Abstract
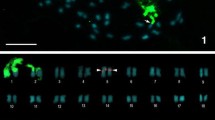
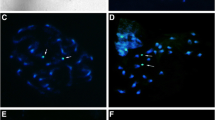
The genus Engystomops is divided into two groups, namely the Duovox clade and the Edentulus clade. The species of Edentulus clade have karyotypes with 2n = 22, while E. pustulatus and E. puyango, which belong to Duovox clade, have 2n = 20. To investigate if 2n = 20 is a synapomorphy of Duovox clade, we cytogenetically analyzed all the species of this group, except for E. puyango, in the present study. All of them had 2n = 20, differing from the species of Edentulus clade. Since the species already karyotyped of the genus Physalaemus, which is considered to be the sister group of Engystomops, also have 2n = 22, we conclude that the 2n reduction is a synapomorphy of Duovox clade. Despite the karyotypes of all the species of Duovox clade were very similar, they varied in the NOR pattern. In E. coloradorum, an additional NOR was found in one homologue of the chromosome pair 10 exclusively in all females, indicating that this could possibly be a sexual pair of the ZZ/ZW system. Also in this species, it was found the first case of natural polyploidy of the genus Engystomops.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral MJV, Cardoso AJ, Recco-Pimentel SM (2000) Cytogenetic analysis of three Physalaemus species (Amphibia, Anura). Caryologia 53(2):283–288
Beçak ML, Beçak W, Rabello MN (1966) Cytological evidence of constant tetraploidy in the bisexual South American frog Odontophrynus americanus. Chromosoma 19(2):188–193
Beçak ML, Denaro L, Beçak W (1970) Polyploidy and mechanisms of karyotypic diversification in Amphibia. Cytogenetics 9:225–238
Bogart JP, Licht LE, Oldham MJ, Darbyshire SJ (1985) Electrophoretic identification of Ambystoma laterale and Ambystoma texanum as well as their diploid and triploid interspecific hybrids (Amphibian: Caudata) on Pelee Island, Ontario. Can J Zool 63:340–347
Boul KE, Funk WC, Darst CR, Cannatella DC, Ryan MJ (2007) Sexual selection drives speciation in an Amazonian frog. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 274:399–406
Bruschi DP, Busin CS, Siqueira S, Recco-Pimentel SM (in press) Cytogenetic analysis of two species in the Phyllomedusa hypochondrialis group (Anura, Hylidae). Hereditas
Cannatella DC, Duellman W (1984) Leptodactylidae frogs of the Physalaemus pustulosus group. Copeia 1984:902–921
Cavallo D, De Vita R, Eleuteri P, Borkin L, Ermechenko V, Odierna G, Balletto E (2002) Karyological and flow cytometric evidence of triploid specimens in Bufo viridis (Amphibia, Anura). Eur J Histochem 46:159–164
Cioffi MB, Martins C, Vicari MR, Rebordinos L, Bertollo LAC (2010) Differentiation of the XY sex chromosomes in the fish Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae): unusual accumulation of repetitive sequences on the X chromosome. Sex Dev 4:176–185. doi:10.1159/000309726
De Lucca EJ, Jim J, Foresti F (1974) Chromosomal studies in twelve species of Leptodactylidae and one Brachycephalidae. Caryologia 27:183–191
Formas RJ (1994) A triploid individual of the Chilean Leptodactylid frog Eupsophus vertebralis. J Herpetol 28(3):394–395
Frost DR (2011) Amphibian species of the world: an online reference. Version 5.5 (31 Jan 2011). Electronic database accessible at http://research.amnh.org/vz/herpetology/amphibia/ American Museum of Natural History, New York, USA
Funk WC, Caldwell JP, Peden CE, Padial JM, De la Riva I, Cannatella DC (2007) Tests of biogeographic hypotheses for diversification in the Amazonian forest frog Physalaemus petersi. Mol Phylogenet Evol 44(2):825–837
Green DM, Sessions SK (1991) Nomenclature for chromosomes. In: Green DM, Sessions SK (eds) Amphibian cytogenetics and evolution. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 431–432
Green DM, Kezer J, Nussbaum RA (1984) Triploidy in Hochstetler’s frogs, Leiopelma hochstetteri, from New Zealand. New Zealand J Zool 11:457–460
Gregory TR, Mable BK (2005) Polyploidy in animals. In: Gregory TR (ed) The evolution of the genome. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 428–501
Guerra MA, Ron SR (2008) Mate choice and courtship signal differentiation promotes speciation in an Amazonian frog. Behav Ecol 13:1–8
Gunther R, Uzzel T, Berger L (1979) Inheritance patterns in triploid Rana “esculenta” (Amphibia, Salientia). Mitt Zool Mus Berlin 55:35–57
Hillis DM, Green D (1990) Evolutionary changes of heterogametic sex in the phylogenetic history of amphibians. J Evol Biol 3:49–64
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014–1015
IUCN (2011) The IUCN red list of threatened species. Version 2011.2. Electronic database accessible at http://www.iucnredlist.org. Downloaded on 17 Nov 2011
King M (1980) C-banding studies on Australian hylid frogs: secondary constriction structure and the concept of euchromatin transformation. Chromosoma 80:191–217
Léon PE (1970) Report of the chromosome numbers of some Costa Rican anurans. Rev Biol Trop 17:119–124
Lourenço LB, Recco-Pimentel SM, Cardoso AJ (1999) Two karyotypes and heteromorphic sex chromosomes in Physalaemus petersi (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Can J Zool 77:624–631
Mahony MJ, Robinson ES (1980) Polyploidy in the Australian leptodactylid frog genus Neobatrachus. Chromosoma 81:199–212
Milani M, Cassini CS, Recco-Pimentel SM, Lourenço LB (2010) Karyotypic data detect interpopulational variation in Physalemus olfersii and the first case of supernumerary chromosome in the genus. Animal Biol J 2:21–28
Nascimento LB, Caramaschi U, Cruz CAG (2005) Taxonomic review of the species groups of the genus Physalaemus Fitzinger, 1826 with revalidation of the genera Engystomops Jiménez-de-la-Espada, 1872 and Eupemphix Steindachner, 1863 (Amphibia, Anura, Leptodactylidae). Arq Mus Nac Rio de Janeiro 63:297–320
Nascimento J, Quinderé YRSD, Recco-Pimentel SM, Lima JRF, Lourenço LB (2010) Heteromorphic Z and W sex chromosomes in Physalaemus ephippifer (Steindachner, 1864) (Anura, Leiuperidae). Genetica 138:1127–1132
Nishioka M, Miura I, Saitoh K (1993) Sex chromosomes of Rana rugosa with special reference to local differences in sex-determining mechanism. Sci Rep Lab Amphibian Biol 12:55–81
Ogata M, Hasegawa Y, Ohtani H, Mineyama M, Miura I (2008) The ZZ/ZW sex-determining mechanism originated twice and independently during evolution of the frog, Rana rugosa. Heredity 100:92–99
Ptacek MB, Gerhardt HC, Sage RD (1994) Speciation by polyploidy in tree frogs: multiple origins of the tetraploid Hyla versicolor. Evolution 48(3):898–908
Quinderé YRSD, Lourenço LB, Andrade GV, Tomatis C, Baldo D, Recco-Pimentel SM (2009) Polytypic and polymorphic cytogenetic variations in the widespread anuran Physalaemus cuvieri (Anura, Leiuperidae) with emphasis on nucleolar organizing regions. Biol Res 42:79–92
Reed KM, Phillips RB (1997) Polymorphism of the nucleolus organizer region (NOR) on the putative sex chromosomes of Arctic char (Salvelinus alpines) is not sex related. Chromos Res 5:221–227
Richards C, Nace GW (1977) The occurrence of diploid ova Rana pipens. J Hered 68:307–313
Ron SR, Cannatella DC, Coloma LA (2004) Two new species of Physalaemus (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from western Ecuador. Herpetologica 60(2):261–275
Ron SR, Coloma LA, Cannatella DC (2005) A new, cryptic species of Physalaemus (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from Western Ecuador with comments on the call structure of the P. pustulosus species group. Herpetologica 61(2):178–196
Ron SR, Santos JC, Cannatella DC (2006) Phylogeny of the túngara frog genus Engystomops (=Physalaemus pustulosus species group; Anura: Leptodactylidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 39:392–402
Ron SR, Toral E, Rivera M, Terán-Valdez A (2010) A new species of Engystomops (Anura: Leiuperidae) from southwestern Ecuador. Zootaxa 2606:25–49
Schmid M (1978) Chromosome banding in amphibia. I. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Bufo and Hyla. Chromosoma 66:361–388
Schmid M, Steinlein C (2003) Chromosome banding in amphibia. XXIX. The primitive XY/XX sex chromosomes of Hyla femoralis (Anura, Leiuperidae). Cytogenet Genome Res 101:74–79
Schmid M, Olert J, Klett C (1979) Chromosome banding in amphibia. III. Sex chromosomes in Triturus. Chromosoma 71:29–55
Schmid M, Haaf T, Geile B, Sims S (1983) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. VIII. An unusual XY/XX-sex chromosome system in Gastrotheca riobambae (Anura, Hylidae). Chromosoma 88:69–82
Schmid M, Ohta S, Steinlein C, Guttenbach M (1993) Chromosome banding in Amphibia. XIX. Primitive ZW/ZZ sex chromosomes in Buergeria buergeria (Anura, Rhacophoridae). Cytogenet Cell Genet 62(238):246
Schmid M, Feichtinger W, Steinlein C, Rupprecht A, Haaf T, Kaiser H (2002) Chromosome banding in amphibia. XXIII. Giant W sex chromosomes and extremely small genomes in Eleutherodactylus euphronides and Eleutherodactylus shrevei (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Cytogenet Genome Res 97:81–94
Schmid M, Feichtinger W, Steinlein C, Visbal Garcia R, Fernández Badillo A (2003) Chromosome banding in amphibia. XXVIII. Homomorphic XY sex chromosomes and a derived Y-autosome translocation in Eleutherodactylus riveroi (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Cytogenet Genome Res 101:62–73
Shreve B (1941) Notes on Ecuadorian and Peruvian reptiles and amphibians with description of new forms. Proc New Engl Zoo Club 18:71–84
Silva APZ, Haddad CFB, Kasahara S (1999) Nucleolus organizer regions in Physalaemus cuvieri (Anura, Leptodactylidae), with evidence of a unique case of Ag-NOR variability. Hereditas 131:135–141
Silva APZ, Baldissera-Jr FA, Haddad CFB, Kasahara S (2000) Karyotypes and nucleolus organizer regions in four species of the genus Physalaemus, (Anura, Leptodactylidae). Ihering Ser Zool 88:159–164
Siqueira S, Aguiar OJ, Strüssmann C, Del-Grande ML, Recco-Pimentel SM (2008) Chromosomal analysis of three Brazilian “eleutherodactyline” frogs (Anura: Terrarana), with suggestion of a new species. Zootaxa 1860:51–59
Stöck M, Ustinova J, Lamatsch DK, Schartl M, Perrin N, Moritz C (2009) A vertebrate reproductive system involving three ploidy levels: hybrid origin of triploids in a contact zone of diploid and tetraploidpaleartic green toads (Bufo viridis subgroup). Evolution 64(4):944–995
Targueta CP, Rivera M, Souza MB, Recco-Pimentel SM, Lourenço LB (2010) Cytogenetic contributions for the study of the Amazonian Engystomops (Anura, Leiuperidae) assessed in the light of phylogenetics relationships. Mol Phylogenet Evol 54:709–725
Tomatis C, Baldo D, Kolenc F, Borteiro C (2009) Chromosomal variation in the species of the Physalaemus henselii group (Anura: Leiuperidae). J Herpetol 43(3):555–560. doi:10.1670/08-122R1.1
Viegas-Péquignot E (1992) In situ hybridization to chromosomes with biotinylated probes. In: Willernson D (ed) In situ hybridization: a practical approach. Oxford University Press-IRL Press, Oxford, pp 137–158
Wiley JE (2003) Replication banding and FISH analysis reveal the origin of the Hyla femoralis karyotype and XY/XX sex chromosomes. Cytogenet Genome Res 101:80–83
Wiley JE, Braswell AL (1986) A triploid male Rana palustris. Copeia 2:531–533
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Santiago R. Ron for identification of the specimens, and Diego Almeida Reinoso, Margarita Baquero, and Ailin Blasco for helping in the field work. This work was supported by the Brazilian agencies FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) and Capes (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), and the Ecuadorian agencies SENESCYT (Secretaría Nacional de Educación Superior, Ciencia, Tecnología y Innovación and PUCE (Pontificia Universidad Católica del Ecuador).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Targueta, C.P., Rivera, M. & Lourenço, L.B. Karyotypic differentiation via 2n reduction and a finding of a case of triploidy in anurans of the genus Engystomops (Anura, Leiuperidae). Genetica 139, 1339–1347 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9636-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9636-y