Abstract
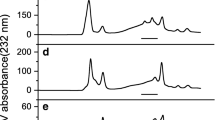
Colla corii asini (CCA) made from donkey-hide has been widely used as a health-care food and an ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine. Heparan sulfate (HS)/heparin is a structurally complex class of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) that have been implicated in a wide range of biological activities. However, their presence within CCA, and their possible structural characteristics, were previously unknown. In this study, GAG fractions containing HS/heparin were isolated from CCA and their disaccharide compositions were analyzed by high sensitivity liquid chromatography-ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-MS-ITTOF). This revealed that, in addition to the eight commonly seen HS disaccharides, the four rare N-unsubstituted disaccharides were also detected in significant quantities. The disaccharide compositions varied significantly between HS/heparin fractions indicating chains with differing domain structures. This novel structural information may lead to a better understanding of the biological activities (i.e. anticoagulation and antitumor action) of CCA.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCA:
-
Colla corii asini
- EIC:
-
extracted ion chromatogram
- GAG:
-
glycosaminoglycan
- GlcNH3 + :
-
N-unsubstituted glucosamine
- GlcNAc:
-
N-acetyl glucosamine
- GlcNS:
-
N-sulfated glucosamine
- HS:
-
heparan sulfate
- LC-MS-ITTOF:
-
liquid chromatography-ion trap/time-of-flight mass spectrometry
- NA domain:
-
N-acetylated domain
- NA/NS domain:
-
transition region
- NaCl:
-
sodium chloride
- UA:
-
uronic acid
- ΔUA:
-
4,5-unsaturated uronate (generated by heparinase excision)
- S-domain:
-
highly sulfated domain
- SE-HPLC:
-
size-exclusion HPLC
References
Su, N.-J., Li, B., Wang, F., Quan, S., Yang, C.L., Shan, D.H., Xing, F.Q.: Clinical effectiveness of colla corii asini on improving uterine receptivity in controlled qvarian stimulation. J. Trop. Med. 9, 155–157 (2009)
Wang, D.L., Ru, W.W., Xu, Y.P., Zhang, J.L., He, X.X., Fan, G.H., Mao, B.B., Zhou, X.S., Qin, Y.F.: Chemical constituents and bioactivities of colla corii asini. Drug. Discov. Ther. 8, 201–207 (2014)
Song, Y.M., Mao, G.N., Huang, X.S., Du, Y.M.: Study on hemopoiesis and anti-fatigue effects of Colla Corri Asini effervescent granules in mice. Prog. Vet. Med. 32, 83–86 (2011)
Peng, L., Yao, S.Y., Wei-Zhong, F.: Evaluation on angelica and donkey-hide gelatin oral liquid in improving iron deficiency anemia in rats. Pract. Prev. Med. 19, 265–267 (2012)
Fan, H.Z., Liu, Y.X., Xie, K.Q., Zhang, A.: Characterization and quantification of dermatan sulfate from donkey skin. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 19(8), 477–480 (1994)
Liu, P.M., You, J.H., Tian, S.S., Xie, X.J., Xie, F.S.: Donkey hide gelatin drug-containing serum induced lung cancer PG cells apoptosis in animal experiments. Pract. J. Med. Pharm. 22, 426–427 (2005)
Liu, P.M., Cai, B.C., Xie, X.J., Tian, S.S., You, J.H., Xie, F.S.: Effect of donkey hide gelatin drug-containing serum on expressing of gene P53 in leukemia K562 cells. Pharm. Clin. Chin. Mat. Med. 21, 33–35 (2005)
Song, Y.M., Mao, G.N., Kang, R.R., Mao, R.J.: Effect of colla corri asini effervescent granules on immune function in mice. Progr. Vet. Med. 32, 73–75 (2011)
Chen, B.F.: Clinical observation on triple therapy of Ejiao and Weifuchun for chronic atrophic gastritis combined with peptic ulcer. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 10, 1622–1623 (2011)
Chang, D.Y., Yang, J., Dong, F.H.: The effect of E-jiao on the multiplicative and differentiative function of osteoblast of wistar rats cultured in vitro. Chin. J. Gerontol. 29, 3230–3232 (2009)
Gao, Y., Dong, F.H., Zheng, J.: Influence of E Jiao on related genes expression during bone repair. Chin. J. Orthop. Trauma. 17, 520–523 (2004)
Couchman, J.R.: Syndecans: proteoglycan regulators of cell-surface microdomains? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 926–938 (2003)
Liu, D.F., Shriver, Z., Venkataraman, G., Shabrawi, Y.E., Sasisekharan, R.: Tumor cell surface heparan sulfate as cryptic promoters or inhibitors of tumor growth and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 568–573 (2002)
Perrimon, N., Bernfield, M.: Specificities of heparan sulphate proteoglycans in developmental processes. Nature. 404, 725–728 (2000)
Robinson, C.J., Stringer, S.E.: The splice variants of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors. J. Cell Sci. 114, 853–865 (2001)
Esko, J.D., Lindahl, U.: Molecular diversity of heparan sulfate. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 168–173 (2001)
Lindahl, U., Kusche-Gullberg, M., Kjellén, L.: Regulated diversity of heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24979–24982 (1998)
Esko, J.D., Selleck, S.B.: Order out of chaos: assembly of ligand binding sites in heparan sulfate. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 435–471 (2002)
Casu, B., Lindahl, U.: Structure and biological interactions of heparin and heparan sulfate. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 57, 159–206 (2001)
Gallagher, J.T.: Heparan sulphate: a heparin in miniature. In: Lever, R., Mulloy, B., Page, C. (eds.) Heparin - A Century of Progress, pp. 347–360. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Murphy, K.J., Merry, C.L.R., Malcolm, L., Thompson, J.E., Roberts, I.S., Gallagher, J.T.: A new model for the domain structure of heparan sulfate based on the novel specificity of K5 lyase. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 27239–27245 (2004)
Cheng, F., Svensson, G., Fransson, L.Å., Mani, K.: Non-conserved, S-nitrosylated cysteines in glypican-1 react with N-unsubstituted glucosamines in heparan sulfate and catalyze deaminative cleavage. Glycobiology. 22(11), 1480–1486 (2012)
Liu, J., Shriver, Z., Pope, R.M., Thorp, S.C., Duncan, M.B., Copeland, R.J., Raska, C.S., Yoshida, K., Eisenberg, R.J., Cohen, G., Linhardt, R.J., Sasisekharan, R.: Characterization of a heparan sulfate octasaccharide that binds to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein D. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 33456–33467 (2002)
Fu, L., Li, L.Y., Cai, C., Li, G.Y., Zhang, F.M., Linhardt, R.J.: Heparin stability by determining unsubstituted amino groups using hydrophilic interaction chromatography mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 461, 46–48 (2014)
Beaudet, J.M., Weyers, A., Solakyildirim, K., Yang, B., Takieddin, M., Mousa, S., Zhang, F., Linhardt, R.J.: Impact of autoclave sterilization on the activity and structure of formulated heparin. J. Pharm. Sci. 100, 3396–3404 (2011)
Shukla, D., Liu, J., Blaiklock, P., Shworak, N.W., Bai, X., Esko, J.D., Cohen, G.H., Eisenberg, R.J., Rosenberg, R.D., Spear, P.G.: A novel role for 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate in herpes simplex virus 1 entry. Cell. 99, 13–22 (1999)
Liu, J., Shriver, Z., Blaiklock, P., Yoshida, K., Sasisekharan, R., Rosenberg, R.D.: Heparan sulfate D-glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase-3A sulfates N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 38155–38162 (1999)
Nadanaka, S., Purunomo, E., Takeda, N., Tamura, J.I., Kitagawa, H.: Heparan sulfate containing unsubstituted glucosamine residues: biosynthesis and heparanase-inhibitory activity. J. Biol. Chem. 289, 15231–15243 (2014)
Wei, Z., Deakin, J.A., Blaum, B.S., Uhrín, D., Gallagher, J.T., Lyon, M.: Preparation of heparin/heparan sulfate oligosaccharides with internal N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues for functional studies. Glycoconj. J. 28, 525–535 (2011)
Liang, Q.T., Du, J.Y., Fu, Q., Lin, J.H., Wei, Z.: Preparation and characterization of heparin hexasaccharide library with N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues. Glycoconj. J. 32, 643–653 (2015)
Liang, Q.T., Xiao, X.M., Lin, J.H., Wei, Z.: A new sequencing approach for N-unsubstituted heparin/heparan sulfate oligosaccharides. Glycobiology. 25, 714–725 (2015)
Du, J.Y., Chen, L.R., Liu, S., Lin, J.H., Liang, Q.T., Lyon, M., Wei, Z.: Ion-pairing liquid chromatography with on-line electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry for the structural analysis of N -unsubstituted heparin/heparan sulfate. J. Chromatogr. B. 1028, 71–76 (2016)
Gao, J.H., Wang, R., Fan, F.: Modern research progress on asini corii colla. Chin. Pharm. Aff. 4, 396–401 (2011)
Wei, Z., Lyon, M., Gallagher, J.T.: Distinct substrate specificities of bacterial heparinases against N-unsubstituted glucosamine residues in heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 15742–15748 (2005)
Toida, T., Yoshida, H., Toyoda, H., Koshiishi, I., Imanari, T., Hileman, R.E., Fromm, J.R., Linhardt, R.J.: Structural differences and the presence of unsubstituted amino groups in heparan sulphates from different tissues and species. Biochem. J. 322(2), 499–506 (1997)
Shi, X., Zaia, J.: Organ-specific heparan sulfate structural phenotypes. J. Biol. Chem. 284(18), 11806–11814 (2009)
Rudd, T.R., Macchi, E., Gardini, C., Muzi, L., Guerrini, M., Yates, E.A., Torri, G.: How to find a needle (or anything else) in a haystack: two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy-filtering with iterative random sampling applied to pharmaceutical heparin. Anal. Chem. 84(15), 6841–6847 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 282 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, J., Liu, S., Liang, Q. et al. Analysis of Heparan sulfate/heparin from Colla corii asini by liquid chromatography-electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Glycoconj J 36, 211–218 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-019-09868-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-019-09868-0