Abstract
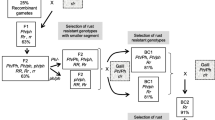
The Lr56/Yr38 translocation consists primarily of alien-derived chromatin with only the 6AL telomeric region being of wheat origin. To improve its utility in wheat breeding, an attempt was made to exchange excess Ae. sharonensis chromatin for wheat chromatin through homoeologous crossover in the absence of Ph1. Translocation heterozygotes that lacked Ph1 were test-crossed with Chinese Spring nullisomic 6A tetrasomic 6B and nullisomic 6A-tetrasomic 6D plants and the resistant (hemizygous 6A) progeny were analyzed with four microsatellite markers. Genetic mapping suggested general homoeology between wheat chromosome 6A and the translocation chromosomes, and showed that Lr56 was located near the long arm telomere. Thirty of the 53 recombinants had breakpoints between Lr56 and the most distal marker Xgwm427. These were characterized with additional markers. The data suggested that recombinants #39, 157 and 175 were wheat chromosomes 6A with small intercalary inserts of foreign chromatin containing Lr56 and Yr38, located distally on the long arms. These three recombinants are being incorporated into adapted germplasm. Attempts to identify the single shortest translocation and to develop appropriate markers are being continued.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corredor E, Lukaszewski AJ, Pachón P, Allen DC, Naranjo T (2007) Terminal regions of wheat chromosomes select their pairing partners in meiosis. Genetics 177:699–706. doi:10.1534/genetics.107.078121
Donini P, Elias ML, Bougourd SM, Koebner RMD (1997) AFLP fingerprinting reveals pattern differences between template DNA extracted from different plant organs. Genome 40:521–526. doi:10.1139/g97-068
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Friebe B, Gill BS (1994) C-band polymorphism and structural rearrangements detected in common wheat (Triticum aestivum). Euphytica 78:1–5
Friebe B, Jiang J, Raupp WJ et al (1996) Characterization of wheat-alien translocations conferring resistance to diseases and pests: current status. Euphytica 91:59–87. doi:10.1007/BF00035277
Gill KS, Gill BS (1996) A PCR-based screening assay of Ph1, the chromosome pairing regulator gene of wheat. Crop Sci 36:719–722
Gupta PK, Varshney RK, Sharma PC, Ramesh B (1999) Molecular markers and their applications in wheat breeding. Plant Breed 118:369–390. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0523.1999.00401.x
Jauhar PP, Chibbar RN (1999) Chromosome-mediated and direct gene transfers in wheat. Genome 42:570–583. doi:10.1139/gen-42-4-570
Kimber G, Feldman M (1987) Wild wheat—an introduction. Special report 353, College of Agriculture, University of Missouri-Columbia, USA, 142 pp
Knott DR (1989) The wheat rusts—breeding for resistance. Springer-Verlag, New York, 201 pp
Lukaszewski AJ (1995) Physical distribution of translocation breakpoints in homoeologous recombinants induced by the absence of the Ph1 gene in wheat and triticale. Theor Appl Genet 90:714–719. doi:10.1007/BF00222138
Lukaszewski AJ, Curtis CA (1993) Physical distribution of recombination in B-genome chromosomes of tetraploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 86:121–127. doi:10.1007/BF00223816
Marais GF, Pretorius ZA, Marais AS, Wellings CR (2003) Transfer of rust resistance genes from Triticum species to common wheat. SAJ Plant Soil 20:193–198
Marais GF, McCallum B, Marais AS (2006) Leaf rust and stripe rust resistance genes derived from Aegilops sharonensis. Euphytica 149:373–380. doi:10.1007/s10681-006-9092-9
Moore G (2008) The Ph1 locus—a story 50 years in the making. In: Appels R, Eastwood R, Lagudah E et al. (ed) 11th international wheat genetics symposium, University of Sydney Press, Sydney, Australia (http://hdl.handle.net/2123/3418)
Okamoto M (1957) Asynaptic effect of chromosome V. Wheat Inf Serv 5:6
Qi L, Friebe B, Zhang P, Gill BS (2007) Homoeologous recombination, chromosome engineering and crop improvement. Chromosome Res 15:3–19. doi:10.1007/s10577-006-1108-8
Raina SN, Rani V (2001) GISH technology in plant genome research. Methods Cell Sci 23:83–104. doi:10.1023/A:1013197705523
Riley R (1958) Chromosome pairing and haploids in wheat. Proceedings of the 10th international congress of genetics, Montreal 2:234–235
Riley R, Chapman V (1958) Genetic control of the cytologically diploid behaviour of hexaploid wheat. Nature 182:713–715. doi:10.1038/182713a0
Riley R, Chapman V, Johnson R (1968) Introduction of yellow rust resistance of Aegilops comosa into wheat by genetically induced homoeologous recombination. Nature 217:383–384. doi:10.1038/217383a0
Röder MS, Korzun V, Wendehake K, Plaschke J, Tixier M-H, Leroy P, Ganal MW (1998) A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 149:2007–2023
Sanchez-Moran E, Benavente E, Orellana J (2001) Analysis of karyotype stability of homoeologous-pairing (ph) mutants in allopolyploid wheats. Chromosoma 110:371–377. doi:10.1007/s004120100156
Schwarz G, Herz M, Huang XQ et al (2000) Application of fluorescence-based semi-automated AFLP analysis in barley and wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:545–551. doi:10.1007/s001220050071
Sears ER (1952) Homoeologous chromosomes in Triticum aestivum. Genetics 37:624
Sears ER (1954) The aneuploids of common wheat. Missouri Agric Exp Stn Res Bull 572:58
Sears ER (1981) Transfer of alien genetic material to wheat. In: Evans LT, Peacock WJ (eds) Wheat science—today and tomorrow. Cambridge University Press, London, pp 75–89
Sears ER, Okamoto M (1958) Intergenomic relationships in hexaploid wheat. Proceedings of the 10th international congress of genetics, Montreal 2:258–259
Sears ER, Sears LMS (1979) The telocentric chromosomes of common wheat. In: Ramanujam S (ed) Proceedings of the 5th international wheat genetics symposium, New Delhi, pp 389–407
Somers DJ, Isaac P, Edwards K (2004) A high-density microsatellite consensus map for bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 109:1105–1114. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1740-7
Sourdille P, Singh S, Cadalen T et al (2004) Microsatellite-based deletion bin system for the establishment of genetic-physical map relationships in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Funct Integr Genomics 4:12–25. doi:10.1007/s10142-004-0106-1
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M et al (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414. doi:10.1093/nar/23.21.4407
Acknowledgment
The Winter Cereal Trust (South Africa) funded the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marais, G.F., Badenhorst, P.E., Eksteen, A. et al. Reduction of Aegilops sharonensis chromatin associated with resistance genes Lr56 and Yr38 in wheat. Euphytica 171, 15–22 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-9973-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-9973-9