Abstract
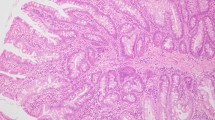
Cowden syndrome is an autosomal dominant condition caused by pathogenic mutations in the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) gene. Only a small proportion of identified pathogenic mutations have been reported to be large deletions and rearrangements. We report on a female patient with a previous history of breast ductal carcinoma in situ who presented to our institution for management of gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis. Although several neoplastic predisposition syndromes were considered, genetic evaluation determined that the patient met clinical diagnostic criteria for Cowden syndrome. Array-based comparative genomic hybridization was performed and revealed a mosaic partial deletion of the PTEN gene. Follow-up clinical history including bilateral thyroid nodules, dermatological findings, and a new primary “triple-negative” adenocarcinoma of the contralateral breast are discussed. We highlight the need for recognition and awareness of mosaicism as it may provide an explanation for variable phenotypic presentations and may alter the genetic counseling risk assessment of affected individuals and family members.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelen MR, Padberg GW, Peeters EA et al (1996) Localization of the gene for Cowden disease to chromosome 10q22-23. Nat Genet 13(1):114–116. doi:10.1038/ng0596-114
Liaw D, Marsh DJ, Li J et al (1997) Germline mutations of the PTEN gene in Cowden disease, an inherited breast and thyroid cancer syndrome. Nat Genet 16(1):64–67. doi:10.1038/ng0597-64
Nelen MR, van Staveren WC, Peeters EA et al (1997) Germline mutations in the PTEN/MMAC1 gene in patients with Cowden disease. Hum Mol Genet 6(8):1383–1387
Mester J, Eng C (2012) Estimate of de novo mutation frequency in probands with PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome. Genet Med Off J Am Coll Med Genet 14(9):819–822. doi:10.1038/gim.2012.51
Nelen MR, Kremer H, Konings IB et al (1999) Novel PTEN mutations in patients with Cowden disease: absence of clear genotype-phenotype correlations. European journal of human genetics EJHG 7(3):267–273. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200289
Eng C (2000) Will the real Cowden syndrome please stand up: revised diagnostic criteria. J Med Genet 37(11):828–830
Haibach H, Burns TW, Carlson HE, Burman KD, Deftos LJ (1992) Multiple hamartoma syndrome (Cowden’s disease) associated with renal cell carcinoma and primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin (Merkel cell carcinoma). Am J Clin Pathol 97(5):705–712
Schrager CA, Schneider D, Gruener AC, Tsou HC, Peacocke M (1998) Clinical and pathological features of breast disease in Cowden’s syndrome: an underrecognized syndrome with an increased risk of breast cancer. Hum Pathol 29(1):47–53
Zbuk KM, Eng C (2007) Cancer phenomics: rET and PTEN as illustrative models. Nat Rev Cancer 7(1):35–45. doi:10.1038/nrc2037
Pilarski R, Burt R, Kohlman W, Pho L, Shannon KM, Swisher E (2013) Cowden syndrome and the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome: systematic review and revised diagnostic criteria. J Natl Cancer Inst 105(21):1607–1616. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt277
National comprehensive cancer network. Genetic/familial high-risk assessment: breast and ovarian. (Version 1.2013). http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/genetics_screening.pdf. Accessed 9 April 2013
Marsh DJ, Coulon V, Lunetta KL et al (1998) Mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype analyses in Cowden disease and Bannayan-Zonana syndrome, two hamartoma syndromes with germline PTEN mutation. Hum Mol Genet 7(3):507–515
Zhou XP, Waite KA, Pilarski R et al (2003) Germline PTEN promoter mutations and deletions in Cowden/Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome result in aberrant PTEN protein and dysregulation of the phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt pathway. Am J Hum Genet 73(2):404–411. doi:10.1086/377109
Chibon F, Primois C, Bressieux JM et al (2008) Contribution of PTEN large rearrangements in Cowden disease: a multiplex amplifiable probe hybridisation (MAPH) screening approach. J Med Genet 45(10):657–665. doi:10.1136/jmg.2008.058131
Lachlan KL, Lucassen AM, Bunyan D, Temple IK (2007) Cowden syndrome and Bannayan Riley Ruvalcaba syndrome represent one condition with variable expression and age-related penetrance: results of a clinical study of PTEN mutation carriers. J Med Genet 44(9):579–585. doi:10.1136/jmg.2007.049981
Orloff MS, Eng C (2008) Genetic and phenotypic heterogeneity in the PTEN hamartoma tumour syndrome. Oncogene 27(41):5387–5397. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.237
Tan MH, Mester J, Peterson C et al (2011) A clinical scoring system for selection of patients for PTEN mutation testing is proposed on the basis of a prospective study of 3042 probands. Am J Hum Genet 88(1):42–56. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.11.013
Bubien V, Bonnet F, Brouste V et al (2013) High cumulative risks of cancer in patients with PTEN hamartoma tumour syndrome. J Med Genet 50(4):255–263. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101339
Gammon A, Jasperson K, Pilarski R, Prior T, Kuwada S (2012) PTEN mosaicism with features of Cowden syndrome. Clin Genet. doi:10.1111/cge.12078
Pritchard CC, Smith C, Marushchak T et al (2013) A mosaic PTEN mutation causing Cowden syndrome identified by deep sequencing. Genet Med Off J Am Coll Med Genet. doi:10.1038/gim.2013.51
Gottlieb B, Beitel LK, Trifiro MA (2001) Somatic mosaicism and variable expressivity. Trends Genet TIG 17(2):79–82
Youssoufian H, Pyeritz RE (2002) Mechanisms and consequences of somatic mosaicism in humans. Nat Rev Genet 3(10):748–758. doi:10.1038/nrg906
Kluwe L, Mautner V, Heinrich B et al (2003) Molecular study of frequency of mosaicism in neurofibromatosis 2 patients with bilateral vestibular schwannomas. J Med Genet 40(2):109–114
Moyhuddin A, Baser ME, Watson C et al (2003) Somatic mosaicism in neurofibromatosis 2: prevalence and risk of disease transmission to offspring. J Med Genet 40(6):459–463
Evans DG, Ramsden RT, Shenton A et al (2007) Mosaicism in neurofibromatosis type 2: an update of risk based on uni/bilaterality of vestibular schwannoma at presentation and sensitive mutation analysis including multiple ligation-dependent probe amplification. J Med Genet 44(7):424–428. doi:10.1136/jmg.2006.047753
Evans DG, Wallace AJ, Wu CL, Trueman L, Ramsden RT, Strachan T (1998) Somatic mosaicism: a common cause of classic disease in tumor-prone syndromes? Lessons from type 2 neurofibromatosis. Am J Hum Genet 63(3):727–736. doi:10.1086/512074
Hes FJ, Nielsen M, Bik EC et al (2008) Somatic APC mosaicism: an underestimated cause of polyposis coli. Gut 57(1):71–76. doi:10.1136/gut.2006.117796
Santarpia L, Sarlis NJ, Santarpia M, Sherman SI, Trimarchi F, Benvenga S (2007) Mosaicism in von Hippel-Lindau disease: an event important to recognize. J Cell Mol Med 11(6):1408–1415. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00122.x
Murgia A, Martella M, Vinanzi C, Polli R, Perilongo G, Opocher G (2000) Somatic mosaicism in von Hippel-Lindau Disease. Hum Mutat 15(1):114. doi:10.1002/(sici)1098-1004(200001)15:1<114:aid-humu20>3.0.co;2-7
Prochazkova K, Pavlikova K, Minarik M, Sumerauer D, Kodet R, Sedlacek Z (2009) Somatic TP53 mutation mosaicism in a patient with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Am J Med Genet Part A 149A(2):206–211. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32574
Gripp KW, Stabley DL, Nicholson L, Hoffman JD, Sol-Church K (2006) Somatic mosaicism for an HRAS mutation causes Costello syndrome. Am J Med Genet Part A 140(20):2163–2169. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.31456
Upadhyaya M, Han S, Consoli C et al (2004) Characterization of the somatic mutational spectrum of the neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) gene in neurofibromatosis patients with benign and malignant tumors. Hum Mutat 23(2):134–146. doi:10.1002/humu.10305
Rasmussen SA, Colman SD, Ho VT et al (1998) Constitutional and mosaic large NF1 gene deletions in neurofibromatosis type 1. J Med Genet 35(6):468–471
Messiaen L, Vogt J, Bengesser K et al (2011) Mosaic type-1 NF1 microdeletions as a cause of both generalized and segmental neurofibromatosis type-1 (NF1). Hum Mutat 32(2):213–219. doi:10.1002/humu.21418
Ainsworth PJ, Chakraborty PK, Weksberg R (1997) Example of somatic mosaicism in a series of de novo neurofibromatosis type 1 cases due to a maternally derived deletion. Hum Mutat 9(5):452–457. doi:10.1002/(sici)1098-1004(1997)9:5<452:aid-humu12>3.0.co;2-1
Verhoef S, Bakker L, Tempelaars AM et al (1999) High rate of mosaicism in tuberous sclerosis complex. Am J Hum Genet 64(6):1632–1637. doi:10.1086/302412
Rushlow D, Piovesan B, Zhang K et al (2009) Detection of mosaic RB1 mutations in families with retinoblastoma. Hum Mutat 30(5):842–851. doi:10.1002/humu.20940
Sippel KC, Fraioli RE, Smith GD et al (1998) Frequency of somatic and germ-line mosaicism in retinoblastoma: implications for genetic counseling. Am J Hum Genet 62(3):610–619. doi:10.1086/301766
Robberecht C, Fryns JP, Vermeesch JR (2010) Piecing together the problems in diagnosing low-level chromosomal mosaicism. Genome Med 2(7):47. doi:10.1186/gm168
Dumanski JP, Piotrowski A (2012) Structural genetic variation in the context of somatic mosaicism. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 838:249–272. doi:10.1007/978-1-61779-507-7_12
Brownstein MH, Wolf M, Bikowski JB (1978) Cowden’s disease: a cutaneous marker of breast cancer. Cancer 41(6):2393–2398
Starink TM, van der Veen JP, Arwert F et al (1986) The Cowden syndrome: a clinical and genetic study in 21 patients. Clin Genet 29(3):222–233
Pilarski R (2009) Cowden syndrome: a critical review of the clinical literature. J Genet Couns 18(1):13–27. doi:10.1007/s10897-008-9187-7
Saal LH, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Persson C et al (2008) Recurrent gross mutations of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene in breast cancers with deficient DSB repair. Nat Genet 40(1):102–107. doi:10.1038/ng.2007.39
Cancer Genome Atlas Network (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490(7418):61–70. doi:10.1038/nature11412
Carlson GJ, Nivatvongs S, Snover DC (1984) Colorectal polyps in Cowden’s disease (multiple hamartoma syndrome). Am J Surg Pathol 8(10):763–770
Marra G, Armelao F, Vecchio FM, Percesepe A, Anti M (1994) Cowden’s disease with extensive gastrointestinal polyposis. J Clin Gastroenterol 18(1):42–47
Merg A, Howe JR (2004) Genetic conditions associated with intestinal juvenile polyps. Am J Med Genet Part C Semin Med Genet 129C(1):44–55. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.30020
Lashner BA, Riddell RH, Winans CS (1986) Ganglioneuromatosis of the colon and extensive glycogenic acanthosis in Cowden’s disease. Dig Dis Sci 31(2):213–216
Heald B, Mester J, Rybicki L, Orloff MS, Burke CA, Eng C (2010) Frequent gastrointestinal polyps and colorectal adenocarcinomas in a prospective series of PTEN mutation carriers. Gastroenterology 139(6):1927–1933. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.061
Brownstein MH, Mehregan AH, Bilowski JB (1977) Trichilemmomas in Cowden’s disease. JAMA J Am Med Assoc 238(1):26
Brownstein MH, Mehregan AH, Bikowski JB, Lupulescu A, Patterson JC (1979) The dermatopathology of Cowden’s syndrome. Br J Dermatol 100(6):667–673
Salem OS, Steck WD (1983) Cowden’s disease (multiple hamartoma and neoplasia syndrome). A case report and review of the English literature. J Am Acad Dermatol 8(5):686–696
Hanssen AM, Werquin H, Suys E, Fryns JP (1993) Cowden syndrome: report of a large family with macrocephaly and increased severity of signs in subsequent generations. Clin Genet 44(6):281–286
Hanssen AM, Fryns JP (1995) Cowden syndrome. J Med Genet 32(2):117–119
Perren A, Komminoth P, Saremaslani P et al (2000) Mutation and expression analyses reveal differential subcellular compartmentalization of PTEN in endocrine pancreatic tumors compared to normal islet cells. Am J Pathol 157(4):1097–1103. doi:10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64624-x
Zhou XP, Marsh DJ, Hampel H, Mulliken JB, Gimm O, Eng C (2000) Germline and germline mosaic PTEN mutations associated with a Proteus-like syndrome of hemihypertrophy, lower limb asymmetry, arteriovenous malformations and lipomatosis. Hum Mol Genet 9(5):765–768
Zhou X, Hampel H, Thiele H et al (2001) Association of germline mutation in the PTEN tumour suppressor gene and Proteus and Proteus-like syndromes. Lancet 358(9277):210–211
Caux F, Plauchu H, Chibon F et al (2007) Segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation and epidermal nevus (SOLAMEN) syndrome is related to mosaic PTEN nullizygosity. Eur J Hum Genet EJHG 15(7):767–773. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201823
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Niehaus, Weissenbach, Southworth fund of the Robert and Kate Niehaus Clinical Cancer Genetics Initiative at MSKCC; the Sabin Family Research fund, the Tavel-Reznik Colorectal Cancer Research fund, and The Romeo Milio Lynch Syndrome Foundation. Z.K.S. is a Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation Clinical Investigator Award recipient.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salo-Mullen, E.E., Shia, J., Brownell, I. et al. Mosaic partial deletion of the PTEN gene in a patient with Cowden syndrome. Familial Cancer 13, 459–467 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-014-9709-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10689-014-9709-4