Abstract
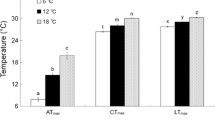
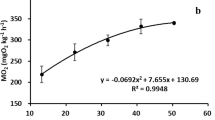
The critical swimming speed (U crit, cm s−1) of juvenile tiger puffer Takifugu rubripes was determined under different temperatures (15, 21, 25 and 30 °C), salinities (5, 10, 20, 32 and 40), body lengths (3.32, 4.08, 5.06 and 5.74 cm) and starvation days (1, 3, 6 and 9 days). Acute temperature change, body length and starvation significantly influenced the U crit of tiger puffers, whereas acute salinity change had no significant effect. The U crit increased as the temperature increased from 15 to 30 °C. The U crit increased as the body length increased from 3.32 to 5.74 cm, whereas relative critical swimming speed (U crit’, body length s−1) decreased. The relationship between the body length (l, cm) and U crit or U crit’ can be described by the quadratic model as U crit = − 1.4088 l 2 + 16.976 l − 11.64, R 2 = 0.9698 (P < 0.01) or U crit’ = − 0.1937 l 2 + 0.9504 l + 7.7666, R 2 = 0.9493 (P < 0.01). The U crit decreased as starvation days increased from 1 to 9 days. Low temperature and starvation can reduce the swimming ability of juvenile tiger puffers. Results can be of value in evaluating the swimming ability of juvenile tiger puffers, understanding ecological processes and improving the population enhancement of tiger puffers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brauner CJ, Shrimpton JM, Randall DJ (1992) Effect of short-duration seawater exposure on plasma ion concentrations and swimming performance in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus Kisutch) parr. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49:2399–2405
Brauner CJ, Iwama GK, Randall DJ (1994) The effect of short-duration seawater exposure on the swimming performance of wild and hatchery-reared juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) during smoltification. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 51:2188–2194
Breen M, Dyson J, O’Neill FG, Jones E, Haigh M (2004) Swimming endurance of haddock (Melanogrammus aeglefinus L.) at prolonged and sustained swimming speeds, and its role in their capture by towed fishing gears. ICES J Mar Sci 61:1071–1079
Brett JR (1964) The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J Fish Board Can 21:1183–1226
Bulletin of China Marine Environmental Status (2016) http://www.coi.gov.cn/gongbao/huanjing/201704/t20170413_35526.html
Chatelier A, McKenzie DJ, Claireaux G (2005) Effects of changes in water salinity upon exercise and cardiac performance in the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Mar Biol 147:855–862
Claireaux G, Couturier C, Groison AL (2006) Effect of temperature on maximum swimming speed and cost of transport in juvenile European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J Exp Biol 209:3420–3428
Cronin TW, Forward RB (1980) The effects of starvation on phototaxis and swimming of larvae of the crab Rhithropanopeus harrisii. Biol Bull 158:283–294
Davison W (1997) The effects of exercise training on teleost fish, a review of recent literature. Comp Biochem Physiol A 117:67–75
De Boeck G, van der Ven K, Hattink J, Blust R (2006) Swimming performance and energy metabolism of rainbow trout, common carp and gibel carp respond differently to sublethal copper exposure. Aquat Toxicol 80:92–100
Deslauriers D, Kieffer JD (2012) The effects of temperature on swimming performance of juvenile shortnose sturgeon (Acipenser brevirostrum). J Appl Ichthyol 28:176–181
Dickson KA, Donley JM, Sepulveda C, Bhoopat L (2002) Effects of temperature on sustained swimming performance and swimming kinematics of the chub mackerel Scomber japonicus. J Exp Biol 205:969–980
Faria AM, Muha T, Morote E, Chícharo MA (2011) Influence of starvation on the critical swimming behaviour of the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) and its relationship with RNA/DNA ratios during ontogeny. Sci Mar 75:87–94
Farrell AP, Steffensen JF (1987) An analysis of the energetic cost of the branchial and cardiac pumps during sustained swimming in trout. Fish Physiol Biochem 4:73–79
Fisher R, Bellwood DR (2001) Effects of feeding on the sustained swimming abilities of late-stage larval Amphiprion melanopus. Coral Reefs 20:151–154
Fuiman L, Batty R (1997) What a drag it is getting cold: partitioning the physical and physiological effects of temperature on fish swimming. J Exp Biol 200:1745–1755
Green BS, Fisher R (2004) Temperature influences swimming speed, growth and larval duration in coral reef fish larvae. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 299:115–132
Guan L, Snelgrove PVR, Gamperl AK (2008) Ontogenetic changes in the critical swimming speed of Gadus morhua (Atlantic cod) and Myoxocephalus scorpius (shorthorn sculpin) larvae and the role of temperature. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 360:31–38
Guderley H (2004) Locomotor performance and muscle metabolic capacities: impact of temperature and energetic status. Comp Biochem Physiol B 139:371–382
Hammill E, Wilson RS, Johnston IA (2004) Sustained swimming performance and muscle structure are altered by thermal acclimation in male mosquitofish. J Therm Biol 29:251–257
Hocutt CH (1973) Swimming performance of three warmwater fishes exposed to a rapid temperature change. Chesap Sci 14:11
Hunt von Herbing I (2002) Effects of temperature on larval fish swimming performance: the importance of physics to physiology. J Fish Biol 61:865–876
Jones EA, Jong AS, Ellerby DJ (2008) The effects of acute temperature change on swimming performance in bluegill sunfish Lepomis macrochirus. J Exp Biol 211:1386–1393
Koizumi K, Hiratsuka S (2009) Fatty acid compositions in muscles of wild and cultured ocellate puffer Takifugu rubripes. Fish Sci 75:1323–1328
Kolok AS, Sharkey D (1997) Effect of freshwater acclimation on the swimming performance and plasma osmolarity of the euryhaline gulf killifish. Trans Am Fish Soc 126:866–870
Koumoundouros G, Sfakianakis DG, Divanach P, Kentouri M (2002) Effect of temperature on swimming performance of sea bass juveniles. J Fish Biol 60:923–932
Landman MJ, van den Heuvel MR, Finley M, Bannon HJ, Ling N (2006) Combined effects of pulp and paper effluent, dehydroabietic acid, and hypoxia on swimming performance, metabolism, and hematology of rainbow trout. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65:314–322
Laurence GC (1972) Comparative swimming abilities of fed and starved larval largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). J Fish Biol 4:73–78
Lee KM, Kaneko T, Aida K (2005) Low-salinity tolerance of juvenile fugu Takifugu rubripes. Fish Sci 71:1324–1331
Leis JM, Clark DL (2005) Feeding greatly enhances swimming endurance of settlement-stage reef-fish larvae of damselfishes (Pomacentridae). Ichthyol Res 52:185–188
Lorenzen K, Leber KM, Blankenship HL (2010) Responsible approach to marine stock enhancement: an update. Rev Fish Sci 18:189–210
Lowe CJ, Davison W (2006) Thermal sensitivity of scope for activity in Pagothenia borchgrevinki, a cryopelagic Antarctic nototheniid fish. Polar Biol 29:971–977
Martínez M, Guderley H, Dutil JD, Winger PD, He P, Walsh SJ (2003) Condition, prolonged swimming performance and muscle metabolic capacities of cod Gadus morhua. J Exp Biol 206:503–511
Masuda R, Tsukamoto K (1998) Stock enhancement in Japan: review and perspective. Bull Mar Sci 62:337–358
McKenzie DJ, Cataldi E, Romano P, Owen SF, Taylor EW, Bronzi P (2001a) Effects of acclimation to brackish water on the growth, respiratory metabolism, and swimming performance of young-of-the-year Adriatic sturgeon (Acipenser naccarii). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:1104–1112
McKenzie DJ, Cataldi E, Romano P, Taylor EW, Cataudella S, Bronzi P (2001b) Effects of acclimation to brackish water on tolerance of salinity challenge by young-of-the-year Adriatic sturgeon (Acipenser naccarii). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 58:1113–1121
Nelson J, Tang Y, Boutilier R (1996) The effects of salinity change on the exercise performance of two Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) populations inhabiting different environments. J Exp Biol 199:1295–1309
Peck MA, Buckley LJ, Bengston DA (2006) Effects of temperature and body size on the swimming speed of larval and juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua): implications for individual-based modelling. Environ Biol Fish 75:419–429
Plaut I (2000) Resting metabolic rate, critical swimming speed, and routine activity of the euryhaline cyprinodontid, Aphanius dispar, acclimated to a wide range of salinities. Physiol Biochem Zool 73:590–596
Plaut I (2001) Critical swimming speed: its ecological relevance. Comp Biochem Physiol A 131:41–50
Plaut I, Chen T (2003) How small puffers (Teleostei: Tetraodontidae) swim. Ichthyol Res 50:149–153
Randall D, Brauner C (1991) Effects of environmental factors on exercise in fish. J Exp Biol 160:113–126
Rome LC (1986) The influence of temperature on muscle and locomotory performance. In: Heller HC (ed) Living in the cold: physiological and biochemical adaptations. Elsevier, New York, pp 485–495
Rome LC, Funke RP, Alexander RM (1990) The influence of temperature on muscle velocity and sustained performance in swimming carp. J Exp Biol 154:163–178
Stobutzki IC (1998) Interspecific variation in sustained swimming ability of late pelagic stage reef fish from two families (Pomacentridae and chaetodontidae). Coral Reefs 17:111–119
Swanson C (1998) Interactive effects of salinity on metabolic rate, activity, growth and osmoregulation in the euryhaline milkfish (Chanos chanos). J Exp Biol 201:3355–3366
Wang Q, Zhuang Z, Deng J, Ye Y (2006) Stock enhancement and translocation of the shrimp Penaeus chinensis in China. Fish Res 80:67–79
Webb P, Kostecki P, Stevens E (1984) The effect of size and swimming speed on locomotor kinematics of rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 109:77–95
Wieser W, Kaufmann R (1998) A note on interactions between temperature, viscosity, body size and swimming energetics in fish larvae. J Exp Biol 201:1369–1372
Yetsko K, Sancho G (2015) The effects of salinity on swimming performance of two estuarine fishes, Fundulus heteroclitus and Fundulus majalis. J Fish Biol 86:827–833
Zeng LQ, Zhang YG, SJ F, Cao ZD (2011) Effects of acute temperature change on resting oxygen consumption rate and critical swimming speed in juvenile southern catfish (Silurus Meridionalis, Chen). Acta Hydrobiol Sin 35:276–282
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. This study was supported by funds from Cultivation Plan for Youth Agricultural Science and Technology Innovative Talents of Liaoning Province (2015007) and Support High-Level Talent Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of Dalian (2016RQ067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Chen, L., Cui, W. et al. Effects of acute temperature and salinity changes, body length and starvation on the critical swimming speed of juvenile tiger puffer, Takifugu rubripes . Fish Physiol Biochem 44, 311–318 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-017-0436-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-017-0436-2