Abstract
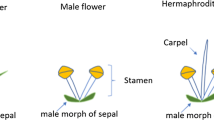
A genetic map of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) was constructed in a classical back cross population using 101 AFLP and 9 microsatellite markers. The map was divided into seven linkage groups with a total length of 585 cM and an average distance between the markers of 5.18 cM. The linkage map was constructed with LOD 3.5, but was quite stable with seven linkage groups remaining until LOD 7.0. Gender segregated 1 male to 1 female in the mapping population and was mapped to a small area of one linkage group with a distance of 1.9 cM to a microsatellite marker termed SO4. This small chromosomal region co-segregating with sex determination in the species is in contrast to previous reports on a heterologous XY chromosome system in spinach. Microsatellite markers used as anchors in the map construction were isolated from sequences of known nuclear encoded genes in spinach. This enabled simultaneous positioning on the map of these genes: Rubisco activase (Rca), Photosytem 1 subunit V (PsaG), Protein Kinase (Pk), Nitrate reductase (Nir), ferrodoxin:thioredoxin reductase (Ftr), Ribosomal protein L1 (Rps22), Choline monooxygenase (Cmo), Pseudogene for BZIP protein (Bzip), Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (Act1) and stromal ascorbate peroxidase, thylakoid-bound ascorbate peroxidase (Apx2). Spinach has a small genome, which makes it suitable for basic genomic studies and many physiologically important genes have been cloned from the species. The present map anchored with user friendly microsatellite markers will be useful for future studies of physiology and genetics of the species as well as studies of the nature of gender determination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth, C.C., J. Lu, M. Winfield & J. Parker, 1999. Sex determination by X: autosome dosage: Rumex acetosa (Sorrel). In: Ainsworth, C.C. (Ed.), Sex determination in plants, pp. 121–136. Bios Scientific Publisher Oxford.
Ainsworth, C., 2000. Boys and Girls come out to play: The Molecular Biology of Dioecious Plants. Ann Bot 86: 211–221.
Bemis, W.P. & G.B. Wilson, 1953. A new hypothesis explaining the genetics of sex determination in Spinacea oleracea L. J Hered 44: 91–95.
Christiansen, M.J., S.B. Andersen & R. Ortiz, 2002. Diversity changes in an intensively bred wheat germplasm during the 20th century. Mol Breed 9: 1–11.
Dressler, O., 1973. Erfarungen bei der Vermehrung und Züchtung monözischer Spinatsorten (Spinacia oleracea L.). Z PflZücht 70: 108–128.
Durand, B. & R. Durand, 1991. Sex determination and reproductive organ differentiation in Mercurialis. Plant Sci 80: 49–65.
Ellis, J.R. & J. Janick, 1960. The chromosomes of Spinacia oleracea. Am J Bot 47: 210–214.
Farbos, I., J. Veuskens, B. Vyskot, M. Oliveira, S. Hinnisdaels, A. Aghmir, A. Mouras & I. Negrutiu, 1999. Sexual dimorphism in white campion: Deletion on the Y chromosome results in a floral asexual phenotype. Genetics 151: 1187–1196.
Filatov, D.A., F. Monéger, I. Negrutiu & D. Charlesworth, 2000. Low variability in a Y-linked plant gene and its implications for Y-chromosome evolution. Nature 404: 388–390.
Grant, S., A. Houben, B. Vyskot, J. Siroky, W.H. Pan, J. Macas & H. Saedler, 1994. Genetics of sex determination in flowering plants. Dev Genetics 15: 214–230.
Groben, R. & G. Wricke, 1998. Occurrence of microsatellites in spinach sequences from computer databases and development of polymorphic SSR markers. Plant Breed 117: 271–274.
Gunter, L.E., G.T. Roberts, K. Lee, F.W. Larimer & G.A. Tuskan, 2003. The development of two flanking SCAR markers linked to a sex determination locus in Salix viminalis L. J Hered 94: 185–189.
Guttman, D.S. & D. Charlesworth, 1998. An X- linked gene with a degenerate Y-linked homologue in a dioecious plant. Nature 393: 263–266.
Haanstra, J.P.W., C. Wye, H. Verbakel, F. Meijer-Dekens, P. van den Berg, P. Odinot, A.W. van Heusden, S. Tanksley, P. Lindhout & J. Peleman, 1999. An integrated high-density RFLP-AFLP map of tomato based on two Lycopersicon esculentum × L. pennellii F2 Populations. Theor Appl Genet 99: 254-271.
Haga, T., 1935. Sex and Chromosomes in Spinacia oleracea L. Jpn J Genet 10: 218–222.
Haldane, J.B.S., 1919. The combination of linkage values and the calculation of distances between the loci of linked factors. J Genet 8: 299–309.
Iizuka, M. & J. Janick, 1963. Sex Chromosome Translocations in Spinacia oleracea. Genetics 48: 273–282.
Iizuka, M. & J. Janick, 1966. The synthesis of heteromorphic sex chromosomes in spinach. J Hered 57: 182–184.
Iizuka, M. & J. Janick, 1971. Sex Chromosome variation in Spinacia oleracea L. J Hered 62: 349–352.
Janick, J. & E.C. Stevenson, 1955. Genetics of the monoecious character in spinach. Genetics 40: 429–437.
Jeuken, M., R. van Wijk, J. Peleman & P. Lindhout, 2001. An integrated interspecific AFLP map of lettuce (Lactuca) based on two L. sativa x L. saligna F2 populations. Theor Appl Genet 103: 638–647.
Jiang, C. & K.C. Sink, 1997. RAPD and SCAR markers linked to the sex expression locus M in asparagus. Euphytica 94: 329-333.
Khadka, D.K., A. Nejidat, M. Tal & A. Golan-Goldhirsh, 2002. DNA markers for sex: Molecular evidence for gender dimorphism in dioecious Mercurialis annua L. Mol Breed 9: 251–257.
Lardon, A., S. Georgiev, A. Aghmir, G. Le Merrer & I. Negrutiu, 1999. Sexual dimorphism in white campion: complex control of carpel number is revealed by Y chromosome deletions. Genetics 151: 1173–1185.
Liu, Z., P.H. Moore, H. Ma, C.M. Ackerman, M. Ragiba, Q. Yu, H.M. Pearl, M.S. Kim, J.W. Charlton, J.I. Stiles, F.T. Zee, A.H. Paterson & R. Ming, 2004. A primitive Y chromosome in papaya marks incipient sex chromosome evolution. Nature 427: 348–352.
Louis, J.P., 1989. Genes for the regulation of the sex differentiation and male-fertility in Mercurialis annua L. J Hered 80: 104-111.
Löptien, H. 1979. Identification of the sex-chromosome pair in asparagus (Asparagus officinalis L.) Z PflZücht 82: 162–173.
Ma, H., P.H. Moore, Z. Liu, M.S. Kim, Q. Yu, M.M.M. Fitch, T. Sekioka, A.H. Paterson & R. Ming, 2004. High-density linkage mapping revealed suppression of recombination at the sex determination locus in papaya. Genetics 166: 419–436.
Pannell, J., 1997. Mixed genetic and environmental sex determination in an androdioecious population of Mercurialis annua. Heredity 78: 50–56.
Parker, J.S., 1990. Sex chromosomes and sexual differentiation in flowering plants. Chromosomes Today 10: 187–198.
Qi, X., P. Stam & P. Lindhout, 1998. Use of locus-specific AFLP markers to construct a high density molecular map in barley. Theor Appl Genet 96: 376–384.
Ramanna, M.S., 1976. Are there heteromorphic sex chromosomes in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.)? Euphytica 25: 277–284.
Reamon-Büttner, S.M., J. Schondelmaier & C. Jung, 1998. AFLP markers tightly linked to the sex locus in Asparagus officinalis L. Mol breed 4: 91–98.
Rozen, S. & H.J. Skaletsky, 2000. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: S. Krawetz & S. Miseners (Eds.), Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology, pp. 365-386. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ.
Seefelder, S., H. Ehrmaier, G. Schweizer & E. Seigner, 2000. Male and female genetic linkage map of hops, Humulus lupulus. Plant Breed 119: 249–255.
Semerikov, V., U. Lagercrantz, V. Tsarouhas, A. Rönnberg-Wästljung, C. Alström-Rapaport & M. Lascoux. 2003. Genetic mapping of sex linked mark Bers in Salix Viminalis L. Heredity 91: 293–299.
Sharp, P.J., M. Kreis, P.R. Shewry & M.D. Gale, 1988. Location of ß-amylase sequences in wheat and its relatives. Theor Appl Genet 75: 286–290.
Siemonsma, J.S. & K. Piluek, 1993. Plant Resources of South-East Asia No 8., Vegetables. pp. 266–268. Pudoc Scientific Publishers, Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Siljak-Yakovlev, S., S. Benmalek, M. Cerbah, T.C. de la Peña, N. Bounaga, S.C. Brown & A. Sarr, 1996. Chromosomal sex determination and heterochromatin stucture in date palm. Sex plant reprod 9: 127–132.
Sondur, S.N., R.M. Manshardt & J.I. Stiles, 1996. A genetic linkage map of papaya based on randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theor Appl Genet 93: 547–553.
Song, Q.J., L.F. Marek, R.C. Shoemaker, K.G. Lark, V.C. Concibido, X. Delannay, J.E. Specht & P.B. Cregan, 2004. A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109: 122–128.
Spada, A., E. Caporali, G. Marziani, P. Portaluppi, F.M. Restivo, F. Tassi & A. Falavigna, 1998. A genetic map of Asparagus officinalis based on integrated RFLP, RAPD and AFLP molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 97: 1083–1089.
Sugimoto, Y., 1948. Studies on the breeding of spinach. 2. Sex expression and genetical explanation. Hort Assoc Japan J 17: 77-83.
Temnykh, S., G. DeClerck, A. Lukashova, L. Lipovich, S. Cartinhour & S. McCouch, 2001. Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11: 1441–1452.
Torp, A.M., A.L. Hansen & S.B. Andersen, 2001. Chromosomal regions associated with green plant regeneration in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) anther culture. Euphytica 119: 377–387.
Utz, H.F. & A.E. Melchinger, 1996. PlabQTL: A program for composite interval mapping of QTL. J. Agric. Genomics 2: http://www.cabi-publishing.org/jag/papers96/paper196/index p196.html.
Van Ooijen, J.W. & R.E. Voorrips, 2001. JoinMap® 3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen, the Netherlands.
Vos, P., R. Hogers, M. Bleeker, M. Reijans, T. van de Lee, M. Hornes, A. Frijters, J. Pot, J. Peleman, M. Kuiper & M. Zabeau, 1995. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 23: 4407–4414.
Vuylsteke, M., R. Mank, R. Antonise, E. Bastiaans, M.L. Senior, C.W. Stuber, A.E. Melchinger, T. Lübberstedt, X.C. Xia, P. Stam, M. Zabeau & M. Kuiper, 1999. Two high-density AFLP linkage maps of Zea mays L: analysis of distribution of AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 99: 921–935.
Young, W.P., J.M. Schupp & P. Keim, 1999. DNA methylation and AFLP marker distribution in the soybean genome. Theor Appl Genet 99: 785–792.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khattak, J.Z.K., Torp, A.M. & Andersen, S.B. A genetic linkage map of Spinacia oleracea and localization of a sex determination locus. Euphytica 148, 311–318 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-9031-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-005-9031-1