Abstract
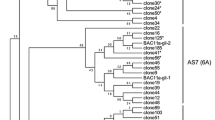
The B-hordein gene family was analyzed from two Tibetan hull-less barley cultivars Z09 and Z26 (Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare). Fourteen B-hordein genes, designated BZ09-2 to BZ09-5 (from Z09) and BZ26-1 to BZ26-10 (from Z26), were sequenced. Seven of them, similar to a previously reported BZ09-1 from Z09, were predicted to encode putative active proteins each with a signal peptide, a repetitive domain, and a C-terminal region; seven of them were predicted to be pseudogenes. The B-hordein gene family was analyzed using all known representatives of B-hordein sequences and two most similar LMW-GSs of Triticum aestivum. Alignment of these seven putative proteins with known B-hordeins and two most similar LMW-GSs of T. aestivum revealed that they shared a common motif. A large variation was observed between numbers of repeat units of predicted B-hordeins of Z26 and Z09. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that all BZ26 clones were clustered in a subgroup, and BZ09-1 formed another subgroup by itself in the putative eight active genes. In addition, six 5′-upstream regulatory sequences of the B-hordein genes were isolated from the two accessions by a single oligonucleotide nested PCR, and several different mutations were identified in the cis-acting element GLM and two distinctive sequences (Z09P-2 and Z26P-3). Phylogenetic analysis of 5′-upstream regulatory regions of the B-hordein genes showed that members from the same accession were clustered together except for two distinct members. Quantitative real time PCR analysis indicated distinct expression levels of B-hordein genes in four developing stages of developing grains in two accessions. These findings suggest B-hordein genes have intrinsic differences between accessions, and this knowledge will be useful for incorporating the B-hordeins protein in barley breeding programs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson OD, Greene FC (1997) The α-gliadin gene family II DNA and protein sequence variation, subfamily structure, and origins of pseudogenes. Theor Appl Genet 95:9–65
Anderson OD, Hsia CC, Torres V (2001) The wheat gamma-gliadin genes: characterization of ten new sequences and further understanding of gamma-gliadin gene family structure. Theor Appl Genet 103:323–330
Antal Z, Rascle C, Fevre M et al (2004) Single oligonucleotide nested PCR: a rapid method for the isolation of genes and their flanking regions from expressed sequence tags. Curr Genet 46:240–246
Atanassov P, Borries C, Zahrieva M et al (2001) Hordein polymorphism and variation of agromorphologicaltraits in a collection of naked barley. Genet Resour Crop Evol 48:353–360
Bevan M, Colot V, Hammond-Kosack M et al (1993) Transcriptional control of plant storage protein genes. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 342:209–215
Brandt A, Montembault A, Cameron-mills V (1985) Primary structure of a B1-hordein gene from barley. Carlsberg Res Commun 50:333–345
Cassidy BG, Dvorak J, Anderson OD (1998) The wheat low-molecular-weight glutenin genes: characterization of six new genes and progress in understanding gene family structure. Theor Appl Genet 96:743–750
D’Ovidio R, Masci S (2004) The low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of wheat gluten. J Cereal Sci 39:321–339
Davies JT, Shewry PR, Harris N (1993) Spatial and temporal patterns of B hordein synthesis in developing barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) caryopses. Cell Biol Int 17:195–203
De-Bustos A, Rubio P, Jouve N (2000) Molecular characterization of the inactive allele of the gene Glu-A1 and the development of a set of AS-PCR markers for HMW glutenin of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:1085–1094
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) A rapid total DNA preparation procedure for fresh plant tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Edney MJ, Langrell DE (2004) Evaluating the malting quality of hulless CDC Dawn, acid-dehusked Harrington, and Harrington barley. J Am Soc Brew Chem 62(1):18–22
Forde BG, Heyworth A, Pywell J et al (1985a) Nucleotide sequence of a B1 hordein gene and the identification of possible upstream regulatory elements in endosperm storage protein genes from barley, wheat and maize. Necleic Acids Res 13:7327–7339
Forde BG, Kreis M, Williamson MS et al (1985b) Short tandem repeats shared by B- and C-hordein cDNAs suggested a common evolutionary origin for two groups of cereal storage protein genes. EMBO J 4:9–15
Furtado A, Henry RJ, Pellegrineschi A (2009) Analysis of promoters in transgenic barley and wheat. Plant Biotechnol J 7:240–253
Gupta RB, Macritchie F (1994) Allelic variation at glutenin subunit and gliadin loci, Glu-1, Glu-3, and Gli-1 of common wheat. II. Biochemical basis of the allelic effects on dough properties. J Cereal Sci 19:19–29
Gupta RB, Paul JG, Cornish GB et al (1994) Allelic variation at glutenin subunit and gliadin loci, Glu-1, Glu-3, and Gli-1, of common wheats. I. Its additive and interaction effects on dough properties. J Cereal Sci 19:9–17
Han ZX, Qian G, Wu F et al (2006) Cloning and characterization of four B-hordein genes from Tibetan hull-less barley (Hordeum vulgare subsp. vulgare). Acta Genetica Sinica 33:948–956
Han ZX, Wu F, Zhao T et al (2007) Cloning of B-hordein gene 5′ upstream regulation sequence in highland barley and sequence analysis. J Triticeae Crops 27(4):613–618
Han ZX, Qian G, Wu F et al (2008) Sequences variation and classification of B-hordein genes in hull-less barley from Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Mol Biol 42(1):56–63
Holdsworth MJ, Muñoz-Blanco J, Hammond-Kosack M et al (1995) The maize transcription factor Opaque-2 activates a wheat glutenin promoter in plant and yeast cells. Plant Mol Biol 29(4):711–720
Hsia CC, Anderson OD (2001) Isolation and characterization of wheat ω-gliadin genes. Ther Appl Genet 103:37–44
Kreis M, Rahman S, Forde B et al (1983) Sub-families of hordein mRNA encoded at the hor 2 locus of barley. Mol Gen Genet 191:194–200
Kreis M, Shewry PR, Forde BG et al (1984) Molecular analysis of the effects of the lys3a gene on the expression of Hor loci in developing endosperms of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Biochem Genet 22:222–231
Kwok S, Kellogg DE, McKinney N et al (1990) Effects of primer-template mismatches on the polymerase chain reaction: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 model studies. Nucleic Acids Res 18:999–1005
Lehfer H, Busch W, Martin R et al (1993) Localization of the B-hordein locus on barley chromosomes using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Chromosoma 102:428–432
Liu CT, Wesenberg DM, Hunt CW et al (1996) Hulless barley: a new look for barley in Idaho. [on line] available: http://info.ag.uidaho.edu/resources/PDFs/CIS1050.pdf
Luan YF, He Y (2004) Tendency and counter measures on breeds improvement of Tibet highland barley. Barley Sci 12:1–4
Marris C, Gallois P, Copley J (1988) The 5′ flanking region of a barley B hordein gene controls tissue and developmental specific CAT expression in tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 10:359–366
Matus IA, Hayes PM (2002) Genetic diversity in three groups of barley germplasm assessed by simple sequence repeats. Genome 45:1095–1106
Molina-Cano JL, Sopena A, Polo JP et al (2002) Relationships between barley hordeins and malting quality in a mutant of cv. Triumph. II. Genetic and environmental effects on water uptake. J Cereal Sci 36:39–50
Munck L, Moller L, Jacobsen S et al (2004) Near infrared spectra indicate specific mutant endosperm genes and reveal a new mechanism for substituting starch with (1–3, 1–4)-β-glucan in barley. J Cereal Sci 40:213–222
Nimazhaxi (1998) Hull-less barley and food safety in the region of plateau. Tibetan Agric Technol 20:20–25
Oñate L, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Lara P (1999) Barley BLZ2, a seed-specific bZIP protein that interacts with BLZ1 in vivo and activates transcription from the GCN4-like motif of B-hordein promoters in barley endosperm. J Biol Chem 274:9175–9182
Payne PI (1987) Genetics of wheat storage protein and the effect of allelic variation on bread-making quality. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 38:141–153
Peltonen J, Rita H, Aikasalo R et al (1994) Hordein and malting quality in northern barleys. Hereditas 120:231–239
Piston F, Dorado G, Martin A et al (2005) Cloning and molecular characterization of B-hordeins from Hordeum chilense Roem et Schult. Theor Appl Genet 111:551–560
Rahman S, Kreis M, Forde BG et al (1984) Hordein-gene expression during development of the barley (Hordeum vulgare) endosperm. Biochem J 223:315–322
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Shewry PR, Tatham AS (1990) The prolamine storage proteins of cereal seeds: structure and evolution. Biochem J 267:1–12
Shewry P, Napier J, Tatham A (1995) Seed storage proteins: structures and biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:945–956
Suprunova T, Krugman T, Fahima T et al (2004) Differential expression of dehydrin genes in wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum, associated with resistance to water deficit. Plant Cell Environ 27:1297–1308
Takahashi R (1955) The origin and evolution of cultivated barley. Adv Genet 7:227–266
Taketa S, Kikuchi S, Awayama T et al (2004) Monophyletic origin of naked barley inferred from molecular analyses of a marker closely linked to the naked caryopsis gene. nud. Theor Appl Genet 108:1236–1242
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tatham A, Shewry P (1995) The S-poor prolamins of wheat, barley and rye. J Cereal Sci 22:1–16
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-speciWc gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Vicente-Carbajosa J, Beritashvili DR, Kraev AS et al (1992) Conserved structure and organization of B hordein genes in the Hor2 locus of barley. Plant Mol Biol 18:453–458
Yanagisawa S (1995) A novel DNA binding domain that may form a single zinc finger motif. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3403–3410
Zadoks J, Chang T, Konzak C (1974) Decimal code for growth stages of cereals. Weed Res 14:415–421
Zhang Q, Maroof MS, Yang G et al (1992) Ribosomal DNA polymorphisms and the Oriental-Occidental genetic differentiation in cultivated barley. Theor Appl Genet 84:682–687
Zhang W, Gianibelli MC, Ma W et al (2003) Identification of SNPs and development of allele-specific PCR markers for γ-gliadin alleles in Triticum aestivum. Theor Appl Genet 107:130–138
Zhao XL, Xia XC, He ZH et al (2006) Characterization of three low-molecular-weight Glu-D3 subunit genes in common wheat. Theor Appl Genet 113:1247–1259
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Special Basic Research Funds of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2006FY110700) and the National Science and Technology Supporting Programs (2006BAD13B02-13). The authors are thankful for the cooperation between USDA-ARS Dale Bumpers National Rice Research Center and Chengdu Institute of Biology, The Chinese Academy of Sciences. For proofreading the authors are thankful to Ellen McWhirter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Z., Wu, F., Deng, G. et al. Structural and expressional analysis of the B-hordein genes in Tibetan hull-less barley. Genetica 138, 227–239 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-009-9415-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-009-9415-6