Abstract
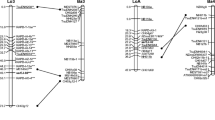
A genetic linkage map of papaya (Carica papaya L.) was constructed using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers and a F2 population derived from a University of Hawaii UH breeding line 356 x ‘Sunrise’ cross. A total of 596 10-mer primers were screened, and 96 polymorphisms were detected. At LOD 4.0, 62 of these markers mapped to 11 linkage groups comprising 999.3 cM. About 80% of the markers conformed to expected Mendelian segregation ratios. We have mapped the locus that determines sex to a 14-cM region flanked by RAPD markers. The results demonstrate the usefulness of RAPD markers for developing a basic genetic linkage map in papaya.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Awada M (1958) Relationships of minimum temperature and growth rate with sex expression of papaya plants (Carica papaya L.). Hawaii Agric Exp Sta Tech Bull No 38
Awada M, Ikeda W (1957) Effects of water and nitrogen on composition, growth, sugar in fruits yield and sex expression of the papaya plants (Carica papaya L.). Hawaii Agric Exp Sta Tech Bull No 33
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Majority of random cDNA clones correspond to single loci in the tomato genome. Mol Gen Genet 203:8–14
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnicks MH, Davis RW (1980) Construction of genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet 2:314–331
Carlson JE, Tulsieram LK, Glaubitz JC, Luk V, Kauffeldt C, Rutledge R (1991) Segregation of randomly amplified DNA markers in F1 progeny of conifers. Theor Appl Genet 83:194–200
Chaparro J, Wilcox P, Grattapaglia P, O'Malley D, McCord S, Sederoff R, McIntyre L, Whetten R (1992) Genetic mapping of pine using RAPD markers. Construction of a 191 marker map and development of half-sib genetic analysis. In: Whelan WJ, Ahmad F, Bialy H, Black S, King ML, Rabin MB, Solomonsen LP and Vasil IK (eds) Advances in gene technology: feeding the world in the 21st century. (Miami Winter Symposium.) ILR Press New York, pp 129
Echt CS, Erdahl LA, McCoy TJ (1992) Genetic segregation of random amplified polymorphic DNA in diploid cultivated alfalfa. Genome 35:84–87
Foolad MR, Jones RA, Rodriguez RL (1993) RAPD markers for constructing intra specific tomato genetic maps. Plant Cell Rep 12:293–297
Gasser CS (1991) Molecular studies on the differentiation of floral organs. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:621–649
Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Debener T, Schachtschabel U, Walkemeier B, Uhrig H, Salamini F (1989) RFLP analysis and linkage mapping in Solanum tuberosum. Theor Appl Genet 78:65–75
Grodzieker T, Williams J, Sharp P, Sambrook J (1974) Physical mapping of temperature sensitive mutations of adenovirus. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 39:439–446
Helentjaris T, King G, Slocum M, Sidenstrang C, Wegman S (1985) Restriction fragment polymorphism as probes for plant diversity and their development as tools for applied plant breeding. Plant Mol Biol 5:109–116
Helentjaris T, Slocum M, Wright S, Schaefer A, Nienhuis J (1986) Construction of genetic linkage maps in maize and tomato using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 72:761–769
Hofmeyr JDJ (1938) Genetical studies of Carica papaya L. S Afr J Sci 35:300–304
Hofmeyr JDJ (1939) Sex-linked inheritance in Carica papaya L. S Afr J Sci 36:283–258
Hofmeyr JDJ (1967) Some genetic breeding aspects of Carica papaya L. Agron Trop 17:345–351
Hu J, Quiros CF (1991) Identification of broccoli and cauliflower cultivars with RAPD markers. Plant Cell Rep 10:505–511
Kashi Y (1985) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in cattle. MSc thesis. The Hebrew University, Jerusalem, Israel
Klein-Lankhorst R, Rietveld P, Machiels B, Verkerk R, Weide R, Gebhardt C, Koornneef M, Zabel P (1991) RFLP markers linked to root knot nematode resistance gene Mi in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 81:661–667
Lander E, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daley M, Lincolin S, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural population. Genomics 1:174–181
Landry BS, Keseseli RV, Farrara B, Michelmore RW (1987) A genetic linkage map of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) with restriction fragment length polymorphism, isozyme, disease resistance and morphological markers. Genetics 116:331–337
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1993) Constructing Genetic Linkage Maps with MAPMAKER/EXP version 3.0: a tutorial and reference manual, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Technical Report, Cambridge, Mass.
Martin GB, Williams JGK, Tanksley SD (1991) Rapid identification of markers linked to a Pseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2336–2340
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Kush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
Meurman O (1925) The chromosome behavior of some dioecious plants and their relatives with special reference to the sex chromosomes. Soc Sci Fenn Comm Biol 2:105
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Lincolin SF, Tanksley SD (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of RFLP. Nature 335:721–726
Reiter RS, Williams J, Feldmann, KA, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV, Scolnik PA (1992) Global and local genome mapping in Arabidopsis thaliana by using recombinant inbred lines and random amplified polymorphic DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1477–1481
Roy A, Frascaria N, Mackay J, Bousquet J (1992) Segregating random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs) in Betula alleghaniensis. Theor Appl Genet 85:173–180
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Erlich HA (1988) Primer-directed amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491
Sondur SN, Manshardt RM, Stiles JI (1995) Genetics of growth rate and flowering time in papaya (Carica papaya L.) J Quant Trait Loci 1 (http://probe.nalusda.gov:8000/otherdocs/jqtl/jqtl1995-04/jq18r2.html)
Stiles JI, Lemme C, Sondur S, Morshidi MB, Manshardt R (1993) Using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA for evaluating genetic relationships among papaya cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 85:697–701.
Storey WB (1938) Segregation of sex types in solo papaya and their application to the selection of seed. Am Soc Hortic Sci 35:83–85
Storey WB (1953) Genetics of papaya. J Hered 44:70–78
Storey WB (1976) Papaya. In: Simmonds NW (ed) Evolution of crop plants. Longman, San Francisco, pp 21–24
Tingey S, Sebestian S, Rafalski AH (1989) A RFLP map of the soybean genome. Agron Abstr, p 180
Tingey SV, del Tufo P (1993) Genetic analysis with random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Plant Physiol 101:349–352
Torres AM, Weeden NF, Martin A (1993) Linkage among isozyme, RFLP and RAPD markers in Vicia faba. Theor Appl Genet 85:937–945
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Finger printing genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Welsh J, Petersen G, McClelland M (1991) Polymorphisms generated by arbitrarily primed PCR in the mouse: application to strain identification and genetic mapping. Nucleic Acids Res 19:303–306
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Lavak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 19:6531–6535
Zee F (1985) Breeding of papaya virus tolerance in solo papayas, Carica papaya L. PhD thesis, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. E. Hart
Journal series No. 4146 of the Hawaii Institute of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sondur, S.N., Manshardt, R.M. & Stiles, J.I. A genetic linkage map of papaya based on randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 93, 547–553 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417946
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417946