Abstract
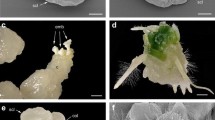
The effect of the Embryo lethality mutant (Eml) of rye was studied in crosses between hexaploid wheat and corresponding inbred rye line (L2). Histological analysis of hybrid embryos revealed morphological differences 16 days after pollination. Eml was found to arrest the formation of shoot meristem but had no influence on root meristem formation. The effect of Eml cannot be overcome by in vitro embryo rescue via direct regeneration on Kruse medium. The possibility of complementary interactions between wheat and rye genes and of changes in gene expression through increased variation in dosage-regulated gene expression during hybrid formation is discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum M, Lagudah ES, Appels R (1992) Wide crosses in cereals. Annu Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 43:117–143
Burke JM, Arnold Ml (2001) Genetics and fitness of hybrids. Ann Rev Genet 35:31–52
Clark JK (1996) Maize embryogenesis mutants. In: Wang TL, Cuming A (eds) Embryogenesis: the generation of a plant. Bios Scientific Publishers, Oxford, pp 89–112
Clark JK, Sheridan WF (1986) Developmental profiles of the maize embryo-lethal mutants dek22 and dek23. J Hered 77:83–92
Clark JK, Sheridan WF (1988) Characterization of the two maize embryo-lethal defective kernel mutants rgh*-1210 and fl*-1253B: Effects on embryo and gametophyte development. Genetics 120:179–290
Comai L, Tyagi AP, Winter K, Holmes-Davis R, Reynolds SH, Stevens Y, Byers B (2000) Phenotypic instability and rapid gene silencing in newly formed Arabidopsis allotetraploids. Plant Cell 12:1551–1567
Dobzhansky TH (1937). Genetics and the origin of species. Columbia University Press, New York
Feldman M, Liu B, Segal G, Abbo S, Levy AA, Vega JM (1997) Rapid elimination of low-copy DNA sequences in polyploid wheat: possible mechanism for differentiation of homeologous chromosomes. Genetics 147:1381–1387
Gernand D, Rutten T, Varshney A, Rubtsova M, Prodanovic S, Brüß C, Kumlehn J, Matzk F, Houben A (2005) Uniparental chromosome elimination at mitosis and interphase in wheat and pearl millet crosses involves micronucleus formation, progressive heterochromatinization, and DNA fragmentation. Plant Cell 17:2431–2438
Gerstel DU (1954) A new lethal combination in interspecific cotton hybrids. Genetics 39:628–639
Gerstel DU, Burns JA, Burk LG (1979) Interspecific hybridizations with an African tobacco, Nicotiana africana Merxm. J Hered 70:342–344
Hermsen JGTh (1963) The genetic basis of hybrid necrosis in wheat. Genetica 33:445–487
Hermsen JGTh (1967) Hybrid dwarfness in wheat. Euphytica 16:134–162
Hollingshead L (1930) A lethal factor in Crepis effective only in an interspecific hybrid. Genetics 15:114–140
Inoue E, Marubashi W, Niwa M (1994) Simple method for overcoming the lethality observed in the hybrid between Nicotiana suaveolens and N. tabacum. Breed Sci 44:333–336
Inoue E, Marubashi W, Niwa M (1996) Genomic factor controlling the lethality exhibited in the hybrid between Nicotiana suaveolens Lehm. and N. tabacum L. Theor Appl Genet 93:341–347
Inoue E, Marubashi W, Niwa M (1997) Improvement of the method for overcoming the hybrid lethality between Nicotiana suaveolens and N. tabacum by culture of F1 seeds in liquid media containing cytokinins. Breed Sci 47:221–216
Inoue E, Marubashi W, Niwa M (2000) Characterization and overcoming of temperature-dependent lethality exhibited by hybrid embryos from the cross Nicotiana suaveolens × N. sylvestris. Breed Sci 50:297–302
Itoh J, Sato Y, Nagato Y, Matsuoka M (2006) Formation, maintenance and function of the shoot apical meristem in rice. Plant Mol Biol 60:827–842
Kaltsikes PJ (1974) Methods for triticale production. Z Pflanzenzücht 71(3):264–286
Kobori S, Marubashi W (2004) Programmed cell death detected in interspecific hybrids of Nicotiana repanda × N. tomentosiformis expressing hybrid lethality. Breed Sci 54:347–350
Krowlow KD (1970) Untersuchungen über die Kreuzbarkeit zwischen Weizen und Roggen. Z Pflanzenzüchtg 64:44–72
Kruse A (1974) An in vivo/vitro embryo culture technique. Hereditas 2:219–224
Larter E, Tsuchiya T, Evans LE (1968) Breeding and cytology of triticale. Proceeding of 3rd Inter. Wheat Symp., Canberra, 1968, pp 213–221
Laurie DA, Bennett MD (1986) Wheat × maize hybridization. Can J Genet Cytol 28:313–316
Laurie DA, Bennett MD (1988a) The production of haploid wheat plants from wheat x maize crosses. Theor Appl Genet 76:393–397
Laurie DA, Bennett MD (1988b) Cytological evidence for fertilization in hexaploid wheat × sorghum crosses. Plant Breed 100:73–82
Lee JA (1981) Genetics of D3 complementary lethality in Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense. J Hered 72:299–300
Levin DA (1983) Polyploidy and novelity in flowering plants. Am Nat 122:1–25
Liu B, Vega JM, Segal G, Abbo S., Rodova M, Feldman M (1998a) Rapid genomic changes in newly synthesized amphiploids of Triticum and Aegilops. I. Changes in low-copy noncoding DNA sequences. Genome 41:272–277
Liu B, Vega JM, Feldman M (1998b) Rapid genomic changes in newly synthesized amphiploids of Triticum and Aegilops. II. Changes in low-copy coding DNA sequences. Genome 41:535–542
Ma X-F, Fang P, Gustafson JP (2004) Polyploidization-induced genome variation in triticale. Genome 47:839–848
Magnard JL, Heckel T, Massonneau A, Wisniewski JP, Cordelier S, Lassagne H, Perez P, Dumas Ch, Rogowski PM (2004) Morphogenesis of maize embryos requires ZmPRPL35-1 encoding a plastid ribosomal protein. Plant Physiol 134:649–663
Marubashi W, Yamada T, Niwa M (1999) Apoptosis detected in hybrids between Nicotiana glutinosa and N. repanda expressing lethality. Planta 210:168–171
Masuda Yu, Yamada T, Marubashi W (2003) Time course analysis of apoptotic cell death during expression of hybrid lethality in hybrid tobacco cells (Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum) Plant Cell Physiol 44(4):420–427
Matzk F, Mahn A (1994) Improved techniques for haploid production in wheat using chromosome elimination. Plant Breed 113(2):125–129
May CE, Appels R (1980) Rye chromosome translocation in hexaploid wheat: a re-evaluation of the loss of heterochromatin from rye chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 56:17–23
May CE, Appels R (1984) Seedling lethality in wheat: a novel phenotype associated with a 2RS/2BL translocation chromosome. Theor Appl Genet 68:163–168
Müntzing A (1979) Triticale: Results and Problems. J Plant Breed Suppl 10:1–103
Oettler G (1983) Crossability and embryo development in wheat-rye hybrids. Euphytica 32:593–600
Oka H (1957) Phylogenetic differentiation of cultivated rice. XV. Complementary lethal genes in rice. Jpn J Genet 32:83–87
Orr HA, Presgraves DC (2000) Speciation by postzygotic isolation: forces, genes and molecules. Bioessays 22:1085–1094
Osborn TC, Pires JC, Birchler JA, Auger DL, Chen ZJ, Lee HS, Comai L, Madlung A, Doerge RW, Colot V, Martienssen RA (2003) Understanding mechanisms of novel gene expression in polyploids. Trend Genet 19:141–147
Pilu R, Consonni G, Busti E, MacCabe AP, Giulini A, Dolfini S, Gavazzi G (2002) Mutations in two independent genes lead to suppression of the shoot apical meristem in maize. Plant Physiol 128:502–511
Raina SK (1984) Crossability and in vitro development of hybrid embryos of Triticum durum × Secale cereale. Indian J Genet 44(3):429–437
Rapp RA, Wendel JF (2005) Epigenetics and plant evolution. New Phytol 168:81–91
Rieseberg LH, Carney SE (1998) Plant hybridisation. New Phytol 140:599–624
Satoh N, Hong SK, Nishimura A, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Nagato Y (1999) Initiation of shoot apical meristem in rice: characterization of four SHOOTLESS genes. Development 126:3629–3636
Sawant AC (1956) Semilethal complementary factors in a tomato species hybrid. Evolution 10:93–96
Sears ER (1940) Monofactorially conditioned inviability of an intergeneric hybrid in the Triticinae. Genetics 25:133
Sears ER (1944) Inviability of intergeneric hybrids involving Triticum monococcum and T. aegilopoides. Genetics 29:113–127
Shao ZZ, Taira T (1990) Production of primary triticale from calluses of immature abnormal hybrid embryos between Triticum durum and Secale cereale. Plant Breed 105:81–88
Sheridan WF, Neuffer MG (1981) Maize mutants altered in embryo development. In: Subtelney S, Abbott U (eds) Levels of genetic control in development. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 137–156
Shii CT, Mok MC, Temple SR, Mok DWS (1980) Expression of developmental abnormalities in hybrid of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Interaction between temperature and allelic dosage. J Hered 71:218–222
Sirkka A, Immonen T (1993) Comparison of callus culture with embryo culture at different times of embryo rescue for primary triticale production. Euphytica 70:185–190
Sitch LA, Snape JW (1987) Factors affecting haploid production in wheat using the Hordeum bulbosum system. 1. Genotypic and environmental effects on pollen germination, pollen tube growth and the frequency of fertilization. Euphytica 36:483–496
Smirnov VG, Sosnikhina SP (1984) Genetika rzhi (Genetics of rye). Leningr Gos Univ., 264 pp
Snape JW, Chapman V, Moss J, Blanchard CE, Miller TE (1979) The crossabilities of wheat varieties with Hordeum bulbosum. Heredity 42:29–298
Stebbins GL (1957) The inviability, weakness and sterility of interspecific hybrids. Adv Genet 9:147–215
Taira T, Larter EN (1978) Factors influencing development of wheat-rye hybrid embryos in vitro. Crop Scien 18:348–350
Takahashi R, Hayashi J, Moriya I (1970) Studies on lethal seedling of barley by complementary genes. I. Mode of inheritance and the geographical distribution of the lethal genes. Nogaku Kenkyu 53:197–204
Tezuka T, Marubashi W (2006) Hybrid lethality in interspecific hybrids between Nicotiana tabacum and N. suaveolens: evidence that the Q chromosome causes hybrid lethality based on Q-chromosome-specific DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 112:1172–1178
Tikhenko ND, Pyukkenen VP, Voylokoy AV (2003) Specific of embryo development in hybrid wheat-rye corn seeds. Proceeding of 5th international symposium “New and nontraditional plants and prospects of their use”. Moscow 2003, vol 2, pp 441–443
Tikhenko ND, Tsvetkova NV, Voylokoy AV (2005) Genetic control of embryo lethality in crosses between common wheat and rye. Russ J Genet 41(8):877–884
Tikhenko N, Tsvetkova N, Börner A, Voylokov V (2006) Genetic study of embryo lethality in wheat-rye hybrids. In: Book of Abstracts International Symposium on Rye Breeding & Genetics, Groβ Lüsewitz, 28–30 June 2006, p 69
Voylokov AV, Tikhenko ND (2002) Triticale as a model for study of genome interaction and genome evolution in allopolyploid plants. Proceeding of 5th international Triticale symposium, Radzikow, 30 June–5 July 2002, vol 1, pp 63–69
Worland AJ, Law CN (1980) The genetics of hybrid dwarfing in wheat. Z Pflanzenzüchtg 85:28–39
Yamada T, Marubashi W, Niwa M (2000) Apoptotic cell death induces temperature-sensitive lethality in hybrid seedlings and calli derived from the cross of Nicotiana suaveolens × N. tabacum. Planta 211:614–622
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr F. Matzk for providing the facilities for embryo rescue and tissue culture together with Dr Richard Pickering for critical reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to K. Kumke, M. Hantschmann, M. Pürschel, H. Büchner and H. Block for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research: project 06-04-48758a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tikhenko, N., Rutten, T., Voylokov, A. et al. Analysis of hybrid lethality in F1 wheat-rye hybrid embryos. Euphytica 159, 367–375 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9528-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9528-x