Abstract
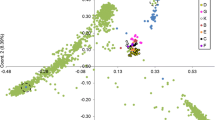
Since Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) is known to have relatively low levels of genetic diversity, a better understanding of variation and relationships among possible sources of novel genes would be valuable. Therefore, analysis of genetic variation of the genus Gossypium, especially the diploids, which are the putative donors of the A and D genomes for the commercially important allotetraploid cottons (AADD), G. hirsutum and G. barbadense, could provide important information about the feasibility of using these genetic resources for cotton improvement. The primary objective of this study was to analyze the genetic diversity in A-genome diploid cotton species, G. herbaceum (A1) and G.␣arboreum (A2) by using microsatellite markers. Forty-one A-genome germplasm accessions were evaluated with 32 microsatellite loci. Genetic similarities between A1 and A2 ranged from 0.62 to 0.86 with a mean of 0.70. Within each A-genome species similarities ranged from 0.80 to 0.97 with a mean of 0.89 for A1 and from 0.82 to 0.98 with a mean of 0.89 for A2. A UPGMA tree and principal coordinate analysis based on genetic similarity matrices showed distinct clusters consistent with the genomic groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla AM, Reddy OUK, El-Zak KM, Pepper AE (2001) Genetic diversity and relationships of diploid and tetraploid cottons revealed using AFLP. Theor Appl Genet 102:222–229
Alvarez AE, Van de Wiel CCM, Smulders MJM (2001) Use of microsatellites to evaluate genetic diversity and species relationship in the genus Lycopersicon. Theor Appl Genet 103:1283–1292
Beasley JO (1940) The origin of American tetraploid Gossypium species. Am Nat 74:285–286
Beasley JO (1942) Meiotic chromosome behavior in species, species hybrids, haploids and induced polyploids of Gossypium. Genetics 27:25–54
Benedict JH, Treacy MF, Altman DW, Schmidt KM (1987) Preference of boll weevils and tobacco budworms for five species of Gossypium. Proc. Beltwide Cotton Prod. Res. Conf., Dallas, TX 4–8 Jan 1987, Natl. Cotton Council of America, Memphis, TN, p 92
Bollenbacher K, Fulton ND (1971) Susceptibility of Gossypium species and varieties to seedling anthracnose. Plant Dis Rptr 55:879–882
Carter WW (1981) Resistance and resistant reaction of Gossypium arboreum to the reniform nematode, Rotylenchulus reniformis. J Nematol 13:368–374
Davierwala AP, Chowdari KV, Kumar S, Peddy APK, Ranjekar PK, Gupta VS (2000) Use of three different marker systems to estimate genetic diversity of Indian elite rice varieties. Genetica 108:269–284
Duvick DN (1984) Genetic diversity in major farm crops on the farm and in reserve. Econ Bot 38:161–178
Endrizzi JE, Turcotte EL, Kohel RJ (1985) Genetics, cytology and evolution of Gossypium. Adv Genet 23:271–375
Enoki E, Sto H, Koinuma K (2002) SSR analysis of genetic diversity among maize inbred lines adapted to cold regions of Japan. Theor Appl Genet 104:1270–1277
Fryxell PA (1984) Taxonomy and germplasm resources. In: Kohel RJ, Lewis CF (eds) Cotton Agron. Monogr. 24. ASA, Madison, WI, pp 27–58
Gutierrez OA, Basu S, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Shoemaker DB, Cheatham CL, McCarty JC (2002) Genetic distance among selected cotton genotypes and its relationship with F2 performance. Crop Sci 42:1841–1847
Iqbal MJ, Reddy OUK, El-Zak KM, Pepper AE (2001) A genetic bottleneck in the ‘evolution under domestication’ of upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. examined using DNA fingerprinting. Theor Appl Genet 103:547–554
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 44:223–270
Kohel JK (1999) Cotton germplasm resources and the potential for improved fiber production and quality. In: Basra AS (ed) Cotton fibers. The Haworth Press, Inc, Binghamton, NY, pp 167–182
Kohel JK, Yu J, Percival E, Dong J, Zhang H (2000) Cotton germplasm resources for improving fiber quality and molecular tools for evaluation. Proc Genetic Control of Cotton Fiber and Seed Quality Workshop, Dec 5–6, 2000, San Antonio, Texas, pp 86–90
Liu S, Cantrell RG, McCarty JC, Stewart JMcD (2000a) Simple sequence repeat – based assessment of genetic diversity in cotton race stock accessions. Crop Sci. 40:1459–1469
Liu S, Saha S, Stelly D, Burr B, Cantrell RG (2000b) Chromosomal assignment of microsatellites in cotton. J Hered 91:326–332
Mei M, Syed NH, Gao W, Thaxton PM (2004) Genetic mapping and QTL analysis of fiber-related traits in cotton (Gossypium). Theor Appl Genet 108:280–291
Meredith WR Jr (1991) Contributions of introductions to cotton improvement. In: Shands HL, Wiesner LE (eds) Use of plant introductions in cultivar development, Part I. CSSA Spec. Publ. 17, CSSA, Madison, WI, pp 127–146
Percival AE, Kohel RJ (1990) The distribution, collection and evaluation of Gossypium. Adv Agron 44:225–256
Reddy OUK, Pepper AE, Abdurakhmonov I, Saha S, Jenks JN, Brooks T, Bolek Y, El-Zik KM (2001) New dinucleotide and trinucleotide microsatellite marker resources for cotton genome research. J Cotton Sci 5:103–113
Reed B, Gannaway J, Tummel DR, Thorvilson HG (1999) Screening for resistance in cotton genotypes to Aphis gossypii Glover, the cotton aphid. Proc Beltwide Cotton Conf 2:1002–1007
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc. Numeric taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Exeter Software, Setauket, New York
Rong J, Abbey C, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chang C, Chee PW, Delmonte TA, Ding X, Garza JJ, Marler BS, Park C, Pierce GJ, Rainey KM, Rastogi VK, Schultze SR, Trolinder NL, Wendel JF, Wilkins TA, Williams-Coplin TD, Wing RA, Wright RJ, Zhao X, Shu L, Paterson AH (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genomic organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166:389–417
Stanton MA, Stewart JMcD, Tugwell NP (1992) Evaluation of the Asiatic cottons for resistance to thrips. Genet Resour Crop Evol 39:89–95
Stanton MA, Stewart JMcD, Percival AE, Wendel JF (1994) Morphological diversity and relationships in the A-genome cottons, Gossypium arboreum and G.␣herbaceum. Crop Sci 34:519–527
Ude G, Pillay M, Ogundiwin E, Tenkouano A (2003) Genetic diversity in an African plantain core collection using AFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 107:248–255
Weir BS (1990) Genetic data analysis: methods for discrete population genetic data. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL (1993) RFLP diversity in Gossypium hirsutum L. and new insights into the domestication of cotton. Am J Bot 80(SUPPL.):71
Wendel JF, Olson PD, Stewart JM (1989) Genetic diversity, introgression, and independent domestication of Old World cultivated cottons. Am J Bot 76:1795–1806
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Percival AE (1992) Genetic diversity in Gossypium hirsutum and the origin of upland cotton. Am J Bot 97:1291–1310
Wheeler TA, Gannaway JR, Keating K (1999) Identification of resistance to Thielaviopsis basicola in diploid cotton. Plant Dis 83:832–833
Yik CP, Birchfield W (1984) Resistant germplasm in Gossypium species and related plants to Rotylenchulus reniformis. J Nematol 16:146–153
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Ray Jackson for his assistance in the cytogenetic analysis. We also thank the Germplasm Unit at the USDA-ARS at College Station, Texas, for providing the cotton germplasm accessions. DNA sequencing was performed at the Texas Tech University Center for Biotechnology and Genomics Core Facility. This research was supported by grants from the Texas Advanced Technology Program and the Texas Cotton Research Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kebede, H., Burow, G., Dani, R.G. et al. A-genome cotton as a source of genetic variability for Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54, 885–895 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9157-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9157-6