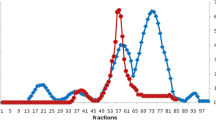
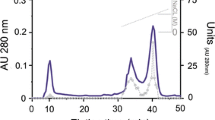
Abstract
Aminopeptidases play important roles in turnover of proteins, metabolism of hormones and neurotransmission, cell maturation and immunological regulations. In the present study, an aminopeptidase was purified to homogeneity from the skeletal muscle of grass carp by ammonium sulfate fractionation and sequential chromatographic steps, including DEAE-Sephacel, Sephacryl S-200, hydroxyapatite and Phenyl-Sepharose. The purified enzyme revealed a molecular mass of approximately 105 kDa both on SDS–PAGE and on gel filtration of Superdex 200. The enzymatic activity toward synthetic substrates was optimal at 40°C and pH 7.0–7.5. Metal-chelating agents such as EDTA and EGTA effectively inhibited the enzyme activity while inhibitors to serine, asparatic and cysteine proteinases did not show much effect, suggesting its belonging to metalloproteinase family. A specific aminopeptidase inhibitor bestatin was most effective in suppressing the enzymatic activity and performed in a competitive fashion. The enzymatic activity was slightly enhanced by metal ions of Mg2+ and Mn2+ while inhibited to different extents by Co2+, Cu2+, Zn2+ and Ca2+. Sulfhydryl reagent was necessary to maintain its activity. Purified enzyme demonstrated amidolytic activity most effectively against synthetic aminopeptidase substrate Leu-methylcoumarylamide (MCA) while N-terminal-blocked substrates and myofibrillar proteins were not hydrolyzed. The enzyme purified in the present study was quite possibly a leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) and functions during muscular protein metabolism.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartoli M, Richard I (2005) Calpains and muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2115–2133
Cao MJ, Jiang XJ, Zhong HC, Zhang ZJ, Su WJ (2006) Degradation of myofibrillar proteins by a myofibril-bound serine proteinase in the skeletal muscle of crucian carp. Food Chem 94:7–13
Cappiello M, Lazzarotti A, Buono F, Scaloni A, D’Ambrosio C, Amodeo P, Mendez BL, Pelosi P, Del Corso A, Mura U (2004) New role for leucyl aminopeptidase in glutathione turnover. Biochem J 378:35–44
Chien HCR, Lin LL, Chao SH, Chen CC, Wang WC, Shaw CY, Tsai YC, Hu HY, Hsu WH (2002) Purification, characterization, and genetic analysis of a leucine aminopeptidase from Aspergillus sojae. Biochim Biophys Acta 1576:119–126
Chiou TK, Matsui T, Konosu S (1989) Purification and properties of an aminopeptidase from Alaska pollack, Theragra chalcogramma, roe. J Biochem (Tokyo) 105:505–509
Deejing S, Yoshimune K, Lumyong S, Moriguchi M (2005) Purification and characterization of hyperthermotolerant leucine aminopeptidase from Geobacillus thermoleovrans 47b. J Ind Microbiol Biotech 32:269–276
Flores M, Aristoy MC, Toldrá F (1993) HPLC purification and characterization of porcine muscle aminopeptidase B. Biochimie 75:861–867
Gonzales T, Robert-Baudouy J (1996) Bacterial aminopeptidases: properties and functions. FEMS Micro Rev 18:319–344
Gu YQ, Walling LL (2002) Identification of residues critical for activity of the wound-induced leucine aminopeptidase (LAP-A) of tomato. Eur J Biochem 269:1630–1640
Guo C, Cao MJ, Liu GM, Lin XS, Hara K, Su WJ (2007) Purification, characterization and cDNA cloning of a myofibril-bound serine proteinase from the skeletal muscle of crucian carp (Carassius auratus). J Agric Food Chem 55:1510–1516
Hajjou M, Le Gal Y (1994) Purification and characterization of an aminopeptidase from tuna (Thunnus albacares) pyloric caeca. Biochim Biophys Acta 1204:1–13
Herrera-Camacho I, Rosas-Murrieta NH, Rojo-Domínguez A, Millán L, Reyes-Leyva J, Santos-López G, Suárez-Rendueles P (2007) Biochemical characterization and structural prediction of a novel cytosolic leucyl aminopeptidase of the M17 family from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. FEBS J 274:6228–6240
Hui KS, Saito M, Hui MA (1998) A novel neuron-specific aminopeptidase in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem 273:31053–31060
Kim H, Lipscomb WN (1993) Differentiation and identification of the two catalytic metal binding sites in bovine lens leucine aminopeptidase by X-ray crystallography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5006–5010
Kohno H, Kanda S, Kanno T (1986) Immunoaffinity purification and characterization of leucine aminopeptidase from human liver. J Biol Chem 261:10744–10748
Kuo LY, Hwang GY, Lai YJ, Yang SY, Lin LL (2003) Overexpression, purification, and characterization of the recombinant leucine aminopeptidase II of Bacillus stearothermophilus. Curr Microbiol 47:40–45
Ladrat C, Verrez-Bagnis V, Noël J, Fleurence J (2003) In vitro proteolysis of myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins of white muscle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L); effects of cathepsins B, D and L. Food Chem 81:517–525
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 277:680–685
Ledeme N, Hennon G, Vincent-Fiquet O, Plaquet R (1981) Purification and enzymatic properties of an L-leucine aminopeptidase from swine liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 660:262–270
Lee GD, Chun SS, Kho YH, Chun HK (1998) Purification and properties of an extracellular leucine aminopeptidase from the Bacillus sp. N2. J Appl Microbiol 84:561–566
Liu BX, Du XL, Zhou LG, Hara K, Su WJ, Cao MJ (2008) Purification and characterization of a leucine aminopeptidase from the skeletal muscle of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Chem 108:140–147
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mantle D, Lauffart B, Gibson A (1991) Purification and characterization of leucyl aminopeptidase and pyroglutamyl aminopeptidase from human skeletal muscle. Clin Chim Acta 197:35–45
Matsui M, Fowler JH, Walling LL (2006) Leucine aminopeptidases: diversity in structure and function. Biol Chem 387:1535–1544
Migita K, Nishimura T (2006) Purification and characterization of a Cl-activated aminopeptidase from bovine skeletal muscle. Biosci Biotech Biochem 70:1110–1117
Nishimura T, Kato Y, Rhyu MR, Okitani A, Kato H (1992) Purification and propertities of aminopeptidase C from porcine skeletal muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol B 102:129–135
Raynaud F, Fernandez E, Coulis G, Aubry L, Vignon X, Bleimling N, Gautel M, Benyamin Y, Ouali A (2005) Calpain 1–titin interactions concentrate calpain 1 in the Z-band edges and in the N2-line region within the skeletal myofibril. FEBS J 272:2578–2590
Reinhold D, Biton A, Goihl A, Pieper S, Lendeckel U, Faust J, Neubert K, Bank U, Täger M, Ansorge S, Brocke S (2007) Dual inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV and aminopeptidase N suppresses inflammatory immune responses. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1110:402–409
Rhyu MR, Nishimura T, Kato Y, Okitani A, Kato H (1992) Purification and properties of aminopeptidase H from chicken skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 208:53–59
Tanioka T, Hattori A, Masuda S, Nomura Y, Nakayama H, Mizutani S, Tsujimoto M (2003) Human leukocyte-derived arginine aminopeptidase: the third member of the oxytocinase sunfamily of aminopeptidases. J Biol Chem 278:32275–32283
Tanioka T, Hattori A, Mizutani S, Tsujimoto M (2005) Regulation of the human leukocyte-derived argine aminopeptidase/endoplasmic reticulum-aminopeptidase 2 gene by interferon-γ. FEBS J 272:916–928
Taylor A (1993) Aminopeptidases: structure and function. FASEB J 7:290–298
Taylor A, Peltier CZ, Torre FJ, Hakamian N (1993) Inhibition of bovine lens leucine aminopeptidase by bestatin: number of binding sites and slow binding of this inhibitor. Biochemistry 32:784–790
Toldrá F, Flores M (1998) The role of muscle proteases and lipases in flavor development during the processing of dry-cured ham. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 38:331–352
Umetsu H, Arai M, Ota T, Kudo R, Sugiura H, Ishiyama H, Sasaki K (2003) Purification and properties of an aminopeptidase from the mid-gut gland of scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis). Comp Biochem Physiol B 136:935–942
Veiseth E, Shackelford SD, Wheeler TL, Koohmaraie M (2004) Indicators of tenderization are detectable by 12 h postmortem in ovine longissimus. J Anim Sci 82:1428–1436
Wagner GW, Tavianini MA, Herrmann KM, Dixon JE (1981) Purification and characterization of an eukephalin aminopeptidase from rat brain. Biochemistry 20:3884–3890
Wilkes SH, Prescott JM (1985) The slow, tight binding of bestatin and amastatin to aminopeptidases. J Biol Chem 260:13154–13162
Wu GP, Cao MJ, Chen Y, Liu BX, Su WJ (2008) Leucine aminopeptidase from red sea bream (Pagrus major) skeletal muscle: purification, characterization, cellular location, and tissue distribution. J Agric Food Chem 56:9653–9660
Acknowledgments
Sponsored by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (Nos. 30571450, 20872049), Natural Scientific Foundation of Fujian Province (2008J0067), Key Project of International Science and Technology Cooperation of Fujian Province (2008I023) and the Foundation for Innovative Research Team of Jimei University (2006A002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, LG., Liu, BX., Sun, LC. et al. Identification of an aminopeptidase from the skeletal muscle of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Fish Physiol Biochem 36, 953–962 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-009-9372-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-009-9372-0