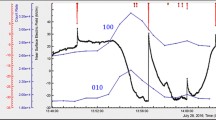
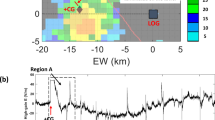
Abstract
An overview of the physics of cloud-to-ground lightning is given, including its initiation, propagation, and attachment to ground. Discharges artificially initiated (triggered) from natural thunderclouds using the rocket-and-wire technique are discussed with a view toward studying properties of natural lightning. Both conventional and runaway breakdown mechanisms of lightning initiation in thunderclouds are reviewed, as is the role of the lower positive charge region in facilitating different types of lightning. New observations of negative-leader stepping and its attachment to ground are compared to similar processes in long laboratory sparks. The mechanism and parameters of compact intracloud lightning discharges that are thought to be the most intense natural producers of HF-VHF (3–300 MHz) radiation on Earth are reviewed. The M-component mode of charge transfer to ground and its difference from the leader/return-stroke mode are discussed. Lightning interaction with the ionosphere and the production of energetic radiation (X-rays and gamma radiation) by cloud-to-ground leaders are considered.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazelyan EM, Raizer YuP (2000) Lightning physics and lightning protection, 325 p. IOP, Bristol
Bazelyan EM, Gorin BN, Levitov VI (1978) Physical and engineering foundations of lightning protection, 223 p. Gidrometeoizdat, Leningrad
Beasley WH, Uman MA, Rustan PL (1982) Electric fields preceding cloud-to-ground lightning flashes. J Geophys Res 87:4883–4902
Betz HD, Schumann U, Laroche P (eds) (2009) Lightning: principles, instruments and applications. Springer, 691 p
Biagi CJ, Jordan DM, Uman MA, Hill JD, Beasley WH, Howard J (2009) High-speed video observations of rocket-and-wire initiated lightning. Geophys Res Lett 36:L15801. doi:10.1029/2009GL038525
Biagi CJ, Uman MA, Hill JD, Jordan DM, Rakov VA, Dwyer JR (2010) Observations of stepping mechanisms in a rocket-and-wire triggered lightning flash. J Geophys Res 115:D23215. doi:10.1029/2010JD014616
Brook M, Ogawa T (1977) The cloud discharge. In R. Golde (ed) Lightning, vol. 1, Physics of lightning. Academic Press, London, pp. 191–230
Chen M, Takagi N, Watanabe T, Wang D, Kawasaki Z-I, Liu X (1999) Spatial and temporal properties of optical radiation produced by stepped leaders. J Geophys Res 104:27573–27584
Cooray GV (ed) (2003) The lightning flash, 574 p. The Institution of Electrical Engineers, London
Cooray V, Becerra M, Rakov VA (2009) On the electric field at the tip of dart leaders in lightning flashes. J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys 71(12):1397–1404. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2009.06.002
Cooray V, Dwyer JR, Rakov VA, Rahman M (2010) On the mechanism of X-ray production by dart leaders of lightning flashes. J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys 72(11–12):848–855. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2010.04.006
Dwyer JR, Babich LP (2011) Low-energy electron production by relativistic runaway electron avalanches in air. J Geophys Res 116:A09301. doi:10.1029/2011JA016494
Dwyer JR, Babich L (2012) Reply to comment by A. V. Gurevich et al. on “Low-energy electron production by relativistic runaway electron avalanches in air”. J Geophys Res 117:A04303. doi:10.1029/2011JA017487
Dwyer JR, Schaal M, Rassoul HK, Uman MA, Jordan DM, Hill D (2011) High-speed X-ray images of triggered lightning dart leaders. J Geophys Res 116:D20208. doi:10.1029/2011JD015973
Eidelman S et al (2004) Review of particle physics. Phys Lett B 592:1–1109. doi:10.1016/j.physletb.2004.06.001
Gorin BN, Levitov VI, Shkilev AV (1976) Some principles of leader discharge of air gaps with a strong non-uniform field. Gas discharges. IEE Conf Publ 143:274–278
Griffiths RF, Phelps CT (1976a) The effects of air pressure and water vapour content on the propagation of positive corona streamers, and their implications to lightning initiation. Q J Roy Meteor Soc 102:419–426
Griffiths RF, Phelps CT (1976b) A model of lightning initiation arising from positive corona streamer development. J Geophys Res 31:3671–3676
Gurevich AV, Zybin KP (2001) Runaway breakdown and electric discharges in thunderstorms. Physics–Uspekhi 44 (11): 1119–1140
Gurevich AV, Milikh GM, Roussel-Dupre R (1992) Runaway electron mechanism of air breakdown and preconditioning during a thunderstorm. Phys Lett A 165:463–468
Gurevich AV, Zybin KP, Roussel-Dupre RA (1999) Lightning initiation by simultaneous effect of runaway breakdown and cosmic ray showers. Phys Lett A 254:79–87
Gurevich AV, Duncan LM, Medvedev YuV, Zybin KP (2002) Radio emission due to simultaneous effect of runaway breakdown and extensive atmospheric showers. Phys Lett A 301:320–326
Gurevich AV, Duncan LM, Karashtin AN, Zybin KP (2003) Radio emission of lightning initiation. Phys Lett A 312:228–237
Gurevich AV, Roussel-Dupre R, Zybin KP, Milikh GM (2012) Comment on “Low-energy electron production by relativistic runway electron avalanches in air” by J. R. Dwyer and L. P. Babich. J Geophys Res 117:A04302. doi:10.1029/2011JA017431
Haddad MA, Rakov VA, Cummer SA (2012) New measurements of lightning electric fields in Florida: waveform characteristics, interaction with the ionosphere, and peak current estimates. J Geophys Res 117:D10101. doi:10.1029/2011JD017196
Hill JD, Uman MA, Jordan DM (2011) High-speed video observations of a lightning stepped leader. J Geophys Res 116:D16117. doi:10.1029/2011JD015818
Inan US, Cummer SA, Marshall RA (2010) A survey of ELF and VLF research of lightning-ionosphere interactions and causative discharges. J Geophys Res 115:A00E36, doi:10.1029/2009JA014775
Jayakumar V, Rakov VA, Miki M, Uman MA, Schnetzer GH, Rambo KJ (2006) Estimation of input energy in rocket-triggered lightning. Geophys Res Lett 33:L05702. doi:10.1029/2005GL025141
Krehbiel PR, Riousset JA, Pasko VP, Thomas RJ, Rison W, Stanley MA, Edens HE (2008) Upward electrical discharges from thunderstorms. Nature Geosci 1:233–237. doi:10.1038/ngeo162
Krider EP, Dawson GA, Uman MA (1968) The peak power and energy dissipation in a single–stroke lightning flash. J Geophys Res 73:3335–3339
Larigaldie S, Roussaud A, Jecko B (1992) Mechanisms of high-current pulses in lightning and long-spark. J Appl Phys 72(5):1729–1739
Lebedev VB, Feldman GG, Gorin BN, Shcherbakov Yu V, Syssoev VS, Rakov VA, Uman MA, Olsen RC (2007) Test of the image converter camera complex for research of discharges in long air gaps and lightning. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on atmospheric electricity, Beijing, China, August 13–17, 2007, pp. 509–512
Loeb LB (1966) The mechanisms of stepped and dart leaders in cloud-to-ground lightning strokes. J Geophys Res 71:4711–4721
Lu G et al (2011) Lightning development associated with two negative gigantic jets. Geophys Res Lett 38:L12801. doi:10.1029/2011GL047662
Malan DJ, Schonland BFJ (1951) The electrical processes in the intervals between the strokes of a lightning discharge. Proc Roy Soc (Lond) A206:145–163
Mallick S, Rakov VA, Dwyer JR (2012) A study of X-ray emissions from thunderstorms with emphasis on subsequent strokes in natural lightning. J Geophys Res 117:D16107. doi:10.1029/2012JD017555
Moss G, Pasko VP, Liu N, Veronis G (2006) Monte Carlo model for analysis of thermal runaway electrons in streamer tips in transient luminous events and streamer zones of lightning leaders. J Geophys Res 111:A02307. doi:10.1029/2005JA011350
Nag A, Rakov VA (2008) Pulse trains characteristic of preliminary breakdown in cloud-to-ground lightning that are not followed by return stroke pulses. J Geophys Res 113:D01102. doi:10.1029/2007JD008489
Nag A, Rakov VA (2009) Some inferences on the role of lower positive charge region in facilitating different types of lightning. Geophys Res Lett 36:L05815. doi:10.1029/2008GL036783
Nag A, Rakov VA (2010a) Compact intracloud lightning discharges: 1. Mechanism of electromagnetic radiation and modeling. J Geophys Res 115:D20102. doi:10.1029/2010JD014235
Nag A, Rakov VA (2010b) Compact intracloud lightning discharges: 2. Estimation of electrical parameters. J Geophys Res 115:D20103. doi:10.1029/2010JD014237
Nag A, Rakov VA, Tsalikis D, Cramer JA (2010) On phenomenology of compact intracloud lightning discharges. J Geophys Res 115:D14115. doi:10.1029/2009JD012957
Nguyen MD, Michnowski S (1996) On the initiation of lightning discharge in a cloud 2. The lightning initiation on precipitation particles. J Geophys Res 101:26675–26680
Paxton AH, Gardner RL, Baker L (1986) Lightning return stroke: a numerical calculation of the optical radiation. Phys Fluids 29:2736–2741
Paxton AH, Baker L, Gardner RL (1987) Reply to comments of Hill. Phys Fluids 30:2586–2587
Phelps CT (1974) Positive streamers system intensification and its possible role in lightning initiation. J Atmos Terr Phys 36:103–111
Pierce ET (1958) Some topics in atmospheric electricity. In: Smith LG (ed) Recent advances in atmospheric electricity. Pergamon, New York, pp 5–16
Qie X, Jiang R, Wang C, Yang J, Wang J, Liu D (2011) Simultaneously measured current, luminosity, and electric field pulses in a rocket-triggered lightning flash. J Geophys Res 116:D10102. doi:10.1029/2010JD015331
Rakov VA (1998) Some inferences on the propagation mechanisms of dart leaders and return strokes. J Geophys Res 103:1879–1887
Rakov VA, Uman MA (2003) Lightning: physics and effects. Cambridge University Press, 687 p
Rakov VA (2006) Initiation of lightning in thunderclouds. In Sergeev AM (ed) Topical problems of nonlinear wave physics. Proceedings SPIE, Vol. 5975, pp 362–373
Rakov VA, Uman MA (1990) Waveforms of first and subsequent leaders in negative lightning flashes. J Geophys Res 95(D10):16561–16577. doi:10.1029/JD095iD10p16561
Rakov VA, Uman MA, Jordan DM, Priore CA III (1990) Ratio of leader to return stroke field change for first and subsequent lightning strokes. J Geophys Res 95(16):579–587
Rakov VA, Thottappillil R, Uman MA, Barker PP (1995) Mechanism of the lightning M component. J Geophys Res 100:25701–25710
Rakov VA, Uman MA, Rambo KJ, Fernandez MI, Fisher RJ, Schnetzer GH, Thottappillil R, Eybert-Berard A, Berlandis JP, Lalande P, Bonamy A, Laroche P, Bondiou-Clergerie A (1998) New insights into lightning processes gained from triggered-lightning experiments in Florida and Alabama. J Geophys Res 103:14117–14130
Rao M, Bhattacharya H (1966) Lateral corona currents from the return stroke channel and slow field change after the return stroke in a lightning discharge. J Geophys Res 71:2811–2814
Saleh Z, Dwyer J, Howard J, Uman M, Bakhtiari M, Concha D, Stapleton M, Hill D, Biagi C, Rassoul H (2009) Properties of the X-ray emission from rocket-triggered lightning as measured by the Thunderstorm Energetic Radiation Array (TERA). J Geophys Res 114:D17210. doi:10.1029/2008JD011618
Solomon R, Schroeder V, Baker MB (2001) Lightning initiation: conventional and runaway-breakdown hypotheses. Q J R Meteorol Soc 127:2683–2704
Solomon R, Adamo C, Baker MB (2002) A lightning initiation mechanism: application to a thunderstorm electrification model. C R Physique 3:1325–1333
Somu VB, Rakov VA, Haddad MA, Cummer SA (2012) Ionospheric reflection heights for wideband electric fields produced by consecutive return strokes within the same lightning flash, Abstract AE43A-0241, presented at 2012 fall meeting, AGU, San Francisco, Calif., December 3–7, 2012
Wang D, Rakov VA, Uman MA, Takagi N, Watanabe T, Crawford DE, Rambo KJ, Schnetzer GH, Fisher RJ, Kawasaki Z-I (1999a) Attachment process in rocket-triggered lightning strokes. J Geophys Res 104:2143–2150
Wang D, Takagi N, Watanabe T, Rakov VA, Uman MA (1999b) Observed leader and return-stroke propagation characteristics in the bottom 400 m of a rocket-triggered lightning channel. J Geophys Res 104:14369–14376
Yashunin SA, Mareev EA, Rakov VA (2007) Are lightning M components capable of initiating sprites and sprite halos? J Geophys Res 112:D10109. doi:10.1029/2006JD007631
Yoshida S, Biagi CJ, Rakov VA, Hill JD, Stapleton MV, Jordan DM, Uman MA, Morimoto T, Ushio T, Kawasaki Z-I, Akita M (2012) The initial stage processes of rocket-and-wire triggered lightning as observed by VHF interferometry. J Geophys Res 117:D09119. doi:10.1029/2012JD017657
Acknowledgments
This paper is largely based on the Tutorial Lecture given by the author at the Thunderstorm Effects on the Atmosphere–Ionosphere System (TEA – IS) Summer School in Torremolinos, Malaga, Spain, June 17–22, 2012, funded by the European Science Foundation (ESF). The work was also supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation and DARPA. Yanan Zhu helped with preparation of the figures. Two anonymous reviewers provided useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakov, V.A. The Physics of Lightning. Surv Geophys 34, 701–729 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-013-9230-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-013-9230-6