Abstract
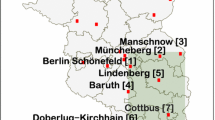
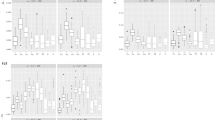
This paper presents a hierarchical regression type model for analyzing the dependency of sample extremes on time, space and a covariate effect. The model is based on the assumption that the observations follow independently a generalized extreme value distribution given location, scale and shape parameters. Then a multivariate spatial process is considered to accommodate the association and spatial correlation in the distribution parameters. The mean of the process incorporates the underlying dynamics which is elaborated on the lower stage of hierarchy. Finally, three spatio-temporal dynamic linear models drive independently this mean function to take the variations in the parameters separately into account. In a Bayesian setting, the model structure leads to parallel implementation of the Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm in a sense that it is less time consuming. Our methodology is applied to the monthly maxima of wind speed with temperature as a covariate for which the relationship is expressed in terms of a penalized spline regression model. The comparison of the proposed model with several simpler ones suggests considerable improvements in wind speed analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlin, B.P., Polson, N.G., Stoffer, D.S.: A Monte carlo approach to nonnormal and nonlinear state-space modeling. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 87, 493–500 (1992)
Carter, C., Kohn, R.: Gibbs sampling for state space models. Biometrika 81, 541–553 (1994)
Casson, E., Coles, S.: Spatial regression models for sample extremes. Extremes 1, 449–468 (1999)
Coles, S.G.: An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values. Springer, New York (2001)
Coles, S.G., Walshaw, D.: Directional modelling of extreme wind speeds. Appl. Stat. 43, 139–157 (1994)
Cooley, D., Nychka, D., Naveau, P.: Bayesian spatial modeling of extreme precipitation return levels. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 102, 824–840 (2007)
Cooley, D., Sain, S.R.: Spatial hierarchical modeling of precipitation extremes from a regional climate model. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 15, 381–401 (2010)
Crainiceanu, C.M., Ruppert, D., Wand, M.P.: Bayesian analysis for penalized spline regression using WinBUGS. J. Stat. Softw. 14, 1–14 (2005)
Cressie, N.A.: Statistics for Spatial Data, Revised edn. Wiley, New York (1993)
Diggle, P.J., Tawn, J.A., Moyeed, R.A.: Model-based geostatistics. Appl. Stat. 47, 299–350 (1998)
Fawcett, L., Walshaw, D.: A hierarchical model for extreme wind speeds. Appl. Stat. 55, 631–646 (2006)
Gamerman, D.: Markov chain Monte Carlo for dynamic generalized linear models. Biometrika 85, 215–227 (1998)
Harvey, A.C.: Forecasting, Structural Time Series Models and the Kalman Filter. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1989)
Higdon, D.: Space and space-time modeling using process convolutions. In: Quantitative Methods for Current Environmental Issues, pp. 37–56. Springer, London (2002)
Huerta, G., Sansó, B.: Time-varying models for extreme values. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 14, 285–299 (2007)
Huerta, G., Sansó, B., Stroud, J.R.: A spatio-temporal model for Mexico city ozone levels. Appl. Stat. 53, 231–248 (2004)
Kyriakidis, P.C., Journel, A.G.: Geostatistical space-time models: a review. Math. Geol. 31, 651–683 (1999)
R Development Core Team: A language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.R-project.org (2008)
Reis, A.E., Salazar, E., Gamerman, D.: Comparison of sampling schemes for dynamic linear models. Int. Stat. Rev. 74, 203–214 (2006)
Revolution Analytics: foreach: Foreach looping construct for R. R package version 1.3.2 (2012a)
Revolution Analytics: doParallel: Foreach parallel adaptor for the multicore package. R package version 1.0.0 (2012b)
Rosenthal, J.S.: Parallel computing and Monte Carlo algorithms. Far East J. Theor. Stat. 4, 207–236 (2000)
Ruppert, D., Wand, M., Carroll, R.: Semiparametric Regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Sang, H., Gelfand, A.E.: Hierarchical modeling for extreme values observed over space and time. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 16, 407–426 (2009a)
Sang, H., Gelfand, A.E.: Continuous spatial process models for spatial extreme values. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 15, 49–65 (2009b)
Schimidberger, M., Morgan, M., Eddelbuettel, D., Yu, H., Tierney, L., Mansmann, U.: State of the art in parallel computing with R. J. Stat. Softw. 31, 1–27 (2009)
Spiegelhalter, D.J., Best, N.G., Carlin, B.P., van der Linde, A.: Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit (with discussion). J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 64, 583–639 (2002)
Stein, M.L.: Interpolation of Spatial Data: Some Theory for Kriging. Springer, New York (1999)
Turkman, K.F., Turkman, M.A., Pereira, J.M.: Asymptotic models and inference for extremes of spatio-temporal data. Extremes 12, 375–397 (2010)
West, M., Harrison, P.: Bayesian Forecasting and Dynamic Models. Springer, New York (1997)
Whiley, M., Wilson, S.P.: Parallel algorithms for Markov chain Monte Carlo methods in latent spatial Gaussian models. Stat. Comput. 14, 171–179 (2004)
Yan, J., Cowles, M.K., Wang, S., Armstrong, M.P.: Parallelizing MCMC for Bayesian spatiotemporal geostatistical models. Stat. Comput. 17, 323–335 (2007)
Zhang, H.: Inconsistent estimation and asymptotically equal interpolations in model-based geostatistics. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 99, 250–262 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudian, B., Mohammadzadeh, M. A spatio-temporal dynamic regression model for extreme wind speeds. Extremes 17, 221–245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10687-014-0180-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10687-014-0180-2
Keywords
- Generalized extreme value distribution
- Dynamic regression model
- Markov chain Monte Carlo
- Parallel computing
- Extreme wind speeds