Abstract
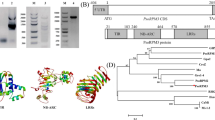
Root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) are destructive pests of crops. Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) contains genes that control resistance to root-knot nematodes. Using suppression subtractive hybridization and RACE strategies, a nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) family gene, CaRKNR (FJ231739), was isolated and cloned from the nematode-resistant pepper line HDA149. CaRKNR is a novel NBS-LRR gene with an open reading frame of 3600 bp that is homologous (70.45 % identity) to the gene Mi-1.2. After Meloidogyne incognita inoculation, real-time qPCR showed that the CaRKNR expression level was increased from 0.63 to 2.16 times. Using the virus-induced gene silencing system, the CaRKNR gene’s expression level was reduced significantly than controls, and the average numbers of galls and egg masses in silenced seedlings were 44.39 and 42.01, respectively, while the controls were 0.13. This study revealed that CaRKNR was induced by M. incognita and its expression correlated with pepper resistance against root-knot nematodes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARC:
-
APAF-1, R proteins, and CED-4
- Blast:
-
Basic local alignment search tool
- LRR:
-
Leucine-rich repeat
- NB:
-
Nucleotide binding
- NJ:
-
Neighbour-joining
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- Pfam:
-
Protein family
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA end
- RKN:
-
Root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.)
- RT-qPCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- SSH:
-
Suppression subtractive hybridization
- VIGS:
-
Virus induced gene silencing
References
Abad P, Gouzy J, Aury JM, Castagnone-Sereno P, Danchin EG, Deleury E, Perfus-Barbeoch L, Anthouard V, Artiguenave F, Blok VC (2008) Genome sequence of the metazoan plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat Biotechnol 26:909–915
Ammiraju JS, Veremis JC, Huang X, Roberts PA, Kaloshian I (2003) The heat-stable root-knot nematode resistance geneMi-9 from Lycopersicon peruvianum is localized on the short arm of chromosome 6. Theor Appl Genet 106:478–484
Belkhadir Y, Subramaniam R, Dangl JL (2004) Plant disease resistance protein signaling: NBS-LRR proteins and their partners. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:391–399
Bleve-Zacheo T, Bongiovanni M, Melillo MT, Castagnone-Sereno P (1998) The pepper resistance genes Me1 and Me3 induce differential penetration rates and temporal sequences of root cell ultrastructural changes upon nematode infection. Plant Sci 133:79–90
Chen R, Li H, Zhang L, Zhang J, Xiao J, Ye Z (2007) CaMi, a root-knot nematode resistance gene from hot pepper (Capsium annuum L.) confers nematode resistance in tomato. Plant Cell Rep 26:895–905
Claverie M, Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Bosselut N, Lecouls A, Voisin R, Kleinhentz M, Lafargue B, Caboche M, Chalhoub B (2004) High-resolution mapping and chromosome landing at the root-knot nematode resistance locus Ma from Myrobalan plum using a large-insert BAC DNA library. Theor Appl Genet 109:1318–1327
Djian-Caporalino C, Pijarowski L, Fazari A, Samson M, Gaveau L, O’byrne C, Lefebvre V, Caranta C, Palloix A, Abad P (2001) High-resolution genetic mapping of the pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) resistance loci Me3 and Me4 conferring heat-stable resistance to root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.). Theor Appl Genet 103:592–600
Djian-Caporalino C, Fazari A, Arguel M, Vernie T, VandeCasteele C, Faure I, Brunoud G, Pijarowski L, Palloix A, Lefebvre V (2007) Root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) Me resistance genes in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) are clustered on the P9 chromosome. Theor Appl Genet 114:473–486
Ernst K, Kumar A, Kriseleit D, Kloos DU, Phillips MS, Ganal MW (2002) The broad-spectrum potato cyst nematode resistance gene (Hero) from tomato is the only member of a large gene family of NBS-LRR genes with an unusual amino acid repeat in the LRR region. Plant J 31:127–136
Gilbert JC, McGuire DC (1956) Inheritance of resistance to severe root knot from Meloidogyne incognitain commercial type tomatoes. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 68:437–442
González-Candelas L, Alamar S, Sánchez-Torres P, Zacarías L, Marcos J (2010) A transcriptomic approach highlights induction of secondary metabolism in citrus fruit in response to Penicillium digitatum infection. BMC Plant Biol 10:194–211
Huang X, McGiffen M, Kaloshian I (2004) Reproduction of Mi-virulent Meloidogyne incognita isolates on Lycopersicon spp. J Nematol 36(1):69–75
Jablonska B, Ammiraju JS, Bhattarai KK, Mantelin S, de Ilarduya OM, Roberts PA, Kaloshian I (2007) The Mi-9 gene from Solanum arcanum conferring heat-stable resistance to root-knot nematodes is a homolog of Mi-1. Plant Physiol 143:1044–1054
Kim S, Park M, Yeom SI, Kim YM, Lee JM, Lee HA, Seo E, Choi J, Cheong K, Kim KT (2014) Genome sequence of the hot pepper provides insights into the evolution of pungency in Capsicum species. Nat Genet. doi:10.1038/ng.2877
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar S (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31:777–786
López-pérez M, Ballester AR, González-candelas L (2014) Identification and functional analysis of Penicillium digitatum genes putatively involved in virulence towards citrus fruit. Mol Plant Pathol. doi:10.1111/mpp.1217
Meyers BC, Kozik A, Griego A, Kuang H, Michelmore RW (2003) Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 15:809–834
Milligan SB, Bodeau J, Yaghoobi J, Kaloshian I, Zabel P, Williamson VM (1998) The root knot nematode resistance gene Mi from tomato is a member of the leucine zipper, nucleotide binding, leucine-rich repeat family of plant genes. Plant Cell Online 10:1307–1319
Nombela G, Williamson VM, Muniz M (2003) The root-knot nematode resistance gene Mi-1.2 of tomato is responsible for resistance against the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:645–649
Paal J, Henselewski H, Muth J, Meksem K, Menéndez CM, Salamini F, Ballvora A, Gebhardt C (2004) Molecular cloning of the potato Gro1-4 gene conferring resistance to pathotype Ro1 of the root cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis, based on a candidate gene approach. Plant J 38:285–297
Qin C, Yu C, Shen Y, Fang X, Chen L, Min J, Cheng J, Zhao S, Xu M, Luo Y, Yang Y, Wu Z, Mao L, Wu H, Ling-Hu C, Zhou H, Lin H, González-Morales S, Trejo-Saavedra DL, Tian H, Tang X, Zhao M, Huang Z, Zhou A, Yao X, Cui J, Li W, Chen Z, Feng Y, Niu Y, Bi S, Yang X, Li W, Cai H, Luo X, Montes-Hernández S, Leyva-González MA, Xiong Z, He X, Bai L, Tan S, Tang X, Liu D, Liu J, Zhang S, Chen M, Zhang L, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Liao W, Zhang Y, Wang M, Lv X, Wen B, Liu H, Luan H, Zhang Y, Yang S, Wang X, Xu J, Li X, Li S, Wang J, Palloix A, Bosland PW, Li Y, Krogh A, Rivera-Bustamante RF, Herrera-Estrella L, Yin Y, Yu J, Hu K, Zhang Z (2014) Whole-genome sequencing of cultivated and wild peppers provides insights into Capsicum domestication and specialization. PNAS 111(14):5135–5140
Rossi M, Goggin FL, Milligan SB, Kaloshian I, Ullman DE, Williamson VM (1998) The nematode resistance gene Miof tomato confers resistance against the potato aphid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9750–9754
Thies JA, Fery RL (1998) Modified expression of the N gene for southern root-knot nematode resistance in pepper at high soil temperatures. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 123:1012–1015
Tytgat T, Meutter JD, Gheysen G, Coomans A (2000) Sedentary endoparasitic nematodes as a model for other plant parasitic nematodes. Nematology 2:113–121
Valentine T, Shaw J, Blok VC, Phillips MS, Oparka KJ, Lacomme C (2004) Efficient virus-induced gene silencing in roots using a modified tobacco rattle virus vector. Plant Physiol 136:3999–4009
Van Der Vossen EA, Der Voort V, Rouppe JN, Kanyuka K, Bendahmane A, Sandbrink H, Baulcombe DC, Bakker J, Stiekema WJ, Klein-Lankhorst RM (2000) Homologues of a single resistance-gene cluster in potato confer resistance to distinct pathogens: a virus and a nematode. Plant J 23:567–576
Zheng J, Zou X, Mao Z, Xie B (2011) A novel pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) WRKY gene, CaWRKY30, is involved in pathogen stress responses. J Plant Biol 54:329–337
Acknowledgments
We thank INRA Versailles for providing the pepper HDA149. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (30971905, 31101425), Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201103018) and the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-25).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, Z., Zhu, P., Liu, F. et al. Cloning and functional analyses of pepper CaRKNR involved in Meloidogyne incognita resistance. Euphytica 205, 903–913 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1438-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1438-8