Abstract
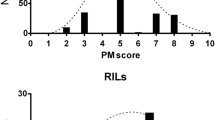
Quantitative resistance to sunflower downy mildew was studied on inbred lines and hybrids not carrying efficient major gene resistance, in field trials in one to four sites over 3 years. Hybrids from factorial crosses showed that inheritance is under additive control and comparison with reactions of parental inbred lines gave narrow sense heritabilities of 27–57%. Analysis of a polymorphic recombinant inbred line population without efficient major gene resistance indicated that two highly significant Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) explained 42% of variation in field reaction to downy mildew. These QTL were mapped on linkage groups 8 and 10, and do not appear related to any of the known major resistance gene clusters. Possible bases of this type of resistance and its use in breeding are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albourie JM, Tourvieille J, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D (1998) Resistance to metalaxyl in isolates of the sunflower pathogen Plasmopara halstedii. Eur J Plant Pathol 104:235–242. doi:10.1023/A:1008691123239
Arcade A, Labourdette A, Falque M, Mangin B, Chardon F, Charcosset A et al (2004) BioMercator: integrating genetic maps and QTL towards discovery of candidate genes. Bioinformatics 20:2324–2326. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth230
Bert PF, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Philippon J, Mouzeyar S, Jouan I, Nicolas P et al (2001) Identification of a second linkage group carrying genes controlling resistance to downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 103:992–997. doi:10.1007/s001220100660
Bert PF, Jouan I, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Serre F, Nicolas P, Vear F (2002a) Comparative genetic analysis of quantitative traits in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.).1. QTL involved in resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Diaporthe helianthi. Theor Appl Genet 105:985–993. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1004-3
Bert PF, Jouan I, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Serre F, Phillipon J, Nicolas P et al (2002b) Comparative genetic analysis of quantitative traits in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). 2. Characterisation of QTL involved in developmental and agronomic traits. Theor Appl Genet 107:181–189
Bert PF, Deschamp-Guillaume G, Serre F, Jouan I, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Nicolas P et al (2004) Comparative genetic analysis of quantitative traits in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) 3. Characterisation of QTL involved in resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Phoma macdonaldii. Theor Appl Genet 109:865–874. doi:10.1007/s00122-004-1701-1
Bouzidi MF, Badaoui S, Cambon F, Vear F, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Nicolas P et al (2001) Molecular analysis of a locus for resistance to downy mildew in sunflower with specific PCR-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 104:592–600. doi:10.1007/s00122-001-0790-3
Brahm L, Rocher T, Friedt W (2000) PCR-based markers facilitating marker assisted selection in sunflower for resistance to downy mildew. Crop Sci 40:676–682
Charcosset A, Mangin B, Moreau L, Combes L, Jourjon MF, Gallais A (2001) Heterosis in maize investigated using connected RIL populations. Quantitative genetics and breeding methods: the way ahead. Les colloques no 96, INRA Editions, Paris
de Givry S, Bouchez M, Chabrier P, Milan D, Schiex T (2005) CARTHAGENE: multipopulation integrated genetic and radiated hybrid mapping. Bioinformatics 21:1703–1704. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bti222
Delmotte F, Giresse X, Richard-Cervera S, M’Baya J, Vear F, Tourvieille J et al (2008a) EST-derived markers highlight pathogen evolution within the causal agent of sunflower downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii). Infect Genet Evol (in press)
Delmotte F, Giresse X, Richard-Cervera S, Vear F, Tourvieille J, Walser P et al (2008b) EST-derived markers highlight genetic relationships among French Plasmopara halstedii races. In: Proc. 17th int. sunflower conf., 8–12/6/2008 Cordoba, Spain, pp 187–192
Falconer DS (1981) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 2nd edn. Longmans Green, London
Gentzbittel L, Vear F, Zhang YX, Berville A, Nicolas P (1995) Development of a consensus linkage map of cultivated sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Theor Appl Genet 90:1079–1086. doi:10.1007/BF00222925
Gentzbittel L, Mouzeyar S, Badoui S, Mestries E, Vear F, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D et al (1998) Cloning of molecular markers for disease resistance in sunflower, Helianthus annuus L. Theor Appl Genet 96:519–525. doi:10.1007/s001220050769
Jeuken M, Lindhout P (2002) Lactuca saligna, a non-host for lettuce downy mildew (Bremia lactucae), harbors a new race-specific Dm gene and three QTLs for resistance. Theor Appl Genet 105:384–391. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0943-z
Jones ES, Breese WA, Lui CJ, Singh D, Shaw DH, Witcombe JR (2002) Mapping quantitative trait loci for resistance to downy mildew in pearl millet: field and glasshouse screens detect the same QTL. Crop Sci 42:1316–1323
Jourjon MF, Jasson S, Marcel J, Ngom B, Mangin B (2005) MCQTL: multi-allelic QTL mapping in multi-cross design. Bioinformatics 21:128–130. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bth481
Parleviet JE (2002) Durability of resistance against fungal, bacterial and viral pathogens; present suituation. Euphytica 124:147–156. doi:10.1023/A:1015601731446
Rachid Al-Chaarani G, Roustaee A, Gentzbittel L, Mokrani L, Barrault G, Dechamp-Guillaume G et al (2002) A QTL analysis of sunflower partial resistance to downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) and black stem (Phoma macdonaldii) by use of recombinant inbred lines (RILs). Theor Appl Genet 104:490–496. doi:10.1007/s001220100742
Radwan O, Bouzidi MF, Vear F, Phillipon J, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Nicolas P et al (2002) Identification of non-TIR-NBS-LRR markers linked to the Pl5/Pl8 locus for resistance to downy mildew in sunflower. Theor Appl Genet 106:1438–1446
Roeckel-Drevet P, Gagne G, Mouzeyar S, Gentzbittel L, Phillipon J, Nicolas P, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Vear F (1996) Colocation of downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) resistance genes in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Euphytica 91:225–228
Tang S, Yu JK, Slabaugh MB, Shgintani DK, Knapp SJ (2002) Simple sequence repeat map of the sunflower genome. Theor Appl Genet 105:1124–1136. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0989-y
Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Serre F, Walser P, Philippon J, Vear F, Tardin MC et al (2004) Partial, non-race specific resistance to downy mildew in cultivated sunflower lines. In: Proc. 16th int. sunflower Conf., Fargo, USA, vol 1, pp 105–110
Tourvieille de Labrouhe D, Serre F, Walser P, Roche S, Vear F (2008) Quantitative resistance to downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Euphytica. doi: 10.1007/s10681-008-9698-1
Vear F, Bony H, Joubert G, Tourvieille De Labrouhe D, Pauchet I, Pinochet X (2003) 30 Years of sunflower breeding in France. OCL 10:66–73
Vear F, Willefert D, Walser P, Serre F, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D (2004) Reaction of sunflower lines to a series of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates. In: Proc. 16th int. sunflower conf., Fargo, USA, vol 1, pp 135–140
Vear F, Serre F, Roche S, Walser P, Tourvieille de Labrouhe D (2007) Recent research on downy mildew resistance useful for breeding industrial-use sunflowers. Helia 30:45–54
Vear F, Jouan-Dufournel I, Bert PF, Serre F, Cambon F, Pont C et al (2008) QTL for capitulum resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in sunflower. In: Proc 17th int. sunflower conf., 8–12/6/2008 Cordoba, Spain, pp 605–610
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the personnel of the INRA farm at Clermont-Ferrand for their help in the trials. Promosol provided financial support for this programme, which was made with the support and collaboration of Cetiom, Caussade, Maïsadour, Monsanto, Pioneer, R.A.G.T., Soltis and Syngenta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vear, F., Serre, F., Jouan-Dufournel, I. et al. Inheritance of quantitative resistance to downy mildew (Plasmopara halstedii) in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Euphytica 164, 561–570 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9759-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-008-9759-5