Abstract
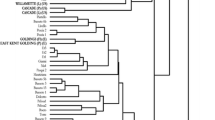
A set of 67 wild and cultivated hop accessions, representative of hop diversity, was genotyped with 29 SSR markers in order to investigate the population structure and genetic diversity among hop genotypes. A total of 314 alleles was detected, with an average of 10.8 alleles per locus and an average PIC content of 0.607. Model-based clustering placed the accessions into five germplasm groups. A distance-based tree showed good agreement with five germplasm groups, and additionally assigned accessions omitted from model-based analysis into two additional germplasm groups. The 67 hop accessions were thus subdivided in seven germplasm groups, with three corresponding to major breeding groups and four to wild hops. This finding is in accordance with two biogeographically separated hop germplasms (European and North American origin) and with the known history of the accessions. North American hop germplasm was partitioned into native and cultivated germplasm groups. European germplasm was divided into two groups of hop cultivars representing distinguishable European germplasms and three new groups of native hops, which were differentiated for the first time by this analysis. Admixture analysis showed shares of various ancestries in hop cultivars, mostly congruent with pedigree data, and the introgression of various ancestries in some native hops. The above results have so far given the most detailed insight to date into the population structure of hop diversity, which is important for its effective use in hop breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bp:
-
Base pair
- EU:
-
European
- Hallertauer Mfr:
-
Hallertauer Mittlefruer
- NA:
-
North American
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- PIC:
-
Polymorphism Information Content
- rDNA:
-
ribosomal DNA
References
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bowcock AM, Ruiz-Linares A, Tomfohrde J, Minch E, Kidd JR, Cavalli-Sforza LL (1994) High resolution of human evolutionary trees with polymorphic microsatellites. Nature 368:455–457
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.5c. Department of Genetics. University of Washington, Seattle
Fitch WM, Margoliash E (1967) Construction of phylogenetic trees. Science 155:279–284
Fukunaga K, Hill J, Vigouroux Y, Matsuoka Y, Sanchez JG, Liu K, Buckler ES, Doebley J (2005) Genetic diversity and population structure of teosinte. Genetics 169:2241–1154
Garris AJ, Tai TH, Coburn J, Kresovich S, McCouch S (2005) Genetic structure and diversity in Oryza sativa L. Genetics 169:1631–1638
Henning JA, Steiner JJ, Hummer KE (2004) Genetic diversity among world hop accessions grown in the USA. Crop Sci 44:411–417
Horner CE, Likens ST, Zimmerman CE, Haunold A (1972) ‘Cascade’–A new continental-type hop variety for the US. Brew Digest 8:56–62
Jakse J, Kindlhofer K, Javornik B (2001) Assessment of genetic variation and differentiation of hop (Humulus lupulus L.) genotypes by microsatellite and AFLP markers. Genome 44:773–782
Jakse J, Satovic Z, Javornik B (2004) Microsatellite variability among wild and cultivated hops (Humulu lupulus L.). Genome 47:889–899
Javornik B (2006a) Genetic structure and differentiation in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) as inferred from microsatellites. Cited July 2006 University site www.genetika.si/Structure/Table2_Micros.pdf
Javornik B (2006b) Genetic structure and differentiation in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) as inferred from microsatellites. Cited July 2006 University site www.genetika.si/Structure/Structure_gene_pools.pdf.
Kralj D, Zupanec J, Vasilj D, Kralj S, Psenicnik J (1991) Variability of essential oils of hops (Humulus lupulus L.). J Inst Brew 97:197–206
Kump B, Javornik B (1996) Evaluation of genetic variability among common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench.) populations by RAPD markers. Plant Sci 114:149–158
Liu J (2002) Powermarker–A Powerful Software for Marker Data Analysis. Bioinformatics Research Center, Relaigh, North Carolina State University, NC. http://www.powermarker.net
Liu K, Goodman M, Muse S, Stephen Smith J, Buckler E, Doebley J (2003) Genetic structure and diversity among maize inbred lines as inferred from DNA microsatellites. Genetics 165:2117–2128
Lu H, Redus MA, Coburn JR, Rutger JN, McCouch SR, Tai TH (2005) Population structure and breeding pattern of 145 US rice cultivars based on SSR marker analysis. Crop Sci 45:66–76
Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Noli E, Tuberosa R (2005) Population structure and long-range linkage disequilibrium in a durum wheat elite collection. Mol Breed 15:271–289
Minch E, Ruiz-Linares A, Goldstein D, Feldman M Cavalli-Sforza LL 1997. MICROSAT: a computer program for calculating various statistics on microsatellite allele data, ver. 1.5d. Stanford University, Stanford, CA http://hpgl.stanford.edu/projects/microsat
Moir M (2000) Hops––a millennium review. J Am Soc Brew Chem 58:131–146
Murakami A, Darby P, Javornik B, Pais MS, Seigner E, Lutz A, Svoboda P (2006a) Microsatellite DNA analysis of wild hops, Humulus lupulus L. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:1553–1562
Murakami A, Darby P, Javornik B, Pais MS, Seigner E, Lutz A, Svoboda P (2006b) Molecular phylogeny of wild hops, Humulus lupulus L. Heredity 97:66–74
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygosuty and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 3:583–590
Neve R A (1991) Hops. Chapman and Hall, London
Patzak J (2001) Comparison of RAPD, STS, ISSR and AFLP molecular methods used for assessment of genetic diversity in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 121:9–18
Pillay M, Kenny ST (1996) Structure and inheritance of ribosomal DNA variants in cultivated and wild hop, Humulus lupulus L. Theor Appl Genet 93:333–340
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Radisek S, Jakse J, Javornik B (2006) Genetic variability and virulence among Verticilium albo-atrum isolates from hop. Eur J Plant Pathol 116:301–314
Seefelder S, Ehrmaier H, Schweizer G, Seigner E (2000) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships among accessions of hops, Humulus lupulus, as determined by amplification fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting compared with pedigree data. Plant Breed 119:257–233
Stajner N, Jakse J, Kozjak P, Javornik B (2005) The isolation and characterisation of microsatellites in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Plant Sci 168:213–221
Stevens JF, Taylor AW, Nickerson GB. Ivancic M, Henning J, Hanunold A, Deinzer ML (2000) Prenylflavonoid variation in Humulus lupulus: distribution and taxonomic significance of xanthogalenol and 4’-O-methylxanthohumol. Phytochemistry 53:759–775
Sustar-Vozlic J, Javornik B (1999) Genetic relationships in cultivars of hops, Humulus lupulus L., as determined by RAPD analysis. Plant Breed 118:175–181
Wagner T (1976) Divji hmelj Humulus lupulus L. v Jugoslaviji (Wild hops Humulus lupulus L. in Yugoslavia). Dissertation, University of Ljubljana
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education, Science and Technology RS; contracts no. PO-0513–0481.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stajner, N., Satovic, Z., Cerenak, A. et al. Genetic structure and differentiation in hop (Humulus lupulus L.) as inferred from microsatellites. Euphytica 161, 301–311 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9429-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9429-z