M, Amer K, Assma R, Kumamaru T (2016b) Population structure and marker-trait association of salt tolerance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). C R Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2016.06.006
Elakhdar A, Kumamaru T, Smith K, Brueggeman R, Capo-chichi L, Solank S (2017) Genotype by environment interactions (GEIs) for barley grain yield under salt stress conditions. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 20:193–204
Ellis RP, Forster BP, Robinson D, Handley LL, Gordon DC, Russell JR et al (2000) Wild barley: a source of genes for crop improvement in the 21st century? J Exp Bot 51:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.342.9
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x
Gong X, Westcott S, Li C, Yan G, Lance R, Sun D (2009) Comparative analysis of genetic diversity between Qinghai-Tibetan wild and Chinese landrace barley. Genome 52:849–861. https://doi.org/10.1139/G09-058
Hamblin MT, Close TJ, Bhat PR, Chao S, Kling JG, Abraham KJ et al (2010) Population structure and linkage disequilibrium in U.S. barley germplasm: implications for association mapping. Crop Sci 50:556–566. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2009.04.0198
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.05.025
Hamrick JL, Godt MJW, Sherman-Broyles SL (1992) Factors influencing levels of genetic diversity in woody plant species. New For 6:95–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120641
Harlan JR, Zohary D (1966) Distribution of wild wheats and barley. Science (80-.) 153:1074–1080. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.153.3740.1074
Keilwagen J, Kilian B, Özkan H, Babben S, Perovic D, Mayer KFX et al (2014) Separating the wheat from the chaff—a strategy to utilize plant genetic resources from ex situ genebanks. Sci Rep 4:5231. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05231
Kilian B, Özkan H, Kohl J, Von Haeseler A, Barale F, Deusch O et al (2006) Haplotype structure at seven barley genes: relevance to gene pool bottlenecks, phylogeny of ear type and site of barley domestication. Mol Genet Genomics 276:230–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0136-6
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti282
Liu F, von Bothmer R, Salomon B (2000) Genetic diversity in European accessions of the Barley Core Collection as detected by isozyme electrophoresis. Genet Resour Crop Evol 47:571–581. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026532215990
Munoz-Amatriain M, Cuesta-Marcos A, Endelman JB, Comadran J, Bonman JM, Bockelman HE et al (2014) The USDA barley core collection: genetic diversity, population structure, and potential for genome-wide association studies. PLoS ONE 9:e94688. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094688
Newman RK, Newman CW (2008) Barley for food and health: science, technology, and products. In: Barley biotechnology: breeding and transgenics, Wiley, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey, p 32–55
Noaman M (2008) Barley development in Egypt. In: Proceedings of the 10th international Barley genetics symposium Alexandria Egypt, pp 3–15
Ovesná J, Kučera L, Vaculová K, Milotová J, Snape J, Wenzl P et al (2013) Analysis of the Genetic Structure of a Barley Collection Using DNA Diversity Array Technology (DArT). Plant Mol Biol Report 31: 280–288
Pakniyat H, Powell W, Baird E, Handley LL, Robinson D, Scrimgeour CM et al (1997) AFLP variation in wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum C. Koch) with reference to salt tolerance and associated ecogeography. Genome 40:332–341
Pandey M, Wagner C, Friedt W, Ordon F (2006) Genetic relatedness and population differentiation of Himalayan hulless barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) landraces inferred with SSRs. Theor Appl Genet 113:715–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0340-0
Pasam RK, Sharma R, Malosetti M, van Eeuwijk FA, Haseneyer G, Kilian B et al (2012) Genome-wide association studies for agronomical traits in a world wide spring barley collection. BMC Plant Biol 12:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-16
Pasam RK, Sharma R, Walther A, Özkan H, Graner A, Kilian B (2014) Genetic diversity and population structure in a legacy collection of spring barley landraces adapted to a wide range of climates. PLoS ONE 9:e116164. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116164
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenALEx 6.5: Genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research-an update. Bioinformatics 28:2537–2539. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts460
Poets AM, Fang Z, Clegg MT, Morrell PL (2015) Barley landraces are characterized by geographically heterogeneous genomic origins. Genome Biol 16:173. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0712-3
Pompanon F, Bonin A, Bellemain E, Taberlet P (2005) Genotyping errors: causes, consequences and solutions. Nat Rev Genet 6:846–847. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1707
Prada D (2009) Molecular population genetics and agronomic alleles in seed banks: searching for a needle in a haystack? J Exp Bot 60:2541–2552. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp130
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01758.x
Russell JR, Ellis RP, Thomas WTB, Waugh R, Provan J, Booth A et al (2000) A retrospective analysis of spring barley germplasm development from “foundation genotypes” to currently successful cultivars. Mol Breed 6:553–568. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011372312962
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tondelli A, Xu X, Moragues M, Sharma R, Schnaithmann F, Ingvardsen C et al (2013) Structural and temporal variation in genetic diversity of European spring two-row barley cultivars and association mapping of quantitative traits. Plant Genome 6:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2013.03.0007
Upadhyaya H, Pundir R, Dwivedi S, Gowda C (2009) Mini core collections for efficient utilization of plant genetic resources in crop improvement programs. Information bulletin no. 78. Monograph. International crops research institute for the semi-arid tropics
Wang N, Ning S, Pourkheirandish M, Honda I, Komatsuda T (2013) An alternative mechanism for cleistogamy in barley. Theor Appl Genet 126:2753–2762
Weber JL (1990) Informativeness of human (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n polymorphisms. Genomics 7, 524–30. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1974878 (Accessed 11 Oct 2016)
Weir BS (1996) Genetic data analysis II: Methods for discrete population genetic data. Sinauer Assoc, Sunderland, p 376
Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution (N Y) 38:1358–1370. https://doi.org/10.2307/2408641
Xie W-G, Zhang X-Q, Cai H-W, Liu W, Peng Y (2010) Genetic diversity analysis and transferability of cereal EST-SSR markers to orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.). Biochem Syst Ecol 38:740–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2010.06.009
Yahiaoui S, Igartua E, Moralejo M, Ramsay L, Molina-Cano JL, Ciudad FJ et al (2008) Patterns of genetic and eco-geographical diversity in Spanish barleys. Theor Appl Genet 116:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0665-3
Yahiaoui S, Cuesta-Marcos A, Gracia MP, Medina B, Lasa JM, Casas AM et al (2014) Spanish barley landraces outperform modern cultivars at low-productivity sites. Plant Breed 133:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12148
Zhang M, Mao W, Zhang G, Wu F (2014) Development and characterization of polymorphic EST-SSR and genomic SSR markers for Tibetan annual wild barley. PLoS ONE 9:e94881. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0094881
Funding
This work was supported by the Agricultural Research Center and the Ministry of Higher Education in Egypt, and the Institute of Genetic Resources in Kyushu University, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AE developed the experimental design, processed data, bioinformatics analyses, and prepared the early stages of the manuscript. TK provided the facilities and markers. KA provided germplasm management, experimental design, and coordination. CQ, RB, and LC reviewed the manuscript for important intellectual content, and final version.
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elakhdar, A., Kumamaru, T., Qualset, C.O. et al. Assessment of genetic diversity in Egyptian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genotypes using SSR and SNP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 65, 1937–1951 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-018-0666-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-018-0666-x