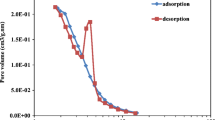
Abstract
Since phenols and phenolic compounds in many industrial wastewaters are toxic organic contaminants for humans and aquatic life, to remove these compounds via the most efficient way is very important for environmental remediation treatment. In this context, almost all of the isotherm models (Freundlich, Langmuir, Temkin, Redlich–Peterson, Sips, and Khan) for adsorption in the literature were applied to explain the adsorption mechanism of 4-chlorophenol on activated carbon in this study. Also theoretical modeling data were obtained using model equations; interpolation and analysis of variance were made to compare data by using statistics software. In addition, the thermodynamic and kinetic studies for adsorption mechanism were included in the article. The adsorption of 4-chlorophenol on activated carbon fits well to the pseudo-first-order kinetic model than the pseudo-second-order, intraparticular diffusion and Bangham models. It is also indicated that 4-chlorophenol adsorption by granular activated carbon would be attributed to a type of transition between physical and chemical adsorption rather than a pure physical or chemical adsorption process. As a result, an environmental remediation problem and the adsorption mechanism on activated carbon that can be regarded as a solution to this problem are described and explained using the mathematical models and calculations in this study.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C 0 :
-
Initial 4-CP concentration (milligrams per liter)
- C e :
-
Equilibrium liquid-phase concentration (milligrams per liter)
- q e :
-
Equilibrium solid-phase concentration (milligrams per gram)
- q :
-
Solid-phase concentration at time t (milligrams per gram)
- q t :
-
Amount of 4-CP adsorbed at time t (milligrams per gram)
- q m :
-
Theoretical maximum adsorption capacity (milligrams per gram)
- q ms :
-
The Sips maximum adsorption capacity (milligrams per gram)
- T :
-
Temperature (kelvin)
- t :
-
Time (minutes)
- k F and 1/n :
-
Constants of Freundlich isotherm
- k L Q 0 :
-
Constants of Langmuir isotherm
- b T a T :
-
Constants of Temkin isotherm
- k S b S, a S :
-
Constants of Sips isotherm
- Q o b k, a k :
-
Constants of Khan isotherm
- k RP p e, a RP and g :
-
Constants of Redlich–Peterson isotherm
- k 1 :
-
Rate constant of pseudo-first-order kinetic model (1/min)
- k 2 :
-
Rate constant of pseudo-second-order kinetic model (grams per milligram minute)
- β :
-
Constant in Elovich’s equation
- k id :
-
Rate constant of intraparticle diffusion model (mg/g min0.5)
- k b :
-
Constant in Bangham’s equation
- C :
-
Constant that gives idea about the thickness of the boundary layer (milligrams per gram)
- m :
-
Adsorbent mass per liter of solution (grams per liter)
- m s :
-
The Sips model exponent
- V :
-
Volume of solution (liters)
- a :
-
Bangham constant (<1)
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (8.314 J/mol K)
- R L :
-
Dimensionless constant separation factor
- ∆G 0 :
-
Gibbs free energy of adsorption (kilojoules per mole)
- ∆H 0 :
-
Enthalpy of adsorption (kilojoules per mole)
- ∆S o :
-
Entropy of adsorption (joules per mole kelvin)
- R 2 :
-
Regression correlation coefficient
- K :
-
Equilibrium constant
References
Kuleyin, A. (2007). Removal of phenol and 4-chlorophenol by surfactant-modified natural zeolite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 144, 307–315.
Hamdaoui, O., & Naffrechoux, E. (2007). Modeling of adsorption isotherms of phenol and chlorophenols onto granular activated carbon Part I. Two-parameter models and equations allowing determination of thermodynamic parameters. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147, 381–394.
Hameed, B. H., Chin, L. H., & Rengaraj, S. (2008). Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Desalination, 225, 185–198.
Bilgili, M. S. (2006). Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol from aqueous solutions by Xad-4 resin: isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B137, 157–164.
Radhika, M., & Palanivelu, K. (2006). Adsorptive removal of chlorophenols from aqueous solution by low cost adsorbent—kinetics and isotherm analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B138, 116–124.
Koumanova, B., Peeva-Antova, P., & Yaneva, Z. (2005). Adsorption of 4-chlorophenol from aqueous solution on activated carbon-kinetic study. Journal The University of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy, 40(3), 213–218.
Rege, S. U., Yang, R. T., & Cain, C. A. (1998). Desorption by ultrasound. Phenol on Activated Carbon and Polymeric Resin Separations, 44(7), 1519–1528.
Khan, A. R., Al-Bahri, T. A., & Al-Haddad, A. (1997). Adsorption of phenol based organic pollutants on activated carbon from multi component dilute aqueous solutions. Water Research, 31(8), 2102–2112.
Rengaraj, S., Moon, S. H., Sivabalan, R., Arabindoo, B., & Murugesan, V. (2002). Agricultural solid waste for the removal of organics: adsorption of phenol from water and wastewater by palm seed coat activated carbon. Waste Management, 22(5), 543–548.
Mollah, A., & Robinson, C. W. (1996). Pentachlorophenol adsorption and desorption characteristics of granular activated carbon: kinetics. Water Research, 30, 2901–2907.
Nadia, R., & Tezel, F. H. (2004). Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption. Journal of Environmental Management, 70, 157–164.
Dabrowski, A., Podkoscielny, P., Hubicki, Z., & Barczak, M. (2005). Adsorption of phenolic compounds by activated carbon—a critical review. Chemosphere, 58, 1049–1070.
Qadeer, R., & Rehan, A. H. (2002). A study of the adsorption of phenol by activated carbon from aqueous solutions. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 26, 357–361.
Juang, R. S., & Shiau, J. Y. (1999). Adsorption isotherms of phenols from water onto macroreticular resins. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B70, 171–183.
Sathishkumar, M., Binupriya, A. R., Vijayaraghavan, K., & Yun, S. (2007). Two and three-parameter isothermal modeling for liquid-phase sorption of Procion Blue H-B by inactive mycelial biomass of Panus fulvus. Journal of Chemistry Technology and Biotechnology, 82, 389–398.
Mellah, A., & Chegrouche, S. (1997). The removal of zinc from aqueous solutions by natural bentonite. Water Research, 31, 621–629.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38, 2221–2295.
Hall, K. R., Eagleton, L. C., Acrivos, A., & Vermeulen, T. (1966). Pore and solid diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant pattern conditions. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 5, 212–223.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Uber die adsorption in losungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–470.
Treybal, R. E. (1981). Mass-transfer operations (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Temkin, M. I. (1941). Adsorption equilibrium and the kinetics of processes on nonhomogeneous surfaces and in the interaction between adsorbed molecules. Zhurnal Fizicheskoy Khimiy, 15, 296–332.
Redlich, O., & Peterson, D. L. (1959). A useful adsorption isotherm. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 63, 1024–1026.
Sips, R. (1948). On the structure of a catalyst surface. Journal of Chemical Physics, 16, 490–495.
Pérez-Marín, A. B., Meseguer Zapata, V., Ortuno, J. F., Aguilar, M., Sáez, J., & Llorens, M. (2007). Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto orange waste. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B139, 122–131.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156, 2–10.
Khan, A. R., Ataullah, R., & AlHaddad, A. (1997). Equilibrium adsorption studies of some aromatic pollutants from dilute aqueous solutions on activated carbon at different temperatures. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 194, 154.
Liu, Y., & Liu, Y. J. (2008). Biosorption isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics, review. Separation and Purification Technology, 61, 229–242.
Blanchard, G., Maunaye, M., & Martin, G. (1984). Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Research, 18, 1501.
Ho, Y. S., Ng, J. C. Y., & McKay, G. (2000). Kinetics of pollution sorption by biosorbents review. Separation and Purification Methods, 29, 189.
Wu, J., & Yu, H. K. (2006). Biosorption of 2,4 dichlorophenol from aqueous solution Phanerochaete chrysosporium biomass: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B137, 498–508.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgili, M.S., Varank, G., Sekman, E. et al. Modeling 4-Chlorophenol Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Granular Activated Carbon. Environ Model Assess 17, 289–300 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-011-9293-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-011-9293-z